End of Chapter Questions 1
advertisement

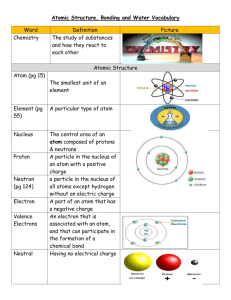
End of Chapter Questions Liam Grinton Section 2-1 review 1). Define element, atom, compound, and molecule. An element is a substance made up of only one type of atom. It cannot be broken down into any other independent stable substances that have all of the characteristics of the element. An atom is a small particle, out of which all other substances consist. It has a nucleus that consists of several protons and neutrons and is circled by a cloud of electrons. A compound is a pure chemical substance that consists of two or more chemical elements and can be broken down into its original, simpler elements through chemical reactions. A molecule is defined as an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms in a definite arrangement held together by very strong chemical bonds. 2). How are particles arranged in an atom? An atom is arranged in the following manner: At its core there is a nucleus. The nucleus consists of a certain number of protons and neutrons. Around the nucleus, there is a “cloud” of electrons. The electrons are separated into different energy levels or “shells” these shells have a certain capacity of electrons that each can contain, if it is not filled completely, the element is not chemically stable and wants to be chemically reactive. 3). How can we predict which elements are stable under natural conditions and which elements tend to undergo chemical reactions? We can predict this based on their outer energy level or “shell” It has a certain amount of electrons that it should contain in order to keep the atom’s charge neutral. If this outer shell of the atom is not filled to its “specified” number of atoms, it will either try to bond with other atoms to acquire or release excess electrons. 4).How does an ionic bond differ from a covalent bond? In an ionic bond one atom is given, or “loses” or acquires an electron from another in order to fill or empty its outer energy level (whichever is easiest). In a covalent bond, these electrons are simply shared between the nuclei of the two atoms and circle around both nuclei. 5). Neon seldom, if ever combines with other elements to form compounds. Why is this so? This is because neon is a so- called “Noble” gas. This means that it has all of its energy levels filled and does not want to bond with other compounds because its charge is already neutral. 6). In the early 1900s, hydrogen gas was used to inflate airships. After one large airship crashed and caught fire, helium gas began to be used to inflate airships. Why was helium preferred over hydrogen? Helium is what is called an inert gas; this means that it is a non- reactive, noble gas. Because combustion is an exothermic chemical reaction, helium will not burn regardless of the temperatures or conditions it is subjected to. This is also why a mixture of gasses, mainly helium and argon are used in TIG (Tungsten inert gas) welding - they prevent the metal from oxidizing under extreme heat created by the electrical arc by excluding non- inert gasses from the area.