9. Lemmings are small mammals that live near the Arctic circle. Their
advertisement
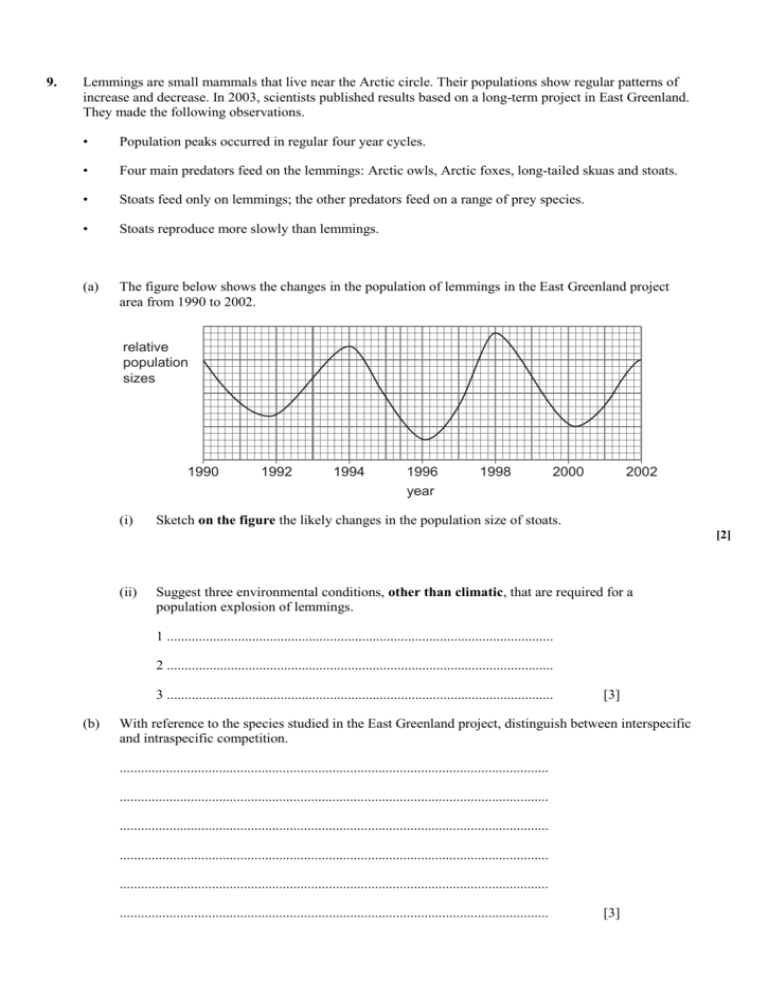
9. Lemmings are small mammals that live near the Arctic circle. Their populations show regular patterns of increase and decrease. In 2003, scientists published results based on a long-term project in East Greenland. They made the following observations. • Population peaks occurred in regular four year cycles. • Four main predators feed on the lemmings: Arctic owls, Arctic foxes, long-tailed skuas and stoats. • Stoats feed only on lemmings; the other predators feed on a range of prey species. • Stoats reproduce more slowly than lemmings. (a) The figure below shows the changes in the population of lemmings in the East Greenland project area from 1990 to 2002. relative population sizes 1990 (i) 1992 1994 1996 year 1998 2000 2002 Sketch on the figure the likely changes in the population size of stoats. [2] (ii) Suggest three environmental conditions, other than climatic, that are required for a population explosion of lemmings. 1 ............................................................................................................. 2 ............................................................................................................. 3 ............................................................................................................. (b) [3] With reference to the species studied in the East Greenland project, distinguish between interspecific and intraspecific competition. ......................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................... [3] (c) The carrying capacities for lemmings and for the various predators in this area are all different. Explain the term carrying capacity. ......................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................... [2] 11. [Total 10 marks] The cyclamen mite is a pest of strawberry crops in California. Populations of these mites are usually kept under control by a species of predatory mite of the genus Typhlodromus . An experiment was carried out to investigate the effectiveness of predation in controlling cyclamen mites. Both predator and prey mites were released on a group of strawberry plants in a greenhouse and the numbers of both types of mite were monitored over a period of 12 months. The results are summarised in Fig. 1. A second investigation was carried out on a crop of strawberry plants growing in a field. The plants were sprayed periodically with parathion, an insecticide that reduces the number of predators, but does not affect the cyclamen mite. The effects of this on the numbers of cyclamen mites is summarised in Fig. 2. key: = cyclamen mite (prey) = Typhlodromus (predator) 5 4 mean number of mites per leaf 3 2 1 0 J F M A M J J A S O N D N D time Fig. 1 5 4 mean number of mites per leaf 3 spray spray 2 spray 1 0 J F M A M J J A S O Fig. 2 (a) The results shown in Fig. 1 illustrate many of the features of a typical predator-prey relationship. Describe and explain these typical features. ......................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................... (b) [4] (i) Sketch a curve on Fig. 2 to show the likely effect of spraying on the population of the predatory mite. [2] (ii) Suggest two reasons for the gradual decrease in the numbers of cyclamen mites over the year, as shown in Fig. 2. 1 ............................................................................................................. ................................................................................................................ 2 ............................................................................................................. ................................................................................................................ (c) [2] Many Californian strawberry growers keep the cyclamen mite under control by ensuring that there are healthy populations of the Typhlodromus mite. (i) State the name given to this type of pest control. ................................................................................................................ (ii) [1] Explain why many would regard the use of predatory mites as preferable to the application of insecticides. ................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................ (d) [5] Suggest two methods of pest control other than the use of predatory mites or insecticides. 1 ...................................................................................................................... 2 ...................................................................................................................... [2] [Total 16 marks] ANSWERS 9. (a) (i) (ii) (b) curve to have peaks to right of lemming peaks and must have two peaks between 1994 and 1996 and 1998 and 2000 respectively ; peaks below level of lemming peaks ; 2 plenty / AW, of food ; few / AW, predators ; high population of alternative prey for predators ; no overcrowding / lots of breeding sites / AW ; less disease ; less competition from other species ; low environmental resistance ; 3 max interspecific between two (or more) species ; two named species (on lemmings) ; intraspecific within species ; named species plus resource ; (c) if definitions of interspecific and intraspecific competition are the wrong way around can still gain one mark for correct examples of both types of competition 3 max maximum, size / number, of a, population / species ; either (supported) in a particular, habitat / ecosystem / area / environment ; or determined by limiting factors ; 2 [10] 11. (a) (b) cyclamen mite / prey populations increase; when conditions are suitable / when predator numbers are low / no or few limiting factors; provides plenty of food for predator mites; which begin to increase later / time lag; cyclamen mites are then eaten by (increasing numbers of) predators; so both decline in numbers; cycle repeated; prey populations reach higher levels than predators; (i) start by looking at end of February increases with appropriate time lag; decreases at spraying times (end of June / beginning of October); final peak for predator numbers is the lowest; (ii) max 4 less food available / less strawberry plants; low temperature / frost; other predators; disease / parasites; max 2 ref to parasitoids; AVP; R spraying idea (c) (d) (i) biological (pest control); (ii) insecticides, are harmful to other organisms / may kill natural predators to the pest; reduces species diversity / disrupts food chains; many insecticides are, slow to biodegrade / long lasting; concentrate along food chains / bioaccumulate / bioconcentrate; stored in fat deposits of organisms; ref to effects on top carnivores; e.g. egg shell thinning poisonous to those applying them; A ref to humans / asthma sufferers pests can build up a resistance; ref to selection; run-off from land carries them into water supplies / causes pollution / poisons aquatic organisms; problems of residues in food; AVP; e.g. pesticides need to be used repeatedly crop rotation; intercropping; release of, irradiated / sterile, males of pest species; AVP; e.g. fly paper max 2 1 max 5 max 2 [16]