Alternating Current Direct Current Voltage
advertisement
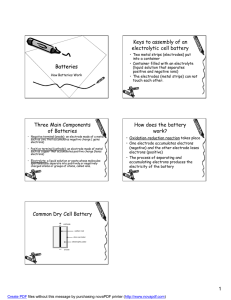
Alternating Current Direct Current Components of Electrical System Voltage source = generator/batteries Conductor = wires Control Element = switch Load = light bulb, motors, appliances Alternating Current Electrons flow back and forth 60 times per second Electrons travel in bidirectional path in circuit EXAMPLES Power generated from power plant Travels over long distance to your home or business VOLTAGE amounts 120v 208v 240v 480v Advantages? Disadvantages? Direct Current Maintains a constant value Electrons travel in a Unidirectional path, point to point EXAMPLES Batteries are the most common source of DC Primary Cells are intended for 1 use Secondary Cells can be recharges for multiple use Battery Construction In its simplest form a battery consists of two different metal (copper&zinc) plates called electrodes which are dipped into an acid solution called electrolytes The cell then produces current through the path of the two metals Battery types Primary cells Nonrechargeable Alkaline Carbon-Zinc Lithium Mercury Silver-Oxide Secondary cells Rechargeable Lead-Acid Nickel-Iron Nickel-Cadmium Lead-Calcium Silver-Zinc ELECTRICAL SYMBOLS Wire Load Switch Battery Lamp AC power