Nick`s-Essential+Biology+03.2+Carbohydrates,+Lipids+
advertisement

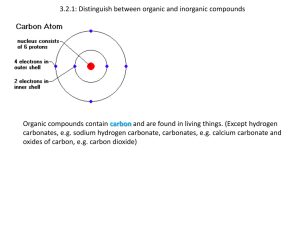
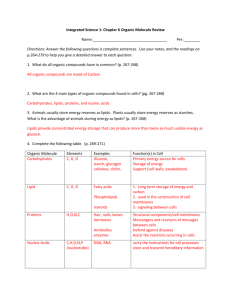
Essential Biology 03.2: Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins 1. Define organic molecule. Organic molecules are molecules that come from living things. Most have carbon with some exceptions. 2. What are three carbon-containing groups or molecules that are not organic? Hydrogen carbonate, carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide. There are many organic molecules in living things. The same (or very similar) molecules are used in many different living things for the same purpose. 3. Saccharides are sugars and carbohydrates. Sugars (monosaccharides and disaccharides) are used to build up carbohydrates (polysaccharides). a. What happens to the structure of monosaccharides when they are placed in water? In water monosaccharides go into a ring structure. b. Draw the simplified (ring) structures of glucose and ribose. Number the carbon atoms correctly. Which sugar is a pentose? Which is a hexose? How are they named this way? Hexose It is named a hexose because it has the shape of a hexagon C6H2OH C5 O H OH Pentose It is named pentose because it has the Shape of a pentagon. O C5H2OH OH H C4 C1 OH H C3 C2 HO H C4 C1 H OH C3 H H H C2 OH H OH c. Draw a generalized hexose and pentose sugar on chemsketch and render it in 3D. Stick the 3D ball-and-stick model below: (http://www.acdlabs.com/download/) Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 03.2: Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins Condensation of monosaccharides is a polymerization reaction. It can continue to create a longer chain of saccharides (a carbohydrate). These building reactions are anabolic metabolism. d. What is a polymer? It is a structure made up of repeated simple monomers. e. Use the diagram below to show how two monosaccharides are converted into a disaccharide through condensation. Complete a word equation. What else is needed to make the reaction occur? Condensation Water is removed Condensation Glucose +glucose f. maltose(disaccharide) + water Condensation of sugars produces a glycosidic bond. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 03.2: Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins Distinguish between 1-6 glycosidic and 1-4 glycosidic bonds in terms of their effect on the shape of the polysaccharide produced. You might want to draw them to help see. g. Complete the table below: -saccharides examples Glucose Mono- Di- Plant or animal? Function/ uses animal Quickly absorbed and used in respiration Galactose Fructose plant Sucrose plant Lactose animal Maltose Glycogen Poly- animal Starch plant Cellulose Soluble but unreactive, can be transported around plant in Phloem. Quickly digested into monosaccharides. Dimer of glucose, broken down from starch. Insoluble storage of glucose in the liver produced using insulin. Insoluble plant energy storage molecule. Structural unit in plant cell walls Anabolic reactions are those which build organic molecules (such as condensation of saccharides). Catabolic reactions break them down (e.g. digestion). Hydrolysis is the catabolic reaction which breaks down organic molecules. h. What is the function of hydrolase? Hydrolase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of a chemical bond. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 03.2: Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins i. Outline this reaction using an example of a dimer of two pentose sugars. Explain the relevance of the name of the reaction. Remember: Condensation makes bonds: Hydrolysis breaks bonds. 4. Fatty acids and glycerol are used in the production of triglycerides. a. In the space below, draw the generalized structures of fatty acids and glycerol. Glycerol H H H H C C C O OH OH OH H C Cn HO H C H H H H O C (CH2)n (CH3) HO b. Distinguish between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids. (Nutrition revision). Bonding Shape of chain (draw) State at room temp Saturated Ester bond The animal fats are solid at room temperature. Unsaturated Ester bond The plant oils are liquid at room temperature. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 03.2: Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins c. Draw a generalized fatty acid or glycerol molecule on chemsketch and render it in 3D. Stick the 3D ball-and-stick model below: (http://www.acdlabs.com/download/) d. What is the relevance of the following properties of lipids? Energy storage* More efficient than carbohydrates, oils in plants and fish, fats in animals. Thermal insulation* Subcutaneous fat insulates against heat loss. Protection Fat acts as a shock absorber. Buoyancy It floats because it is less dense than water. Membranes Phospholipid bilayer, cholesterol Hormones *Essential exam examples e. Write a word equation for the formation of one triglyceride from fatty acids and glycerol. HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OH + RCO2H + R'CO2H + R''CO2H → RCO2CH2CH(O2CR')CR'' + H2O(water) f. Outline how condensation reactions produce one triglyceride molecule (including the name of the bonds produced): A glycerol molecule bonds with carboxylic acid. Water is then pulled out to cause them to bond to make triglyceride. g. Explain why condensation of fatty acids and glycerol to produce a triglyceride is not an example of polymerization. Polymerization has a dimer which involves two monomers which are identical. However, fatty acids and glycerol are not identical, and is therefore not a polymerization. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 03.2: Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins h. Compare lipids and carbohydrates in terms of energy storage: carbohydrates lipids Stored as…? Glucose/fructose Oils in plants and fish or as fat in animals. Long/short term storage? Short term Long term Ease of digestion/ release of energy? Quick and easy. It also requires less oxygen to release the energy. Requires more oxygen to release the stored energy. Energy per gram? 17KJ g-1 38 KJ g-1 Solubility in water? (and consequence) Some vitamins are dissolved. Use of oxygen in metabolism? (and consequence) Less oxygen use for metabolic processes More oxygen use for metabolic processes 5. Proteins are the tertiary (or quaternary) structure of polypeptides, polymers of amino acids. a. In the space below, draw the structure of a general amino acid. Include (and label) the amine group, carboxyl group and ‘R’ group. H N H b. How many different amino acids are there? What is different about each one? There are only 20 different amino acids found in proteins. c. What is a polypeptide? Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 03.2: Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins A peptide contains 10 to more than a 100 amino acids. d. How does the diversity of amino acids lead to infinite possibilities of polypeptides? Because the amino acids can be arranged in any order. i. Could be any length Polypeptide length: ii. Amino acid sequence: Can be in any order or combination. e. Use a diagram to show condensation and hydrolysis of peptides. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 03.2: Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com