PRE-AP BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM A nucleotide, DNA or RNA

PRE-AP BIOLOGY
FINAL EXAM
1.
A nucleotide, DNA or RNA, basically has 3 principal components: a phosphate group, a 5carbon sugar and a nitrogen base.
2.
During the 1990’s and early 2000’s, a research project was undertaken to sequence the complete nucleotide sequence of the species Homo sapiens (human). The purpose of the project was to try and identify the roughly 40,000 genes involved in creating a human, male or female. The project was referred to as the Human Genome Project.
3.
A genetics research scientist is conducting research on the genome of the
Tyrannosaurus Rex using preserved DNA found in a bone fossil. The scientist wants to know the percentage composition of each nucleotide within the genome. The scientist found that there existed 27% adenine and because adenine equals the amount for thymine, it has to be 27%. That leaves 46% left. Since cytosine and guanine have the same amount, each would have 23%.
4.
The transmission of traits from one generation to the next by inheriting DNA from the parent is called heredity.
5.
Genetics is the science that deals with the transmission of information in the form of
DNA.
6.
The father of genetics was Gregor Mendel.
7.
The phenotype of an organism refers to the physical trait that can be seen.
8.
If the individual possesses 2 recessive alleles for the same trait, the individual is said to be homozygous for the trait.
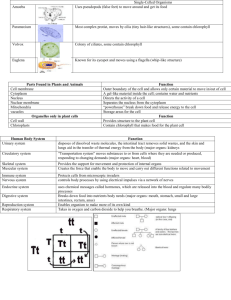
9.
Tallness (T) is dominant to shortness (t) in pea plants. The genotype Tt would be heterozygous for tallness.
10.
Abnormalities of chromosomes can either be numerical or structural. Inversion is associated with part of a chromosome breaking away and then reattaching to the same chromosome, but in reverse orientation.
11.
Translocation is associated with part of a chromosome breaking away and attaching to a nonhomologous chromosome.
12.
A diagram that shows a family history of trait occurrence in chart form is called a pedigree.
13.
Human blood type is controlled by multiple alleles.
14.
The first filial (F₁) generation is the result of crosses between true breed individuals of the parental generation.
15.
The difference between a monohybrid and a dihybrid cross is that monohybrid crosses involve 1 trait, dihybrid crosses involve 2 traits.
16.
Information from both alleles is expressed in the cell. The heterozygous phenotype appears to be blended. This is called incomplete dominance.
17.
Crossing over occurs during Prophase I of Meiosis I.
18.
The process of producing offspring is called reproduction and can be asexual or sexual.
19.
The amount of precipitation over a year, the amount of sunlight in a given day and the temperature at various times of the year are all abiotic factors.
20.
When crossing over takes place, a genetic swapping occurs between homologous chromosomes.
21.
Swamps have trees and marshes have reed grasses.
22.
Maximum growth over a period of time due to ideal environmental conditions existing is called intrinsic growth.
23.
Farmers plowing up the old soil in a field and allowing it to aerate is an example of secondary succession as the soil already existed.
24.
The levels of ecology from SMALLEST TO LARGEST is organism, population, community, ecosystem, landscape and biosphere.
25.
A biome refers to large ecosystems in general with similar climate conditions.
26.
A symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits and the other is harmed is called parasitism.
27.
A symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits and the other is not affected is called commensalism.
28.
Abiotic factors are environmental factors without life.
29.
The term community refers to a collection of interacting populations in an area.
30.
Ecology is the study of the interactions occurring between organisms and their environment.
31.
Logistic growth results in a S curve graph.
32.
Biotic factors are environmental factors that posses life.
33.
A food web is a model showing ALL possible feeding relationships in an area.
34.
Mutualism is a symbiotic relationship where both organisms benefit.
35.
Detritivores feed on dead organic matter.
36.
Herbivores eat plants.
37.
Carnivores eat meat.
38.
Omnivores eat both plants and animals.
39.
Exponential growth results in a J curve graph.
40.
Carolus Linnaeus is the naturalist that was known as the father of taxonomy.
41.
Taxonomy is the science of species classification.
42.
In the scientific name of an organism, the first word is always the genus.
43.
The 8 classification levels in proper descending order (from largest to smallest) is domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus and species.
44.
Binominal nomenclature is the two word naming system.
45.
Latin is used to write scientific names.
46.
The scientific names for humans using the rules for binominal nomenclature is Homo
sapiens.
47.
Charles Lyell proposed the Theory of Uniformitarism.
48.
Jean Baptist Lamarck proposed the Theory of Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics by
Means of Use and Disuse.
49.
Aristotle proposed the Theory of Scale Naturae.
50.
An example of Intersexual Competition would be a male Blue-Footed Boobies performing a mating dance.
51.
The characteristics of living things are: composed of cells, different levels of complexity, use energy in metabolic processes, respond to their environment, adapt to their environment, reproduce and grow and develop.
52.
Archaeabacteria consists of: methanogens, halophiles and thermophiles.
53.
All fungi are eukaryotic, heterotrophic organisms with cell walls.
54.
The nonvascular plants consist of: Hepatophyta (liverworts), Anthocerophyta
(hornworts) and Bryophyta (mosses). They are small in size and only have cellulose in their cell walls. The gametophye generation is dominant over the sporophyte generation. They have no true roots, stems or leaves but have structures that carry out similar functions. They move water and other materials by diffusion or osmosis because there is no vascular tissue present.
55.
The seedless vascular plants consist of two phyla (divisions): Lycophyta and Psilophyta
(psilophytes, spenophytes and ferns). Ferns have megaphylls (leaves) called fronds.
They develop from fiddleheads. On the underside of the fronds are clusters of spores called sori. The sporophyte generation is dominant over the gametophyte generation.
56.
Epiphytes grow on the branches of trees and are called air plants.
57.
The seed bearing vascular plants consist of: gymnosperms and angiosperms.
58.
The gymnosperms have leaves that remain all year and are called evergreens. Cones are used for reproduction. The female cones (large and hard) contain the seeds. The male cones (small and yellow) contain the pollen grains that contain the sperm. The wind and rain carry the pollen grains to the female cones for reproduction.
59.
The angiosperms are the flowering plants. The sporophyte is the dominant generation.
Sepals are the green protective leaves that protect the petals. Petals are the colored leaves that attract pollinators. The male reproductive structure is called the stamen. It consists of the anther (part with the yellow pollen grains) and filament (stalk that supports the anther). The female reproductive structure is called the pistil/carpel. It consists of the stigma (sticky top), style (the neck) and ovary (contains the ovules and
eggs). The fruit is the ripened ovary developed to promote seed dispersal by animals eating the fruit.
60.
Advantages of seeds for survival: dispersal from the parent plant, dormancy until the rainy season and a nutrient supply for the developing embryo.
61.
Fruits contributed to the evolutionary success of angiosperms by facilitating dispersal of seeds by using animals.
62.
Know the parts of the flowering plant (you drew this in your notes).
63.
Animals are multicellular heterotrophs that have to ingest food for their energy. They have no cell walls. They exhibit diploid dominant life styles. They reproduce sexually.
The male gamete (sperm) and female gamete (egg) fuse together to form a fertilized egg called a zygote. The zygote will continue to grow, by mitosis, and develop into the organism.
64.
Cephalization is the accumulation of senses in the head region of an animal.
65.
Acoelomates are animals that do not have a body cavity.
66.
Pseudocoelomates are animals that have a false cavity.
67.
Coelomates are animals that have a true body cavity.