Unit_1_Student_Syllables_Handout 167KB Aug 02 2013 05
advertisement

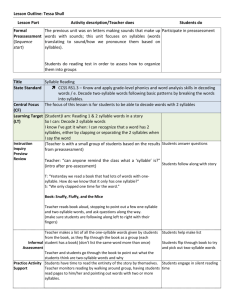
Unit 1, Syllables Preparation What are the following words/phrases in Chinese? Look up these words in your dictionary then write down their meaning in Chinese. 1. efficient 2. clearly 3. rhythm 4. melody 5. prosody 6. practice 7. syllables 8. basic unit 9. vowel 10. consonant 11. listen 12. tap 13. pound 14. stamp 15. clearly 16. table 17. cell (in a table) 18. column (in a table) 19. row (in a table) 20. letter (part of a sentence) 21. tone 22. monotone Optional Practice Write a sentence using each word. This will help you remember the word. A - Introducing Syllables1 The basic unit of English rhythm is the syllable2. Listen. ☐ 1 2 3 4 ease care paint call ☐☐ 5 6 7 8 easy careful painted recall ☐☐☐ 9 10 11 12 easily carefully repainted recalling Homework Make a recording of your own voice using your smart phone or computer. Speak the words above emphasizing each syllable but try to make the words sound natural (don’t make them sound unnatural). Tap out template words ‘ease’ and ‘easy’ to illustrate syllables. Ask student how many ‘syllables’ after tapping each a second time. Encourage student to do it with you at the same time once or twice (this choiring can build confidence) then on his or her own. 2 For advanced students: explain the sonority hierarchy http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sonority_hierarchy Lowest to highest: [a] > [e o] > [i u] > [r] > [l] > [m n] > [z v ð] > [s f θ] > [b d ɡ] > [p t k] and how the use of low sonority signals a new syllable to native English speakers. Demonstrate legal patterns of onset/nucleus/coda - V CV VC CVC and illegal nucleus C. 1 Pronunciation Course (based on ‘Clear Speech’ by Gilbert) Unit 1, Syllables Page 1 of 10 B – Which word is different? Listen. You will hear three words. Place a tick in the column for the word that is different. When finished, help your teacher by writing your final answer A, B or C in the left column. Example Person 1: “A. Fish, B. Fish, C. Fishy” Person 2: [Places a tick in column C] A C B C 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 C – Tapping the syllables ☐☐☐ Listen and repeat the words while tapping your hand or foot for each syllable. ☐ 1 2 3 4 5 one two three four can't ☐☐ 6 7 8 9 10 seven sentence focus eighteen cannot Pronunciation Course (based on ‘Clear Speech’ by Gilbert) ☐☐☐ 11 12 13 14 15 eleven direction continue emphasis syllable Unit 1, Syllables ☐☐☐☐ 16 17 18 19 20 identify analysis it’s important he wants a book. I have to go. Page 2 of 10 D – Which word do you hear? Listen. Write A or B in the left hand column depending on which word in the pair you hear. Example Person 1: “mess” Person 2: [Writes ‘A’ in the left hand column’.] ☐A 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 mess blow prayed loud sport round claps clone state squeeze ☐☐ B 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 messy below parade aloud support around collapse cologne estate excuse E – Pair work: One or two syllables? ☐☐☐ Take turns saying words. Do not always say the first word in each pair. Example 1 Person 1: [Says one word from each pair of words.] Person 2: [Holds up one finger if the word has one syllable or two fingers if the word has two syllables.] Example 2 Person 1: “Sunny” Person 2: [Holds up two fingers.] ☐A ☐☐ B 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 sun red flow rose steam paint boss sport blow sunny ready fellow roses esteem painted bosses support below 10 sleep asleep Pronunciation Course (based on ‘Clear Speech’ by Gilbert) Unit 1, Syllables Page 3 of 10 F – Extra syllable in past tense verbs ☐☐☐ Usually, when ‘–ed’ is added to a verb to make it past tense, the number of syllables in the verb does not change. But with some verbs, adding ‘-ed’ does add an extra syllable. 1 Listen to how ‘-ed’ changes the following verbs. Present Tense Past Tense 1 2 ☐A ☐☐ B rent plant rented planted 2 Listen. Hold up one finger if you hear one syllable and two fingers if you hear two syllables. ☐ or ☐☐? 1 2 3 4 fainted laughed Started landed ☐ or ☐☐? 5 6 7 8 added watched worked folded ☐ or ☐☐? 9 10 11 12 closed3 caused treated asked ☐ or ☐☐? 13 14 15 planned4 counted cooked Do you know the rule for when ‘-ed’ is pronounced as an extra syllable? If not, work out the following puzzle. 3 Puzzle: The verbs in lists A and B below have an extra syllable in the past tense. How are they different from the verbs in lists C and D? A plant start treat wait heat attract B land fold add raid load record C work live save laugh call arrange D wash walk cause plan close contain Clue: Look at how the verbs in list A and list B are spelled. What do all the verbs in list A have in common? What do all the verbs in list B have in common? Can you figure out the rule for saying an extra syllable in the past tense? Write down what you think it is. Here it can be useful to explain the difference between voiced and unvoiced consonants. Students should touch their throat and feel the vibration difference between /p/ and /b/, /t/ and /d/ and /k/ and /ɡ/. 4 Here it could be explained that past tense words that do not have extra syllables can be pronounced either /d̥ / (which is devoiced /d/) or /t/. Of course words that have an extra syllable in past tense are /d/ which means there is a continua of sonority from /d/ to /d̥ / to /t/. 3 Pronunciation Course (based on ‘Clear Speech’ by Gilbert) Unit 1, Syllables Page 4 of 10 G – Counting syllables in past tense verbs ☐☐☐ 1 Listen. You will hear the present tense and the past tense of the following verbs. Write down the past tense of each verb. Present Tense Syllables Past Tense 1 2 3 4 5 6 paint clean need decide dislike prepare 1 1 1 2 2 2 painted 7 8 represent entertain 3 3 2 Listen again, write down the words again but also write the number of syllables in each past tense verb. Note that present tense words7-8 have more than 2 syllables! Present Tense Syllables Past Tense Syllables 1 2 3 4 5 6 paint clean need decide dislike prepare 1 1 1 2 2 2 painted 2 7 8 represent entertain 3 3 H – Pair work: Past or present? Take turns saying the sentences. Do not always choose sentence A. Example 1 Person 1: [Says sentence A or B.] Person 2: [Says "Past" or "Present".] Example 2 Student 1: "We wanted to buy a used car." Student 2: "Past." Past 1 2 3 4 5 A B We want to buy a used car. We start by looking in the newspaper. The doctors treat sick people. We rent a house every summer. The teachers want a pay raise. We wanted to buy a used car. We started by looking in the newspaper. The doctors treated sick people. We rented a house every summer. The teachers wanted a pay raise. Pronunciation Course (based on ‘Clear Speech’ by Gilbert) Unit 1, Syllables Page 5 of 10 6 7 8 9 10 They start at 8 o'clock. I intend to go shopping. People crowd into trains. Children skate on the frozen lake. They started at 8 o'clock. I intended to go shopping. People crowded into trains. Children skated on the frozen lake. They never visit the library. They never visited the library. I – Silent Letters Some English words have letters that are silent. Silent letters can affect the number of syllables in a word. It is important that you pronounce words in English with the correct number of syllables. 1 Listen. Draw an ‘X’ through the silent letters in these words. Some words will have 2 or more silent letters. ☐ 1 2 3 4 5 6 ☐☐ walked planned closed talked 7 8 9 10 11 12 business several chocolate wednesday every family 13 14 15 16 17 18 ☐☐☐ ☐☐☐☐ vegetable interesting laboratory elementary 2 Write two (2) words of your own in the blank cells like those in the columns. Homework Fill in the rest of the words in the blank cells like those in the columns. 3 Read the words aloud at least two times. Speak each syllable in the word but try to make the words sound natural (don’t make them sound unnatural). J – Dictation: How many syllables? Listen and write the sentences you hear. Then count the number of syllables in each sentence. You will hear each sentence two times. 1 2 3 4 5 Sentence Syllables He works in an interesting business. 9 Pronunciation Course (based on ‘Clear Speech’ by Gilbert) Unit 1, Syllables Page 6 of 10 K – Music of English5 1 Listen to these sentences. [04.mp3] How do you spell "ease"? E- A-S- E6 How do you spell "easy"? E-A-S-Y 2 Listen again. Say the sentences at least three times, or as many times as you need to be able to say them easily. Learn them like little songs. L – Pair work: Asking about spelling Take turns asking and answering. Example 1 Person 1: [Asks question A or question B.] Person 2: [Answers the question.] Person 1: [If the answer is wrong, repeats the question.] Example 2 Person 1: "How do you spell 'support'?" Student 2: "S-P-0-R-T." Student 1: "No. How do you spell 'support'”? Student 2: "S-U-P-P-0 -R-T." A T/S 1 2 3 4 5 6 How do you spell "ease"? How do you spell "sport"? How do you spell "traffic"? How do you spell "squeeze"? How do you spell "boss"? How do you spell "close"? T/S B How do you spell "easy"? How do you spell "support"? How do you spell "terrific"? How do you spell "excuse"? How do you spell "bosses"? How do you spell "close it"? Although simple, to Give the example of telephone numbers and how tone drops a little between number groups and a lot at the end of the utterance. Play ‘Zohan_Telephone_Dictation_Video_Clip.mp4’ clip and ask student why the character dialing the number is having trouble knowing when to stop pressing buttons. 6 This is just a happy tone rise for the last letter when spelling. In such short utterances using only a tone drop would sound very serious and likewise simply a tone rise would generate the wrong meaning, namely a question tone. 5 Pronunciation Course (based on ‘Clear Speech’ by Gilbert) Unit 1, Syllables Page 7 of 10 Pronunciation Course (based on ‘Clear Speech’ by Gilbert) Unit 1, Syllables Page 8 of 10 M – Music of English 1 Listen to the music of these sentences. [05.mp3] What does "easy" mean? "Easy" means "not hard." B Listen again. Practice saying the sentences until you can say them easily. N – Pair work: Asking about meaning Take turns asking and answering. Example 1 Person 1: Ask question ‘a’ or question ‘b’. Person 2: Say the matching answer. Example 2 Person 1: "What does 'easy' mean?" Person 2: "'Easy' means 'not hard."' 1 a b 2 a b 3 a b 4 a b 5 a b 6 a b Person 1/2 Person 1/2 What does "ease" mean? What does "easy" mean? What does "need" mean? What does "needed" mean? What does "closed" mean? What does "closet" mean? Where is the first? Where is the forest? What does "traffic" mean? What does "terrific" mean? What does "cracked" mean? What does "correct" mean? "Ease" means "comfort." "Easy" means "not hard." "Need" means "must have." "Needed" is the past tense of "need. The opposite of "open." A place to put things. At the beginning. In the mountains. Lots of cars. "Great!" Something like "broken." "Right." Pronunciation Course (based on ‘Clear Speech’ by Gilbert) Unit 1, Syllables Page 9 of 10 O – Check yourself: Counting syllables ☐☐☐ 1 Listen. Write the number of syllables over the underlined words. This is the first city they visited when they traveled here on business. They were so pleased that they decided to stay seven extra days. 2 If you have a tape recorder, record yourself saying these sentences. Listen to hear how well you did. P - Syllable number game ☐☐☐ Divide into teams. In five minutes, how many foods can you think of that have one, two, three, or four syllables? ☐ rice ☐☐ ice cream ☐☐☐ banana ☐☐☐☐ asparagus Another possible category: countries and cities. ☐ France ☐☐ Japan ☐☐☐ Singapore Pronunciation Course (based on ‘Clear Speech’ by Gilbert) Unit 1, Syllables ☐☐☐☐ Argentina Page 10 of 10