General Physical Science Unit 3: Properties of Matter. Chapter 16
advertisement

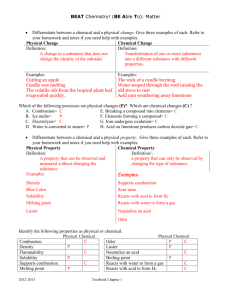
General Physical Science Unit 3: Properties of Matter. Chapter 16 Oregon State Content Standards Exam Date: Dec 8,9. Haspela p7 Dec 5 H.1 Structure and Function: A system’s characteristics, form, and function are attributed to the quantity, type, and nature of its components. H.2E.1 Identify and predict the effect of energy sources, physical forces, and transfer processes that occur in the Earth system. Describe how matter and energy are cycled between system components over time. H.2E.2 Explain how Earth’s atmosphere, geosphere, and hydrosphere change over time and at varying rates. Explain techniques used to elucidate the history of events on Earth. H.2P.3 Describe the interactions of energy and matter including the law of conservation of energy. Objectives Meeting benchmark 1) I will be able to classify samples of matter from everyday life as heterogeneous mixtures, homogenous mixtures, compounds, or elements. 2) I will be able to explain the difference between a homogeneous mixture and a heterogeneous mixture. 3) I will be able to measure mass with a balance. 4) I will be able to measure volume using a graduated cylinder and metric length using a ruler. 5) I will be able to distinguish between mass and volume and the appropriate unit for each. 6) I will be able to find the volume of a solid through direct and indirect measurement. 7) I will be able to explain how matter changes state. 8) I will be able to explain why temperature does not change during phase changes. 9) I will be able to describe the set of processes through which water is continuously recycled on Earth. 10) I will be able to explain the role of the sun in the water cycle. 11) (EXCEEDS): I will be able to convert from one unit of measurement to another. Exceeding benchmark To show my ability to exceed the benchmarks I will use; words, drawing, mathematical relationships or other methods; to further analyze patterns and/ or relationships in the benchmarks. Vocabulary displacement Condensation Matter indirect measurement Evaporation Mass phase change Transpiration Gram, Kilogram solid Sublimation Volume liquid Deposition Milliliter, Liter gas Precipitation cm3 plasma Groundwater Centimeter, Meter, Kilometer boiling point HOMEWORK FOR THIS UNIT: mixture melting point substance heat of fusion 1.) Read 277-279. Concept Review #1,2,3, on 287. homogeneous mixture heat of vaporization 2.) Read 280-286. Concept Review #49 on p 287. Problem #2 on 288. heterogeneous mixture boiling/condensation 3.) Phase change Lab Report element freezing/melting 4.) Problems #1,3 on 288. compound sublimation/deposition 5.) Read 429-432. Vocab review set 1 on pg 446. Concept Rev #1,2 on 447 Practice Questions 1. Match the item with the correct classification of matter: Homogeneous mixture Heterogeneous Mixture Element Compound Vanilla Ice Cream Chocolate Chip Cookie Dough Ice Cream Carbon Dioxide Water Pizza Jello Apple Juice Gold 2. What is the difference between an element and a compound? 3. How would you measure an irregular solid (like a rock)? 4. What are two units used for mass? 5. What are two units for volume? 6. Fill in the blanks: _____________ is a phase change from a liquid to a solid. Deposition is a phase change from a _______ to a solid. Evaporation is a phase change from a __________ to a _____________. 7. What is the definition of matter? Give an example of something that is not matter. 8. How could you use indirect measurement to determine the volume of one drop of water from a leaky faucet? 9. Explain what happens to the kinetic energy of molecules as something freezes. 10. Convert 5 cm to meters. 11. What change in states of matter occurs in the following phase changes? (Ex, Melting = solid liquid) Condensation= Transpiration= Evaporation = Freezing = Sublimation = 12. How does the sun power the water cycle? Answers: 1. Vanilla Ice Cream = Homogeneous mixture Chocolate Chip Cookie Dough Ice Cream= Heterogeneous Mixture Carbon Dioxide = Compound Water = Compound Pizza = Heterogeneous Mixture Jello = Homogeneous Mixture Apple Juice = Homogeneous Mixture Gold = Element 2. Element is made of one type of matter. Compound is made of more than one type of matter. Both cannot be separated. 3. Displacement. Put water in graduated cylinder. Put rock in. Subtract initial volume from final volume. 4. Gram, Kilogram 5. mL, Liter, cm3 6. freezing, gas, liquid, gas 7. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Energy is not matter. 8. You could count the number of drops until you get to 5 mL. Then divide 5mL by the number of drops. 9. Kinetic energy decreases. 10. 5cm = 0.05m