Stress at Boundaries
advertisement

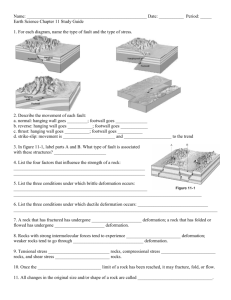
Name:_________________________________ Date:___________ Period:_____ Lab – Modeling Stress at Plate Boundaries Introduction: Rocks undergo stress when they are being pulled apart, pushed together or rubbed with other rocks. When stress occurs, pressure builds up and is released as an earthquake. Any change in the volume or shape of Earth’s crust is called deformation. Most changes occur very closely so you cannot observe them directly. But if you could speed up time, you would see the crust bend, stretch, break, tilt, fold, and slide. The slow shift of Earth’s plates causes this deformation. Vocabulary: Deformation – Compression – Shearing – Tension Faults – Normal fault – Reverse fault – Strike slip fault – Procedure: 1. Roll out three colors of clay into sheets about 1 centimeter thick 2. Place the layers on top of each other 3. Cut the clay sheets into 3 sections of equal size. (Each section will be used to model the 3 types of stress) 4. Draw the before picture of one of the sections of clay. Be sure to identify the layers. 5. Follow the directions to create each stress situation. 6. Draw the results for each stress. Data: Draw what your model layers look like BEFORE any added stress. Use proper colors. Shearing Cut this section in half and pull the halves in opposite directions but keep them touching. Draw what your model looks like. Tension Pull on opposite sides of your clay like plates moving apart at a divergent boundary. Note what happens in the middle. Draw what your model looks like. Compression Push on opposite sides of your clay section. Do not squish completely. Note what happened in the middle. Draw what your model looks like. Analysis Questions: 1. What kind of boundary would create shearing stress? 2. What kind of boundary would create tensional stress? 3. What kind of boundary would create compressional stress? 4. Which stress, in your own opinion, creates the most amount of change in the Earth’s crust? Why? 5. If rocks don’t break, they fold. What is the difference between an anticline and a syncline? 6. How can you explain how building up stress creates earthquakes? 7. Which type of stress creates the greatest number of earthquakes and why? Conclusion: There are 3 different stresses, 3 different faults and 3 different plate boundaries. Use your ESRT to find a real life example of each boundary. Name the stress and the fault at these boundaries. 1– 2– 3-