Different plants Botanist divide plants into groups base on three
advertisement

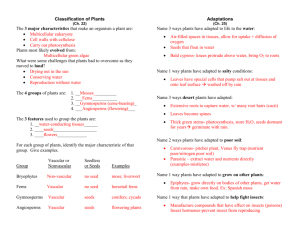
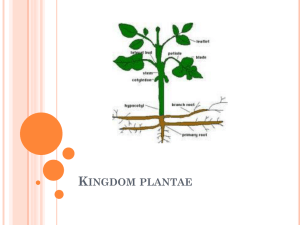
1. Different plants a. Botanist divide plants into groups base on three characteristics: i. If the plant contains vascular tissue (xylem and phloem) ii. If the plant produces spores iii. If the plant produces seeds in fruits (flowers) or seeds in cones b. There are 4 main families of plants i. Mosses – plants that have no vascular tissue and produce spores ii. Ferns- plants that have vascular tissue and produce spores iii. Cone Plants- plants that have vascular tissue, and produce seeds in cones iv. Flowering Plants- plants that have vascular tissue, and produces seeds in fruits (flowers) 2. Evolution of plants a. Plants evolved from green algae and where some of the first organisms to live completely outside the ocean about 400 million years ago. b. Plants had to develop a number of structures to help them survive out of water: i. Dermal and vascular tissues to prevent them from dehydrating out of water ii. Structural components to help hold them upright in the air iii. Ways to allow sperm to reach the egg cells without water c. The first true plants to develop from algae where mosses 3. Evolution of plants: Bryophytes a. Bryophytes –mosses, all bryophytes have no vascular tissue and produce spores i. Bryophytes (mosses) don’t have roots, stems and leaves like most other plants ii. Bryophytes are short because they all lack vascular tissue iii. Bryophytes need water for reproduction so the sperm can swim to the egg. 4. Evolution of plants: Ferns a. Ferns - plants that have vascular tissue and produce spores i. Bryophytes evolved into ferns by developing vascular tissue. 1. Vascular tissues allowed ferns to grow much taller than their moss predecessors ii. Ferns where the first plants to develop true roots stems and leaves iii. Like bryophytes ferns still need water to reproduce 5. Evolution of plants: Gymnosperms a. Gymnosperms – cone plants, all gymnosperms have vascular tissue, and produce seeds in cones i. Gymnosperms evolved from ferns by developing the first seeds. 1. Seeds are more evolved than spores because it has a protective coat and a supply of food that can keep the embryo inside alive for a long time ii. Gymnosperm literally means “Naked Seed” because the seeds are exposed in cones iii. The most recognizable group of gymnosperms are conifers iv. Gymnosperms produce pollen which gives the plant the ability to reproduce without water v. Conifers – the group of gymnosperms that include pine trees 1. conifers produce stems made out of “soft wood” 2. The resin that makes conifers smell “piney” is a adaptation that is antibacterial, antifungal, and helps stop insect attacks 6. Evolution of plants: Angiosperms a. Angiosperms – flowering plants, all angiosperms have vascular tissue and produce seeds in flowers i. Angiosperms evolved from gymnosperms by developing fruits that help spread their seeds ii. All the fruit that is consumed was produces by some type of angiosperm iii. Angiosperms produce pollen which gives the plant the ability to reproduce without water iv. Angiosperms have become the most diverse phyla of plants, and so botanists have developed ways of classifying them 1. Monocots vs. Dicots (based on the seed that the flowering plant produces) a. Monocots produce seeds with 1 cotyledons i. Monocot leaves have parallel vanes ii. Monocot flowers have parts in multiples of 3 iii. The xylem and phloem in monocot stems is scattered throughout the stem iv. monocot roots are fibrous b. Dicots produce seeds with 2 cotyledons i. Dicots leaves have branched vanes ii. Dicots flowers have parts in multiples of 4 or 5 iii. The xylem and phloem in Dicot stems is arranged in a ring iv. Dicots have a tap root (like a carrot)