Chapter 4 Review - The Taft School | Haiku Learning
advertisement

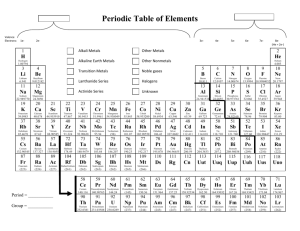
Chapter 4 – Chemical Foundations: Elements, Atoms, and Ions General Chapter Outline Elements & Symbols Dalton’s Atomic Theory Law of Constant Composition Law of Conservation of Matter Formulas of Compounds Atomic Structure Protons Neutrons Electrons Nucleus Atomic Number (Z) Mass Number (A) JJ Thompson William Thompson Gold Foil Experiment – Rutherford Isotopes (Names, Symbols, Percent Abundance Problems) Periodic Table Metals Nonmetals Metalloids Alkali Metals Alkaline Earth Metals Transition Metals Inner Transition Metals: Lanthanide Series, Actinide Series Halogens Noble gases Natural States of the Elements Diatomic Elements (H, O, Cl, Br, F, I, N) Allotropes Ions Cation Anion Monatomic Ions Polyatomic Ions (the BIG 5) Trends on the Periodic Table Ionic Compounds Electrolytes (when molten or dissolved in water) High Melting and Boiling Points Textbook Homework Problems: (1, 2, 9, 10, 19, 21, 22, 24, 25, 29, 35, 37, 39, 45, 47, 51, 53, 63, 64, 67, 69, 73, 75, 77, 83) Questions and Problems 1) Know the symbols and proper spellings for the elements on your list. 2) Outline how the atomic theory has progressed since the time of the early Greek philosophers. Be sure to include Dalton’s Atomic Theory, the Plum Pudding Model, and Rutherford’s Gold Foil Experiment. 3) What are the three subatomic particles? Indicate the relative charge and relative mass of each of these particles. Where are each located within an atom? What purpose does each particle serve? 4) What are isotopes? 5) Define atomic number and mass number? 6) How many protons, neutrons and electrons are in each of the following atoms/ions? a) Calcium – 41 b) Tin – 119 c) 50Cr2+ d) 79Br17) Naturally occurring sulfur has an average atomic mass of 32.066amu and consists of two isotopes, 32S and 34S. If their respective atomic masses are 31.972amu and 33.968amu, calculate the relative abundance of each isotope. 8) Describe the periodic table of elements. a) How are the elements arranged in the table? b) Why are the elements are arranged into vertical groups? c) What general area contains the metallic elements? Nonmetallic elements? d) Give the locations of the following: noble gases, transition metals, alkali metals, lanthanide series, alkaline earth metals, halogens, nonmetals, actinide series, metals, representative elements, metalloids, inner-transition metals, and the staircase line. 9) List the physical properties of metals and nonmetals. 10) Define: ion, cation, anion, monatomic ion, polyatomic ion 11) How is a cation formed? How is an anion formed? 12) Does the nucleus change when an atom is converted to an ion? Explain. 13) How is the periodic table used to predict what ion an element’s atoms will form? 14) Write formulas for the ionic compounds that will form between the following pairs of elements. a) lithium and oxygen ______________ b) magnesium and nitrogen ______________ c) aluminum and bromine ______________ d) calcium and sulfur ______________ 15) Write names for the following ionic compounds. a) KF _______________________________ b) Ba3P2 _______________________________ c) Na2S _______________________________ d) SrI2 _______________________________ 16) List three properties that are representative of ionic compounds. 17) List the seven diatomic elements. BONUS: List the BIG 5 polyatomic ions (names and formulas)