Objectives & Vocabulary Chapter 18 Moisture, Clouds & Precipitation
advertisement

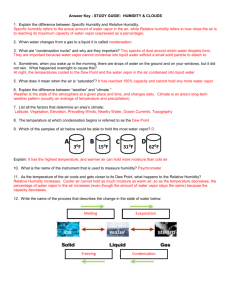
Objectives & Vocabulary Chapter 18 Moisture, Clouds & Precipitation 18.1 Water in the Atmosphere Objectives: 1. During phase changes when is energy absorbed and when is energy released? a. Draw and label a diagram of phase changes including when energy is released and absorbed DO THIS: Below each phase (solid, liquid, gas) draw the arrangement of molecules. Label the letters A – D with the correction description of what phase change is occurring. Label which “arrows” are absorbing energy and which “arrows” are releasing energy. What is “latent heat?” 2. Compare relative humidity and dew point. Define the following: Humidity – Relative Humidity – Dew Point – Saturation - a. How do warm and cold air compare in their ability to hold water vapor? Draw in circles to represent molecules of air for each temperature. Which temperature has more “room” to add water vapor molecules to the diagram? Therefore, which temperature of air can “hold” more water vapor? Which diagram will be saturated with water vapor first? (have the least amt. of water vapor) Therefore, which temperature reaches saturation point/dew point first? b. Use a psychrometer to measure relative humidity Answer the following: Which thermometer will register a cooler temperature? Why? The farther apart the temperature readings of the thermometers indicates what about the surrounding air? The closer the temperature readings on the thermometer indicates what about the surrounding air? c. What can change the relative humidity of air? What two things can you do to change the humidity of the air in a room? Explain why a cold room can have a higher humidity than a warm room. Vocabulary: Melting Sublimation Humidity Evaporation Deposition relative humidity Freezing latent heat dew point condensation saturation 18.2 Cloud Formation Objectives: 1. How do clouds form? a. What happens to air as it rises? 2. What is the difference between stable and unstable air? a. List 4 mechanisms that cause air to rise. Vocabulary: Condensation nuclei Orographic lifting dry adiabatic rate fron wet adiabatic rate 18.3 Cloud Types and Precipitation Objectives: 1. How are clouds classified? a. Identify different types of clouds b. Differentiate between types of precipitation Vocabulary: Cirrus stratus cumulus Nimbus (nimbostratus & cumulonimbus) alto (altostratus, altocumulus) types of precipitation (rain,snow,sleet,hail,rime,glaze) Chapter 19 Air Pressure and Wind 19.1 Understanding Air Pressure Objectives: 1. Describe the direction of air movement in high pressure and in low pressure. a. What is the ultimate energy source for wind? b. What direction does general weather patterns move across the U.S.? Vocabulary: High Pressure System Coriolis effect Low Pressure System jet stream 19.2 & 19.3 Pressure Centers and Winds Objectives: 1. Label the general pressure belts and how they create wind belts 2. How is an El Nino or La Nina event triggered? Vocabulary: Trade Winds Easterlies Doldrums Westerlies Horse Latitudes El Nino/La Nina Chapter 20 Weather Patterns and Severe Storms 20.1, 20.2 and 20.3 - Air Masses, Fronts, and Severe Weather Objectives: 1. Classify the different types of air masses. 2. Most severe weather happens along what type of front? 3. Describe the atmospheric conditions that produce severe weather. a. Describe the characteristics of: thunderstorms, tornados, hurricanes and monsoons b. How do we measure the severity of tornados and hurricanes? c. What does climate change indicate about severe weather? Vocabulary: Air mass front thunderstorm tornado Fujita scale Monsoon hurricane eye of the storm eye wall/storm surge Saffir-Simpson scale