Syllable Reading Lesson Plan: Decoding Two-Syllable Words
advertisement

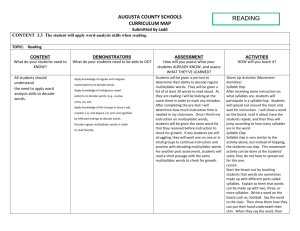
Lesson Outline: Tessa Shull Lesson Part Formal Preassessment (Sequence start) Activity description/Teacher does Students do The previous unit was on letters making sounds that make up Participate in preassessment words with sounds; this unit focuses on syllables (words translating to sound/how we pronounce them based on syllables). Students do reading test in order to assess how to organize them into groups Title Syllable Reading State Standard CCSS RS1.3 – Know and apply grade-level phonics and word analysis skills in decoding words / e. Decode two-syllable words following basic patterns by breaking the words into syllables. Central Focus The focus of this lesson is for students to be able to decode words with 2 syllables (CF) Learning Target (Student)I am: Reading 1 & 2 syllable words in a story (LT) So I can: Decode 2 syllable words I know I’ve got it when: I can recognize that a word has 2 syllables, either by clapping or separating the 2 syllables when I say the word Instruction (Teacher is with a small group of students based on the results Students answer questions Inquiry from preassessment) Preview Review Teacher: “can anyone remind the class what a ‘syllable’ is?” Students follow along with story (intro after pre-assessment) T: “Yesterday we read a book that had lots of words with onesyllable. How do we know that it only has one syllable?” S: “We only clapped one time for the word.” Book: Snuffy, Fluffy, and the Mice Teacher reads book aloud, stopping to point out a few one-syllable and two-syllable words, and ask questions along the way. (make sure students are following along left to right with their fingers) Teacher makes a list of all the one-syllable words given by students Students help make list from the book, as they flip through the book as a group (each Informal student has a book) (don’t list the same word more than once) Students flip through book to try Assessment and pick out two-syllable words Teacher and students go through the book to point out what the students think are two-syllable words and why Practice Activity Students have time to read the entirety of the story by themselves. Students engage in silent reading Support Teacher monitors reading by walking around group, having students time read pages to him/her and pointing out words with two or more syllables. Students have mini flip book activity with pictures from the book, Informal then they have to write out the two-syllable words underneath the Assessment pictures Students participate in activity Practice Activity Students will write 3 sentences using one and two-syllable (or more) Students write sentences Support words. The sentences can be about the story, but they don’t have to be. Closure Assessment of Student Voice T: “Do you think you can pick out how many syllables a word has? Do you like clapping out the sounds or saying the word slowly better? Do you like this book/is it one you’d want to read again by yourself outside of school?” Formal [The section for formal postassessment ends the lesson sequence Postassessment and does not need to be shown on preceding lessons.] (Sequence end) you can give a general statement/ type of assessment here- “end of unit or benchmark assessment” Within the text: Use knowledge of syllables to help in voice-print match Beyond the text: Make predictions based on personal experiences and knowledge About the text: Share opinions about books Students answer questions in discussion edTPA Training Prompts Context for Learning 1. In what type of school do you teach? 2. Describe special features of the classroom setting. 3. Describe district, school, or cooperating teacher requirements or expectations that affect teaching. 4. What is the name of the course? What is its length? What is the schedule? 5. Is there any ability grouping? 6. Identify textbooks and other instructional programs used during instruction. 7. Describe other resources, such as dry boards or laptops, used during instruction. 8. What is the grade level composition? How many males and females? 9. Summarize the composition of students needing support, such as English Language Learners, gifted, students with IEPs or 504s, struggling readers, underperforming students. Identify each student’s accommodation, modification, or method of support. Task 1: Planning 1. Central Focus a1. Describe the central focus and purpose for the content you will teach in this learning segment. a2. Explain how the learning target is measurable, includes a verb (language function), and a few subject specific vocabulary words. a3. Explain how the learning target is worded so that students can self-assess their progress toward meeting it. b. How is the learning target related to the central focus? How are the learning targets unified by the central focus? c. Explain how your plans build on each other to help students learn. How do learning targets add knowledge or skills from one lesson to the next? d. How and when will you give students opportunities to express their understanding of the learning targets and why they are important to learn? 2. Knowledge of Students to Inform Teaching a. Prior learning, prerequisite skills, and understanding: What do students know, what can they do, and what are they learning to do? b. Personal/cultural/community assets related to the central focus—What do you know about your students’ everyday experiences, cultural backgrounds and practices, and interests? 3. Supporting Students’ Learning a. Explain how your understanding of your students’ prior learning and personal/cultural/community assets (from prompts 2a–b above) guided your choice or adaptation of learning tasks and materials. b. Describe and justify why your instructional strategies and planned supports are appropriate for the whole class and students with similar or specific learning needs. c. How will students identify resources to support their progress toward the learning targets? d. Describe common preconceptions (based on prior learning and experiences) within your content focus and how you will identify and address them. 4. Supporting Science Development through Language a. Language function: What verb appears in your learning target that represents the language function? b. Language demand: What learning activities or products will student write, speak, or do to represent the language demand and an opportunity to practice the language function? c. Additional language demand: How will students practice content vocabulary words shown in the learning targets? d. What learning activities enable students to practice using symbols or abstract representations of information (syntax), if these are part of the lesson? e. How is discussion (discourse) structured in activities? f. What other writing or speaking activities enable students to practice vocabulary and the verb shown in the learning target? 5. Monitoring Student Learning a. Describe how your planned formal and informal assessments will provide direct evidence for you and your students to monitor learning. b. Explain how the design or adaptation of your planned assessments allow students with specific needs to demonstrate their learning. c. Describe when and where you will elicit student voice (oral or written) during instruction to raise awareness in both you and the students of where students are relative to the learning targets. d. What tools and strategies will students use to monitor their own learning process during the learning segment?