Drama Terminology: Key Terms & Definitions
advertisement
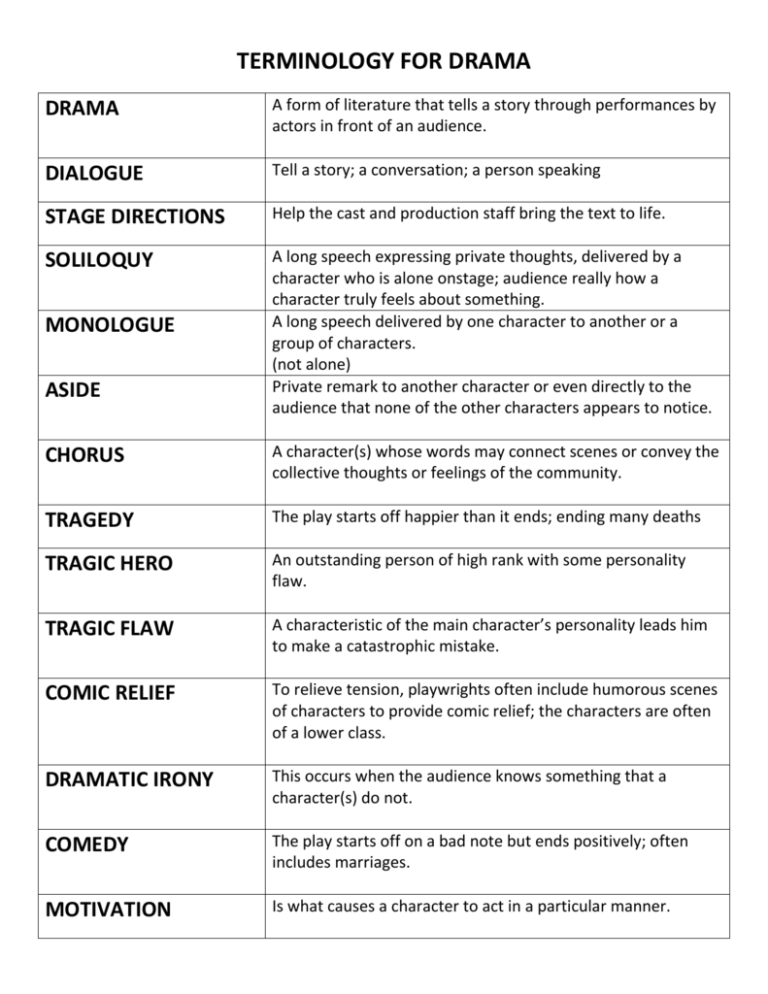
TERMINOLOGY FOR DRAMA DRAMA A form of literature that tells a story through performances by actors in front of an audience. DIALOGUE Tell a story; a conversation; a person speaking STAGE DIRECTIONS Help the cast and production staff bring the text to life. SOLILOQUY A long speech expressing private thoughts, delivered by a character who is alone onstage; audience really how a character truly feels about something. A long speech delivered by one character to another or a group of characters. (not alone) Private remark to another character or even directly to the audience that none of the other characters appears to notice. MONOLOGUE ASIDE CHORUS A character(s) whose words may connect scenes or convey the collective thoughts or feelings of the community. TRAGEDY The play starts off happier than it ends; ending many deaths TRAGIC HERO An outstanding person of high rank with some personality flaw. TRAGIC FLAW A characteristic of the main character’s personality leads him to make a catastrophic mistake. COMIC RELIEF To relieve tension, playwrights often include humorous scenes of characters to provide comic relief; the characters are often of a lower class. DRAMATIC IRONY This occurs when the audience knows something that a character(s) do not. COMEDY The play starts off on a bad note but ends positively; often includes marriages. MOTIVATION Is what causes a character to act in a particular manner. BLANK VERSE Unrhyming lines of iambic pentameter (10 syllables in a line with 5 of the syllables stressed) PROSE Not poetry; regular sentences; Shakespeare assigns prose to lower born characters. IAMBIC PENTAMETER Iambic=unstressed syllable followed by a stressed syllable (aboard, about, above); pentameter=5 stressed syllables in a line PUN When someone uses a word playfully, often with homonyms with a different meaning LOADED DICTION Words with strong connotation (emotional response to a word) IMAGERY Word picture; words that refer to the five human senses TONE The author’s attitude toward the subject; how is tone created in two ways: diction and imagery. MOTIFS Is a repeating pattern in literature or music