Meteorology Land Vs. Water N. Hemi
advertisement

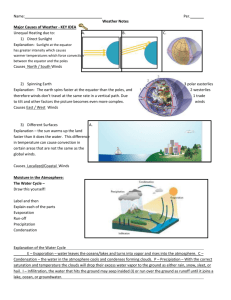
Meteorology Land Vs. Water N. Hemi- 60% Water, 40% Land S. Hemi- 81% Water, 19% Land Water heats up and cools down slowly-specific heat N. hemi has higher highs and lower lows than s. hemi Composition and Evolution of our ATM 78%N 21%O Traces of: S, Ar(other noble gasses), CH4, CO2, H2O Sources of our ATM: Volcanoes- SO2, CH4 Meteorites Lightning Erosion Mauna Loa Graphx-axis= time y-axis= CO2 concentration in ppm Shows: steady and ever increasing slope Yearly jogs in slope indicate seasons. Peak per year = fall and Valley per year = spring. Aerosols- suspended fine(small) particles in the ATM. Solid particles dissolved in air that are too small to see, but can get in your body. React with other gasses to make a hole in our ozone layer(CFC’s) and acid rain(Sulfur). Can affect climate by affecting cloud formation(they help make clouds) and reflecting sunlight. Sources of Aerosols: Volcanoes, Dust Storms, Forest/Grass Fires, All Fossil Fuels Burning, Factories, Dead Skin Cells, Space Dust Hydrologic(water) Cycle- no start/stop, but continuous procedure where water changes forms and places, but is never lost or gained. Condensation: gas to liquid(clouds) Precipitation: H20 back to earth Evaporation: liquid to gas Transpiration: evap. from plants Also includes sinks(places where it looks like water is removed from the cycle): ocean, groundwater, the rock cycle, glaciers Hydrologic Cycle- describes the continuous motion of water above and below the surface(powered by the sun) Evaporation- water transported from the surface to the ATM(liquid to gas). Affected by temp, humidity, amount of moisture available. Condensation(vaporization)- transfer of H2O from gas to liquid. Affected by temperature and amount of moisture available. Condensation creates clouds. Precipitation- buildup of moisture in cloud. Transfer of water from ATM to ground. Transpiration- water evaporates from the leaves of plants Pressure Vs. Altitude: Air gets thinner when you go higher. It’s going to weigh things down. For every height increase there is less air on top of you. As the air on top of you decreases the air will expand. Air pressure decreases with altitude. Layers of the atmosphere In the troposphere the temp goes down The top of the mesosphere is 80 km In the mesosphere the temperature decreases this is where the meteors get burned. The thermosphere the shuttles fly here and the temps go up. at 10,000ft, pressure is 65% sea level. At 30,000ft(top of Mt. Everest) there is less than 30% air pressure left. As you leave the earth, there is less ATM above, so there is less pressure, which allows air to expand. The decrease in pressure with height forces the temp to drop. Troposphere is 80% mass of the atmosphere (0-10km). All earth’s weather is in the troposphere. Stratosphere (10-30km) has the ozone layer. Planes fly here. The temperature increases. Mesosphere (30-55km) is where meteors get burned. The temperature decreases. Thermosphere (up to 160km) Space shuttles fly here. Temps increase here. Exosphere (55120km) is the boundary of earth/space. Heat: form of energy, can transfer between objects Parcel of air: imaginary volume of air used in meteorology to explain the ATM. Temperature: degree of “hotness” or “coldness” of an environment- measure of the average kinetic(moving particles)energy. (what we feel as hot or cold) Temperature scales: Fahrenheit- Boiling Pt = 212F Freezing Pt= 32F Absolute Zero= 460F Most of Life is Spent Between 100F and 0F Celsius- boiling point of water= 100C Freezing point = 0 C. absolute zero = -273 C Most of Life is Spent Between 35C and -10C Kelvin- boiling point= 373 K freezing point= 273 K. absolute zero = 0 K. Most of Life is Spent Between 263K and 310K. Specific heat: The amount of heat required to raise one gram of a substance by 1 C. Low specific heat = rocks, sand, pavement High specific heat = air, water, liquids Convection: transfer of heat in a vertical direction. Form of heat transfer, works in a vertical direction. Hot material rises and cool material falls. Sensible heat- a change in the temperature because of a change in energy. Conduction- transfer of heat between molecules that are touching. Examples: metal, soil, Poor conductors: water, air, Radiation- transfer of energy through waves/particles through space. Advection- transfer of energy that works horizontally. Caused by pressure differences which are caused by temperature which are caused by unequal heating of the earth. Adiabatic cooling- cooling of a parcel of air as it rises. As air rises there is less pressure on it so it expands, reduces air pressure and cools. Lapse Rate: The rate of decrease of temp with height equals 10C/ 1000m for dry air. Lapse rate equals 6c per 1000m for moist air. Stefan- Boltzmann Law: E = T4 hot objects emit a lot more energy then cool objects. Wien’s Law: objects of different temperatures emit different color light. Hot objects emit short wave length light. Short wave length light has high energy The Seasons: Are based on the 23.5 degree tilt of Earth’s axis. During the s-hemi summer the s-hemi receives 3X the light of the n-hemi. Vernal equinox: Late March marks the beginning of Spring. Autumnal equinox: Begins late September and marks the beginning of Fall. Solstices: Winter (late December) = start of winter, Summer (June) = start of summer (apogee) Atmospheric Window: Wave lengths of light that go through the atmosphere. There is a window for: IR, sunlight, and radio waves. There is no window for UV, X-rays, Gamna rays. a parcel of air rising gets cooler. Air pressure decreases with alt. That causes a parcel of air to expand. LAPSE rate- decrease in temp with height. When air is dry the lapse rate is 10c/1000m. When air moist the lapse rate is 6c/1000m. The dryer the air the steeper the lapse rate. Diabatic cooling- is moist lapse rate. Stefan-Boltzmann Law- E=T4- High temps= high E. Wein’s Law= short wavelengths are emitted by hot objects Albedo- reflectivity of a surface. High albedo= metal Low albedo= rubber, black paper The higher the albedo of a surface, the cooler it stays. The Seasons - earth orbits sun on tilted axis of 23.5 degrees earth does not receive sunlight evenly Summer = n. hemi. Tilted towards sun Winter = n. hemi. Tilted away from the sun Fall/Spring = both hemis. Receive equal light June 21st longest day in n. hemi. w/ most direct sunlight- summer solstice Dec. 21st shortest day in the n. hemi. w/ the least amount of sunlight- winter solstice Sept. 22nd autumnal/ fall equinox March 22nd vernal/ spring equinox Atmospheric window- the wavelengths of light that can go through our atm. No Window- x-ray, gamma, uv Window – visible light, radio light, infrared (partial) The Greenhouse Effect(GHE) Rise in temperature because of gasses present in our ATM. The main gasses are CO2, methane, nitrous oxide, H2O. All of those gasses transmit sunlight(short wavelengths). All of these gasses absorb and then emit earthlight. With the GHE, earth’s average temp is 57F. without the GHE, earth’s temp would plummet to 0F. When people talk about the effect humans have, they are talking about global warming which includes the added anthropogenic GHG’s. Chapter 3 Notes $Temperature$ Daily Mean Temp- Average of the daily max and min. Temps Annual temp cycle- Seasonal change in temps. Caused by tilt of earth Annual mean temp- The average temp. for the year. Add up monthly means and divide by 12. Temp range- Difference between max and min Factors that effect daily (diurnal) temp range- Cloud cover/ Reduces range, Wind/Reduces range, Humidity/ Reduces range Factors that effect yearly temp range1. Latitude 2. elevation 3. Being near water/sand 4. Persistent clouds 5. 6. 7. Surface type Persistent Humidity Aspect Interannual Temp Changes(Global Climate Change) El Nino/ La Nina changes in the ocean temp. Volcanoes add chemicals to our atmosphere that blocks sunlight Glaciers make earths albedo go way up Sunspots make earth warmer Earths tilts various between 21-25 degrees. More equals colder Earths orbit flattens which makes earth colder Carbon dioxide Water temperature increases/climate would change Glaciers melting-when they melt earths albedo decreases El nino Volcanoes-make the earth colder, by putting gases in the air that reflect sunlight Earth’s tilt wabbles Earth’s orbit gets more elliptical which makes the earth colder Temperature Inversions: Normal Conditions: Temperature Drops with Height Inverted Conditions: Temperature Increases with Height How?Why?Where?-occurs when less dense(warm) air moves over more dense air (cold) Warm front-when the clouds are warmer than the ground Cold front-cold air moves in at ground underneath warm air Nocturnal inversion- the winter season especially October-March, longer nights earth cools faster than air Just before daybreak is the most inverted air. Valley inversion- cold air gets trapped between mountains Lapse Rate- rate of decrease in temp with height. 10C/Km when dry. Will be less if humid. Stable Air- actual lapse rate less than 10C. Air will not rise- no clouds Unstable Air- actual lapse rate greater than 10C. Air will rise and form clouds. Wind Chill- how much the wind makes the temp feel colder. Caused by blowing away the warm conducted air your body creates. Farmers Vs. The Cold- 1-spray crops to freeze them because the latent heat of freezing is exothermic. 2- cover them with tarps 3- fans that mix the air Chapter 4 Measuring Moisture in the Air Mixing Ratio- ratio of mass of moisture in air vs. mass of dry air. This is an absolute value and does not depend on temp. Saturation Vapor Pressure- pressure exerted by a gas on its container. Saturation means the most moisture air can hold before condensation occurs. Relative term because it depends on how cold/hot the air is. Cold air can’t hold much moisture, so a little bit of moisture is a high vapor pressure. Hot air can hold a ton of moisture, so the same little bit of moisture seems bone dry. Evaporation- reverse of condensation- when water is turned to a gas. Factors that affect evap rate: 1sun/heat 2wind 3moisture already in air 4amount of water 5shape of water Dew Pt- temp at which a given parcel of air must be cooled to to create condensation Dew Pt Depression- difference between air temp and dew pt temp(always lower than air temp) Lab ReviewSurface Area-What is the effect of surface area on evaporation rate? More surface=more evaporation Constant- ml of water, air pressure, air temp Control- the least s.area Temperature- What is the effect of temp on evaporation rate? Hotter=more evap Constant- amount of water, surface area Control- coldest trial Cloud FormationCome from evaporated water. Must be higher than 50ft. Have to have rising air that cools adiabatically. Rising air cools to reach its dew pt and condenses into droplets. Condensation Nuclei- smoke, pollen, pollution, dust. These particles provide a surface for the vapor to condense around. Situations that help clouds to form(cause air to rise): 1Recent Rain 2Solar Energy(heat) 3Mountains 4Fronts(warm or cold) Cloud TypesLow- stratus(flat or layered), stratocumulus(puffy, tall), nimbo(rain)stratus(low, flat, raincloud) Middle- alto(high)stratus(layered), cumulonimbus(puffy, tall raincloud), altocumulus(high, puffy- lower than a cirrus, but higher than a stratus) High- cirrus(high, thin, icy), cirrocumulus(high, wispy, puff), cirrostratus(high, layered cloud) Special Clouds- contrails- aircraft exhaust, lenticular- lens- form as wind goes past a mountain or hill, congestus- warm, moist air rising in cauliflower shapes Precipitation Types Liquid- rain- cloud temp(either above or below 32F) air temp(above 32F)ground temp(above 32F) Freezing- freezing rain- cloud temp(usually below 32F)air temp(warmer than 32F)ground temp(below 32F) Frozen- sleet- cloud temp(below32F) air temp(above 32F) ground temp(below 32F)A thicker layer of ATM is below 32F for sleet, therefore it is frozen before it hits the ground and makes a “tink” sound when it hits. Snow-cloud(below 32F) air(below32F) ground(below 32F) Hail- cloud(below 32F) air(above32F) ground(above 32F)- forms in the updraft of severe tstorms in the summer. Nimbus(root)- raining Cumulo(prefix), cumulus(root)- puffy, taller rather than wide Alto(prefix)- high Strato(prefix), stratus(root- layered, sheetlike Cirro(prefix), Cirrus(root)- curly, wispy Altostratus= high layered cloud Cumulonimbus= puffy, raincloud Cirrus= highest, wispy, icy Stratocumulus= puffy, layered cloud Cirrostratus= thin, wispy, layered(sundog- icy ring around sun) Nimbostratus= raining, sheet cloud Chapter 5 Weather Instruments ASOS- automated surface observing system. Resistance thermometer- temp is sensed by using predictable changes in the resistivity of a wire at different temps. (Pt)(Ni) Alcohol thermometer- used to measure temps. From -115C-785C. Liquids are used because they expand and contract easily. Rules for Placement of Thermometers-6ft above ground -away from structures -in the shade Dew point hygrometer- an instrument that measures dew point by measuring the temp. at which water vapor condenses Psychrometer- measures humidity by using two thermometers. One having a wet bulb (should be colder) and one having a dry bulb (should warmer) Mercury barometer- an instrument that determines atmospheric pressure using liquid (Hg) Aneroid barometer- measures air pressure by using thin metal which expands and contracts due to pressure changes Anemometer- measures wind speed by using cups Wind vane- measures wind direction Wind sock- measures direction and speed Rain gauge- measures liquid precipitation that falls RadiosondeWeather MapsCeilometer- measures the height of the lowest cloud. Can help determine precipitation type and amount. Visibility Sensor- measures the presence, intensity and duration of fog. Give secondary info on precipitation rate. GEO- Geostationary Earth Orbit(satellite)- Orbit earth exactly as fast as earth spins, so it appears in one spot. GEO’s orbit around the equator and are designed to track hurricanes. Orbit height is 35,000km or 20,000mi. LEO- Low Earth Orbit- orbit at 850km or 500mi. Provide very clear pictures. Move around the earth so they provide information on more than one storm, but none for any length of time. Also, they orbit from pole to pole so they give info on winter storms. Visible Satellite- provides a picture from space of how the earth and clouds would actually look from space. Useless at night. Infrared Satellite- uses heat to show cloud height. Cold weather clouds(stratus) grow wide rather than tall and show up as warm clouds. Warm weather clouds(cumulus) grow tall rather than wide and show up as cold clouds. Water Vapor Satellite- shows moisture as bright green and dry air as black and really dry as orange. Excellent because it clearly shows the general flow of airmasses. RADAR- uses Radio Detection and Ranging to tell where precipitation is. Doppler RADAR- uses the Doppler effect to measure speed of storms. Wind Profiler- represents rotation among thunderstorms as signs of tornadoes. Wind Chapter 6 Gravitational Force- force of attraction between all objects in the universe. The strength of the force is based on mass and distance. The earth pulls strongest on everything we see because we are VERY close to the center of the earth. The next strongest pull on objects is from the moon as seen by the tides. The next strongest gravitational pull is from the sun. Pressure Gradient Force(PGF)- acceleration of air due to pressure -Usually responsible for excelling a parcel of air from a high pressure to lower Coriolis Force- Changes the direction but not the overall speed of anything moving with respect to the ground (including air) -Apparent reflection of moving objects when they are viewed from a rotating reference frame. -Objects deflect to the right in the northern hemisphere -Objects deflect to the left in the southern hemisphere -The amount of deflection the air makes is directly related to both the speed at which the air is moving and its latitude. Frictional Force- caused by air flowing over a rough surface, reduces wind speed, works opposite the flow of wind Surfaces with High Friction: Mtn’s/Volcanoes Bldg’s Trees Surfaces with Low Friction: Water(ocean/lake) Grassland(Neb/Iowa/Kansas) Centrifugal Force- outward force associated with rotation- seen in meteorology as air flows from H to L pressure and is curved by coriolis Hydrostatic Balance- balance between gravity and upward PGF caused by high pressured air at earth’s surface vs. low pressured air at altitude Geostrophic Balance- wind that results from balance between PGF and Coriolis(basically, the wind we feel on earth) Buys Ballot’s Law- Wind flows at right angle to PGF. Way of determining where low pressure is by putting back to wind and reaching out with left hand that will point to where storm is. Gradient Balance- A more accurate method of determining the wind because it is a three way balance of Coriolis, PGF and centrifugal force. It is the wind you feel when you stand on Earth. Guldberg-Mohn Balance- The three way balance of Coriolis, PGF and Friction. Because of friction wind flows across iso-bars. Scales of MotionMicroscale- smaller, 1 km or less, tornado Mesoscale- 1km-100’s km, thunderstorms, fronts, sea/land breezes, snow storms, hurricanes Synoptic- 100’skm-1000’s km, when the total cloud outflow surrounding a storm is included, it is synoptic scale Global- a wind is an established pattern of weather over a given area over time Local BreezesLand Breeze- at night, sand cools faster than water. This creates L over the water and H over the sand. PGF goes from H to L so at night there is a breeze from the land to the sea. Sea Breeze- during the day, sand heats faster than water. This creates L over the sand and H over the water. PGF goes from H to L so during the day there is a breeze from the sea to the land. Hadley Cells- direct sunshine at equator causes high heat, low pressure, rising air. As that air rises it becomes high pressure spreading air. That air sinks at 30N. Half of that sinking air heads S and is bent by coriolis and forms the trade winds. The other half of that sinking air heads N and is bent by coriolis and forms the westerlies that bring us our weather. Jet stream- Fast flowing stream of air moving from West to East Polar Jet- W to E. Stronger than subtropical jet, AVG 600 N Subtropical Jet- W to E. AVG 300 N Doldrums- A belt between 5 N and 5 S where neither trade wind dominates. Doldrum means no air movement. Subtropical high- Heavy sinking air at 30 N/S where air from Hadley Cell descends. Rossby Waves- Giant meanders in high-altitude winds that are a major influence on weather. Patterns of Rossby Wave 1. 2. 3. 4. Zonal Flow- General w to e pattern of air. Northern areas are cold, southern areas are warm. A small amplitude wave Meridional Flow- the general flow pattern is extremely high amplitude. The weather becomes extreme. Split Flow- Northern and Southern branches of jet stream have different patterns. Blocking Pattern- Nearly stationary pool of air that blocks the flow of weather from w to e. Leads to both floods and droughts. Zonal Index- Positive=Zonal, Negative=Meridional ITCZ- (Intertropical Convergence Zone) Formed by trade winds meeting at the equator. Causes clouds from the air converging, shifts seasonally with the sun. Monsoons- A seasonal wind that reverses therefore creating a climate of rainy and drought. Persistent wind flowing off the ocean and uphill creates rainy season and persistent wind flowing downhill creates a dry season. El Nino- Periodic alteration in the trade winds that alters the globe’s weather. Invloves more warmth in SA and coolness in SE Asia. Both of which are extremely damaging to the culture there. SE Asia experiences a drought which leads to crop failures and SA will have flooding. Upwelling- A wind driven surface current that pushes warm water away which brings in cold water which is usually nutrient rich. Instead of crop failure there is no catch which would lead to starvation. PDO- (Pacific Decadal Oscillation) Multi- decade shifting of the climate in the pacific. A larger cycling of the waters of the Pacific than El Nino. AO- (Arctic Oscillation) H and L pressures swap from Arctic to Tropics. This causes blocking pattern in NA and therefore big snow storms for NE and warmth in the Arctic. La Niña- Stronger than normal tradewinds. (amplifies the normal conditions) Hurricane (Atlantic)/Typhoon(Pacific)/Cyclone(Indian) formation- forms over warm water (78F). Warmth is fuel/energy. Thunderstorm complex High humidity low air pressure- allows air to rise, cool, condense rotation- change in direction and speed of wind preexisting condition- trough of low pressure in place allows other ingredients to form. Stages: 1. 2. 3. 4. Wave- no closed formation, no structure Tropical depression- organized circulation with sustained winds less than 38mph. Tropical storm- organized circulation with winds between 39 and 73mph Hurricane- closed circulation with eye and winds over 74mph a. 1- 74-95mph b. 2- 96-110mph c. 3- 111-130mph d. 4- 131-154mph e. 5- 155+mph Structure of a hurricane Spiral- counterclockwise rain bands Eye wall- surrounds the eye consisting of most intense rain and wind Eye- calm winds, warmest part of storm, sunny, clear, high pressure sinking air Destructive forces of hurricane 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 1. Wind- north east quadrant is most dangerous because storms forward motion adds to wind speed Storm surge- high winds blowing on shore plus low pressure allows water to rise quite a bit. Rain Tornadoes upon landfall Mudslides in mountainous Socioeconomic factors a. Infrastructure to deal with damage. b. Structural stability determines how much damage a given wind speed does