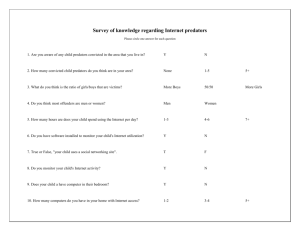
The arthropod predators of insects and mites include beetles, true

Beneficial Insects Informational Powerpoint Project
Background Information:
The arthropod predators of insects and mites include beetles, true bugs, lacewings, flies, midges, spiders, wasps, and predatory mites. Insect predators can be found throughout plants, including the parts below ground, as well as in nearby shrubs and trees. Some predators are specialized in their choice of prey, others are generalists.
Some are extremely useful natural enemies of insect pests. Unfortunately, some prey on other beneficial insects as well as pests. Insect predators can be found in almost all agricultural and natural habitats. Each group may have a different life cycle and habits. Major characteristics of arthropod predators:
● adults and immatures are often generalists rather than specialists
● they generally are larger than their prey
● they kill or consume many prey
● males, females, immatures, and adults may be predatory
● they attack immature and adult prey
Relative Effectiveness
Most beneficial predators will consume many pest insects during their development, but some predators are more effective at controlling pests than others. Some species may play an important role in the suppression of some pests while others may provide good late season control, but appear too late to suppress the early season pest population. Many beneficial species may have only a minor impact by themselves but contribute to overall pest mortality. Surveys of agricultural systems give an indication of the potential number and diversity of predators in a crop. For example, over 600 species of predators in 45 families of insects and 23 families of spiders and mites have been recorded in Arkansas cotton. There may be thousands of predators per acre, in addition to many parasitoids. Although the impact of any one species of natural enemy may be minor, the combined impact of predators, parasitoids, and insect pathogens can be considerable.
Procedure:
You will examine one of the organisms that can be a potential alternative to expensive and toxic pesticide treatment. You will create a powerpoint on your predator. (Be creative)
1
Beneficial Insects Informational Powerpoint Project
Rubric:
Scientific and Common Name
Description of Predator and Life Cycle
Where is it naturally found? (include type of ecosystem/climate)
What pest(s) does it prey upon?
What crops can be affected by this pest?
Is a predator commercially available or not?
Benefits of using this predator over a pesticide
Potential problems with using biological controls
Neat, Proofread, Typed, Creative
1 2
1 2 3 4 5
1
1 2 3
1 2 3
1 2
1 2
1 2
1 2 3 4 5
TOTAL ________ / 25 points
You can organize your powerpoint in any way, but be sure to be creative and eye catching!
2
Beneficial Insects Informational Powerpoint Project
List of Predatory Beneficial Insects (natural)
Beetles
1-Lady Beetles
2Chilocorus kuwanae
3Chilocorus stigma
4-Coccinella septempunctata
5Coleomegilla maculata
6-Cryptolaemus montrouzieri
7-Harmonia axyridis
8-Hippodamia convergens
9-Pseudoscymnus tsugae
10-Rodolia cardinalis
11-Stethorus punctum
12-Lebia grandis,
13-Aleochara bilineatis
Bugs
14-Campylomma verbasci
15-Deraeocoris nebulosus
16-Geocoris spp.
17-Orius spp.
18-Podisus maculiventris
Lacewings:
19 -Chrysoperla carnea/Chrysoperla rufilabris
20-Hemerobius spp.
Flies:
21-Syrphid fly
Midges:
22-Aphidoletes aphidimyza
Mites:
23 -Apple orchard mite control
24-Neoseiulus (=Amblyseius) fallacis
25-Zetzellia mali
26 -Predatory mites (general)
27-Euseius tularensis
28-Phytoseiulus persimilis
Other Predators:
29-Harvestmen
30 -Phalangium opilio
3