Water in the Atmosphere Notes
advertisement
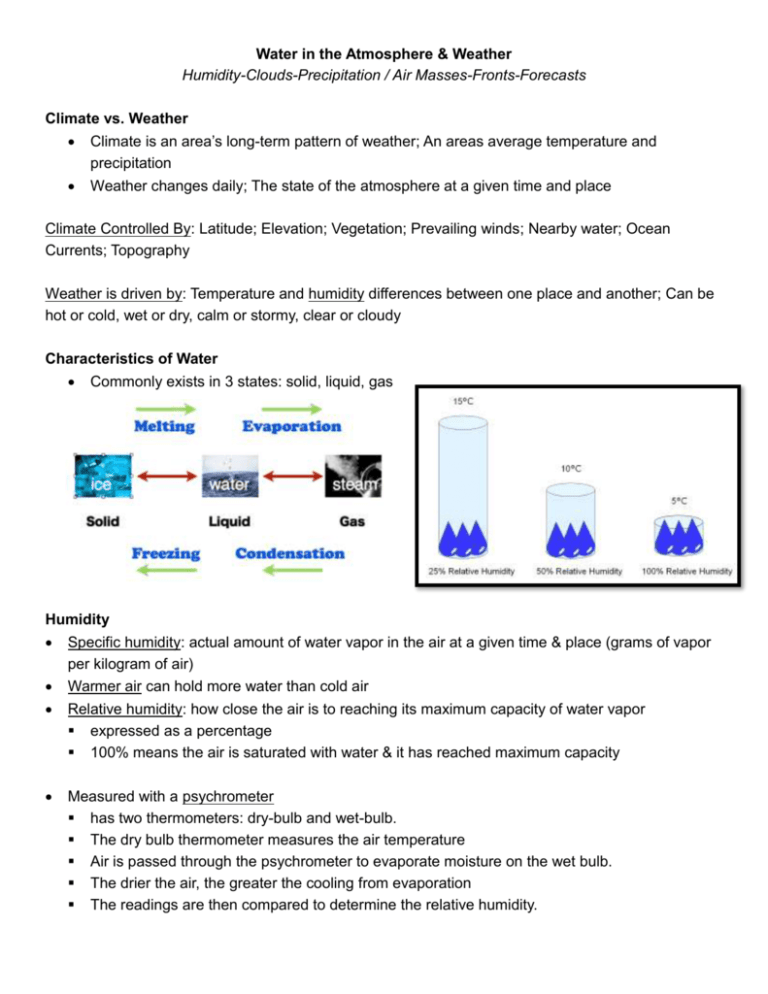
Water in the Atmosphere & Weather Humidity-Clouds-Precipitation / Air Masses-Fronts-Forecasts Climate vs. Weather Climate is an area’s long-term pattern of weather; An areas average temperature and precipitation Weather changes daily; The state of the atmosphere at a given time and place Climate Controlled By: Latitude; Elevation; Vegetation; Prevailing winds; Nearby water; Ocean Currents; Topography Weather is driven by: Temperature and humidity differences between one place and another; Can be hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy Characteristics of Water Commonly exists in 3 states: solid, liquid, gas Humidity Specific humidity: actual amount of water vapor in the air at a given time & place (grams of vapor per kilogram of air) Warmer air can hold more water than cold air Relative humidity: how close the air is to reaching its maximum capacity of water vapor expressed as a percentage 100% means the air is saturated with water & it has reached maximum capacity Measured with a psychrometer has two thermometers: dry-bulb and wet-bulb. The dry bulb thermometer measures the air temperature Air is passed through the psychrometer to evaporate moisture on the wet bulb. The drier the air, the greater the cooling from evaporation The readings are then compared to determine the relative humidity. Dew Point Condensation: when water changes from a gas to a liquid Dew point: the temperature at which the air becomes saturated with water vapor & condensation occurs If air cools below the dew point, water starts condensing into a liquid, forming dew or cloud droplets Cloud Formation Clouds (or fog) form only when there are condensation nuclei (like dust particles) for the water to condense on Air must cool below its dew point When warm, wet air from the surface rises, it begins to cool. Eventually, the temperature drops to its dew point, and the water vapor can condense onto the condensation nuclei Condensation level: the atmospheric level at which condensation occurs Clouds form in the troposphere – where temperatures decrease as altitude increases; Barrier at the tropopause because temperatures stop decreasing, so the air will not continue to rise. Cloud Types Classified by altitude and shape Main Cloud Types Stratus: clouds that form in layers Cumulus: fluffy clouds with flat bases Cirrus: high, feathery ice clouds Nimbus: dark rainclouds Notes: Water in the Atmosphere & Weather Humidity, Clouds & Precipitation Precipitation Any form of water that falls from a cloud to Earth’s surface Types of Precipitation Rain Snow Sleet: raindrops that refroze on their way to the surface Freezing Rain: raindrops that only freeze when they hit the surface Hail: when frozen raindrops are bounced up & down in the cloud until they fall in a huge ball of ice Types of Precipitation depend on the temperature of the atmosphere, both at the surface & on the way down Measuring Precipitation Rain gauge: measures liquid precipitation Measuring stick: measures frozen precipitation Where is Precipitation? Equatorial low and subpolar lows (60oN and 60oS) Rain Shadow effect: near a mountain range, the windward side gets lots of rain and the leeward side gets little/no rain – the rain shadow