Plant Book 14-15 -
advertisement
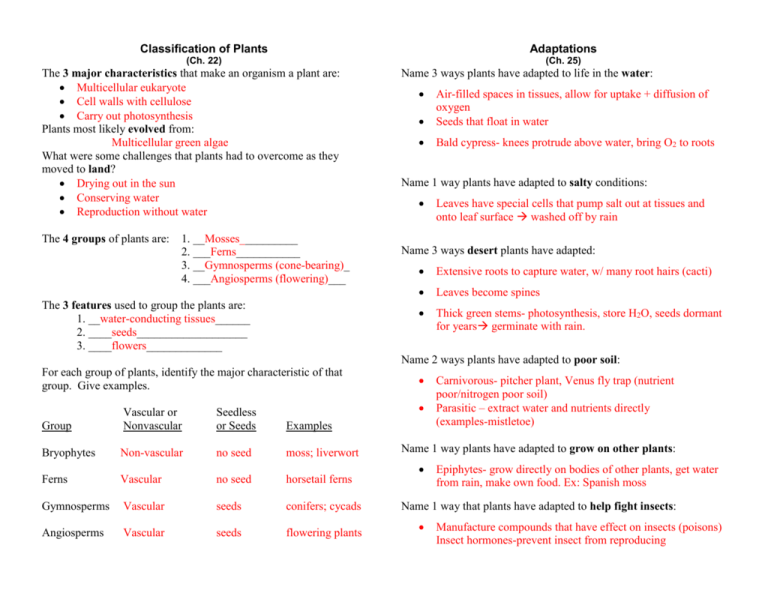
Classification of Plants Adaptations (Ch. 22) (Ch. 25) The 3 major characteristics that make an organism a plant are: Multicellular eukaryote Cell walls with cellulose Carry out photosynthesis Plants most likely evolved from: Multicellular green algae What were some challenges that plants had to overcome as they moved to land? Drying out in the sun Conserving water Reproduction without water The 4 groups of plants are: 1. __Mosses__________ 2. ___Ferns___________ 3. __Gymnosperms (cone-bearing)_ 4. ___Angiosperms (flowering)___ The 3 features used to group the plants are: 1. __water-conducting tissues______ 2. ____seeds___________________ 3. ____flowers_____________ Name 3 ways plants have adapted to life in the water: Air-filled spaces in tissues, allow for uptake + diffusion of oxygen Seeds that float in water Bald cypress- knees protrude above water, bring O2 to roots Name 1 way plants have adapted to salty conditions: Leaves have special cells that pump salt out at tissues and onto leaf surface washed off by rain Name 3 ways desert plants have adapted: Extensive roots to capture water, w/ many root hairs (cacti) Leaves become spines Thick green stems- photosynthesis, store H2O, seeds dormant for years germinate with rain. Name 2 ways plants have adapted to poor soil: For each group of plants, identify the major characteristic of that group. Give examples. Group Vascular or Nonvascular Seedless or Seeds Examples Bryophytes Non-vascular no seed moss; liverwort Ferns Vascular no seed horsetail ferns Gymnosperms Vascular seeds conifers; cycads Angiosperms Vascular seeds flowering plants Carnivorous- pitcher plant, Venus fly trap (nutrient poor/nitrogen poor soil) Parasitic – extract water and nutrients directly (examples-mistletoe) Name 1 way plants have adapted to grow on other plants: Epiphytes- grow directly on bodies of other plants, get water from rain, make own food. Ex: Spanish moss Name 1 way that plants have adapted to help fight insects: Manufacture compounds that have effect on insects (poisons) Insect hormones-prevent insect from reproducing Growth Evolutionary Relationships of Plants (Ch. 25) (diagram p. 554) What is the role of hormones? Chemical substances that control: 1- pattern of growth and development. 2- plant’s response to environmental conditions Flowering PlantsAngiosperms For each hormone listed below, give the effect that it has on the plant: auxin (3): growth- branching; phototropism- bend toward light; gravitropism – root growth downward cytokinins (2): stimulate cell division; growth of lateral buds; cause dormant seeds to sprout gibberellins (1): growth hormone-dramatic increase in size especially in stems and fruit ethylene (1): stimulates fruit to ripen ConifersGymnosperms Flowers Ferns Responses For each type of response listed, explain and give an example. Tropism response to external stimuli Seeds Gravitropism: response to gravity. Shoots grow up-against gravity. Roots grow down- with force of gravity Phototropism response to light Thigmotropism response to touch: growing tip grows + twist Around object; stunted growth Mosses Vascular System Photoperiodism: response to amt of day light (seasonal changes) winter dormancy: plant growth + activity decrease or stops. leaf abscission: layer of cells forms at petiole; seals leaf off from plant’s vascular system Multicellular green algae Reproduction (Ch. 24) Parts of Plants (Ch. 23) Define pollen grain: male sex cell What are the 3 main organs and their functions? Roots- absorb water and nutrients Leaves – Photosynthetic Stems-support; connect root + leaves; carry H2O + nutrients In gymnosperms, the male cone is called the _pollen_ cone and the female cone is called the _seed__ cone. Tissues: name the 3 main types and their functions: Dermal Vascular xylem: carries water phloem: carries nutrients + carbs from photosynthesis Ground tissue-cells between dermal and vascular tissue The 4 kinds of specialized leaves: 1. __Sepals_ 2. _Petals___ 3. __Carpel/Pistil (female)_ 4. __Stamens (male)_ Roots: name the 2 main types, draw an example, give advantage of each: Tap Roots Fibrous Root Reach water deep spread outward Within the soil water absorption near surface Stems: name 3 major parts, draw and label node internode bud Leaves: name 2 major parts, draw and label Leaf blade Petiole In angiosperms, the reproductive organs are the __flowers__. Seeds Define a fruit: ripened ovary containing angiosperm seeds. Fruit protects seed, helps in dispersal. Give 10 examples of fruits: apple, pear, beans, grape, peach, pea, strawberry, tomato, corn, cucumber, grape, pear Compare and give examples of fleshy and dry fruit: Fleshy: apple Dry: maple, ash Name 3 methods of seed dispersal and give examples: Animals – insects, birds, bats + other mammals Wind – maple, dandelion Water Germination Explain transpiration and the role of stomata Transpiration: loss of water through plant’s leaves Stomata: pore-like opening on underside of leaf; allow O2 + CO2 to diffuse in and out of leaves Describe a monocot: 1 seed leaf; parallel veins; flower multiples of 3 Fibrous roots Describe a dicot: 2 seed leaves; branched veins; flower multiples of 4 or 5, tap root Define germination: early growth stage of the plant embryo Describe the 3 steps of germination: 1. absorb water 2. food – storing tissues swell, crack open seed coat 3. young root emerges, begins to grow Flower diagram: (p. 612) Stamens Stigma Pistil/Carpal Anther Style Filament Ovary Petal Ovules Sepal NAME: ______KEY______ Stamen ♂ : anther + filament CLASS PERIOD: __________________ Carpal or pistil ♀ : stigma + style DATE: ________________________











