Battery Charging Safe Operating Procedures
advertisement

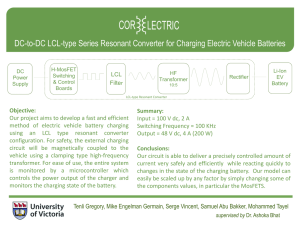
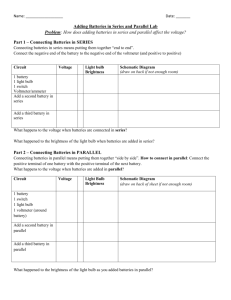
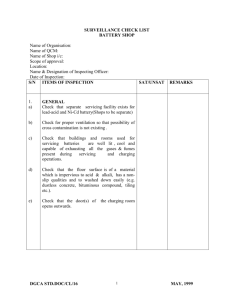
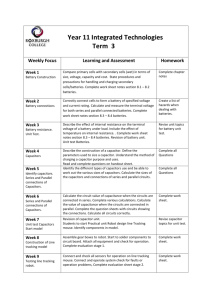
Safe Operating Procedures for Battery Charging Purpose To define the safe operating procedures in a manner that informs and instructs employees of [Employer/Organization Name] of the key health and safety hazards and controls to remember when charging batteries. Hazards The following hazards may occur when charging batteries: Burns Chemical exposure Sulphuric acid is contained in the battery. Exposure can occur while filling a battery with acid (electrolyte), or while charging or boosting it, causing a chemical burn and/or inhalation hazard. Electric shock Short circuits may occur from metal on clothing or in jewelry coming into contact with the electrodes. Fire or explosion Hydrogen and oxygen are produced when you charge or boost a battery, and can be ignited by a flame or spark. Note: Install plumbed eye wash stations, neutralizer containers and wash basins near where you handle the batteries so you can administer first aid treatment for acid and alkali burns if necessary. Personal Protective Equipment Eye protection (e.g. splash-proof safety goggles or face shield) Rubber gloves No metal or jewelry Safe Operating Procedure Complete a pre-use inspection. If any defects are noted, the equipment must be removed from service and the supervisor must be notified immediately to ensure equipment is repaired. Operators must have read and understood the operator’s manual. Ensure operator’s manual for equipment is available to operators. Ensure guards and shields are firmly in place and in good condition. Do not operate the equipment without appropriate guards, shields, plates and other safety protective devices in place. Ensure safety decals are legible, order replacements if they are not. Ensure the equipment is used properly as per manufacturer’s directions. Prohibit smoking in the work area. Charge batteries in a properly ventilated area and performed in a place specifically designated for charging batteries. Ensure the room for charging batteries is equipped with a non-sparking floor kept clean and washed with fresh water promptly when electrolyte is spilled. Make sure the power is shut off at the charger before removing the alligator clips. Break live circuits by connecting the negative cable to the frame or motor block instead of breaking them at the battery terminals. Shut off the charger before making any connections, such as hooking up cables to the battery. Check that battery ventilation holes are clear and clean to allow the hydrogen gas to escape and prevent the battery from exploding. If the battery is not maintenance-free, remove the filler caps to vent hydrogen gas. Ground the negative cable to the frame or motor block to prevent short circuits. Rinse batteries and clean terminals before charging. Clean battery areas safely, first with a solution of sodium carbonate or sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) to neutralize any spilled acid, and then with large volumes of water to rinse the area clean. Clean your hands with soap and water immediately after servicing batteries. Do not attempt to charge or jump a frozen battery. Repairs to the equipment must be performed by qualified personnel, using original equipment manufacturer (OEM) parts or equivalent. First Aid If acid splashes on your body, immediately remove all contaminated clothing and flush the burned areas thoroughly with water. If acid gets into your eyes, flood them with water for at least 20 minutes, paying particular attention to the areas under the eyelids. Get to a doctor as soon as possible. Contact emergency services at 911 if necessary. Document Management Effective Date: Revision Date: