Chapter 2vocab list
advertisement

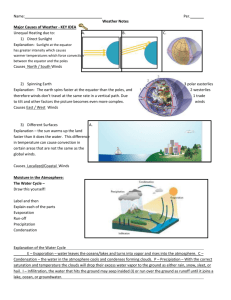
Chapter 2: Understand Weather Vocabulary Weather- the short-term state of the atmosphere, including temp., humidity, precipitation, wind, & visibility Humidity- the amount if water vapor in the air Relative humidity- ratio of amt. of water vapor in air to max. amt. of water vapor air can hold at a set temp. Condensation- change of state from a gas to a liquid Cloud- collection of sm. Water droplets or ice suspended in air, which forms when the air is cooled & condensation occurs Precipitation- any form of water that falls to the Earth’s surface from the clouds (rain, snow, sleet, hail, etc.) Air mass- lg. body of air where temp. & moisture content are similar throughout Front- boundary between air masses of different densities & usually different temp. Cyclone- an area in atmosphere that has lower pressure than surrounding areas and has winds that spiral toward the center Anticyclone- rotation of air around high-pressure center in direction opposite Earth’s rotation Thunderstorm- usually brief, heavy storm that consisting of rain, strong winds, lightning, & thunder Lightning- electric discharge that takes place between 2 opposite charged surfaces (ex: cloud and ground; 2 diff. parts of one cloud) Thunder- sound caused by raid expansion of air along an electrical strike Tornado- destructive, rotating column of air that has very high wind speeds, is visible as a funnel-shaped cloud, & touches the ground Hurricane- severe storm that develops over tropical oceans and has strong winds (>120 km/h) that spiral in toward low-pressure storm center Thermometer- instrument that measures and indicates temperature Barometer-instrument that measures atmospheric pressure Anemometer- instrument that measures wind speed Chapter 2: Understand Weather Vocabulary Weather- the short-term state of the atmosphere, including temp., humidity, precipitation, wind, & visibility Humidity- the amount if water vapor in the air Relative humidity- ratio of amt. of water vapor in air to max. amt. of water vapor air can hold at a set temp. Condensation- change of state from a gas to a liquid Cloud- collection of sm. Water droplets or ice suspended in air, which forms when the air is cooled & condensation occurs Precipitation- any form of water that falls to the Earth’s surface from the clouds (rain, snow, sleet, hail, etc.) Air mass- lg. body of air where temp. & moisture content are similar throughout Front- boundary between air masses of different densities & usually different temp. Cyclone- an area in atmosphere that has lower pressure than surrounding areas and has winds that spiral toward the center Anticyclone- rotation of air around high-pressure center in direction opposite Earth’s rotation Thunderstorm- usually brief, heavy storm that consisting of rain, strong winds, lightning, & thunder Lightning- electric discharge that takes place between 2 opposite charged surfaces (ex: cloud and ground; 2 diff. parts of one cloud) Thunder- sound caused by raid expansion of air along an electrical strike Tornado- destructive, rotating column of air that has very high wind speeds, is visible as a funnel-shaped cloud, & touches the ground Hurricane- severe storm that develops over tropical oceans and has strong winds (>120 km/h) that spiral in toward low-pressure storm center Thermometer- instrument that measures and indicates temperature Barometer-instrument that measures atmospheric pressure Anemometer- instrument that measures wind speed