Unit #1 Study Guide
advertisement

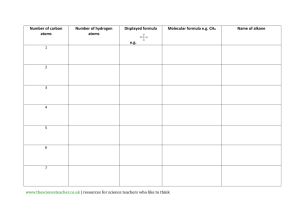
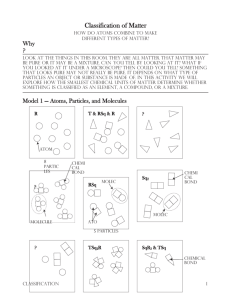
Unit #1 Study Guide: Lab Safety, Introduction to science, and matter. Name: __________________________________ Lab Safety You should wear safety goggles if you are working with a heat source, working with chemicals, or working with anything that might get into your eyes. To see if a piece of glassware is hot you should place the back of your hand near it. Introduction to Science Technology can best be defined as applied science. Pure science is best defined as the continuing search for new knowledge. Scientific theories can be changed or replaced when new discoveries are made. Weight is the force with which gravity pulls on a quantity of matter. The unit used to measure the height in science is the meter. The unit is used to measure mass in science is the kilogram. The SI units for measuring temperature are Celsius or kelvin. A line graph is used to show a change in data over time. A bar graph is used to show a comparison of several items or events. A pie chart is used to show data that are parts of a whole. The main branches of natural science are life, physical and Earth science. A scientific law is a description of a natural event. Scientists test a hypothesis by doing experiments. The two main branches of science are natural and social science. A scientific theory is an explanation that has been tested by many observations. A scientific model is a representation of a real event or object. Matter A molecule of water (H2O) is made from chemically combining two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. A pure substance is a material that can be represented by a chemical formula. (Compounds & elements) The chemical formula for water, H2O, means that each water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. The production or release of gas, and the change of color are all potential signs of chemical change. Evaporation is a physical change not a chemical change. An Atom is the smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element. Solids, liquids, and gases are three forms of matter, they all have mass, take up space and are made of atoms. There are 5 atoms in a single molecule of Fe2O3? (2 +3 = 5 Atoms) The chemical symbol for sulfuric acid is H2SO4. It has 7 atoms. (2+1+4=7 atoms) Elements, compounds, and molecules are all pure substances, mixtures are not. A molecule is group of atoms that acts as a unit. Chemical properties include: reactivity, flammability, nonflammability Physical properties include: melting point, density, color, freezing point, boiling point, solubility. An object’s volume can be found by dividing its mass by its volume. d= m/v Size, shape and position can all be affected by a physical changes. The different substances in a mixture keep their properties. Signs of chemical change include change in color, fizzing, burning and changes in color. Boiling, evaporation, freezing, melting, moving, shattering, dissolving, bending and condensing are all physical changes. A chemical change can only be reversed by a chemical change. Not a physical change. A chemical change occurs whenever a new substance is formed. Matter is defined as anything that has mass and takes up space. The smallest unit of a substance that behaves like the substance is a molecule. A compound is made of at least two different types of atoms? A pure substance has a fixed composition, a mixture does not. Examples of a chemical changes include: paint fading, and food being digested. An element is a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances. The chemical formula for table sugar is C12H22O11. It contains 12 Carbon atoms (C), 22 Hydrogen atoms, and 11 Oxygen atoms (O). (12+22+11= 42 atoms) Knowing the chemical properties of a substance will tell you how the substance reacts with other substances.