BIOL/PBIO 3333 Genetics Quiz 2 9/27/13 For the answers to the quiz
advertisement

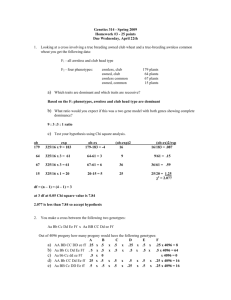
BIOL/PBIO 3333 Genetics Quiz 2 9/27/13 For the answers to the quiz, click here 1. Which of the following dihybrid x dihybrid ratios show independent assortment? a) 9:3:3:1; b) 9:7; c) 9:3:4; d) all of the above; e) none of the above. 2. Tribbles are animals that have a sex determination mechanism similar to humans. The trait marine (m), with short, stiff hair, is recessive to long furry hair (m+), and purple color (p) is recessive to black color (p+). A purple, furry female is crossed to a black, marine male. All of the progeny are furry black. If the marine trait was sex linked and the purple trait was autosomal, which of the following phenotype frequencies would be expected in the F2 generation? a) 3/8 black furry females; b) 3/16 black marine males; c) 1/8 purple, furry females; d) 1/16 purple marine males; e) all of the above. Questions 3-4 refer to the following. In a group of tribbles, you discover three different eye color phenotypes: red (R), brown (B) and green (G). To understand the inheritance pattern, you conduct a number of different crosses between animals of these phenotypes. The results are depicted on the right (the phenotypes segregate independent of sex): 3. True or false. These results indicate that there are two independently assorting gene loci involved in these phenotypes. cross number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 parental phenotypes phenotypes of progeny RxG all R BxG all B RxG 1R:1B BxG 1B: 1G GxG all G RxR 3R: 1B BxB all B RxG 1:R:2G:1B RxR 9R:3B:4G RxB 3R:3B:2G 4. If the red parent from cross #3 and the brown parent from #10 are crossed, what progeny ratios would be produced? a) 1 R: 1 B; b) all R: c) all B; d) 3 R: 1 B; e) none of the above. Questions 5-6 pertain to the following: In hobbits, the recessive genes for non-hairy feet (f), allergy to pipe-weed (p) and poor appetite (a) are all recessive to the wild type alleles. Females heterozygous for all three genes were mated to males homozygous recessive for all traits. The phenotypes of the recovered progeny are given in the table on the right: 5. The distance, in map units, between the f and a loci is: a) 2 ; b) 5; c) 16; d) 21; e) these genes are not linked. 6. The coefficient of coincidence for this experiment is: Phenotype f+a +pa ++a fp+ fpa +p+ f++ +++ Number of Progeny 391 81 25 20 2 404 74 3 a) 0.005; b) 0.25; c) 0.625; d) 0.75; e) none of the above. 7. A testcross between an individual who is trihybrid for three different gene loci (A/a, B/b, C/c) and an individual homozygous recessive for all three loci yields the following progeny: Which of the following are true? a) the three gene loci are linked and A/a is the middle gene; b) the A and C genes are located on the same chromosome and separated by 50 map units; c) the B locus is located 15 map units from the C locus; d) all of the above; e) none of the above. Questions 8-9 pertain to the data on the right, showing the ordered tetrad pairs arising from the cross between two strains, cd and ++. Phenotype ABC abc ABc AbC aBC Abc aBc abC Number of Progeny 34 40 204 215 41 35 221 210 Tetrad Class spore pairs 1 cd cd ++ ++ 41 2 c+ ++ cd +d 5 3 cd ++ cd ++ 3 4 c+ cd ++ +d 17 5 +d c+ c+ +d 1 6 c+ +d cd ++ 1 8. The distance between the c gene and the centromere is: a) 5 m.u.; b) 7.3 m.u. ; c) 10 m.u.; d) 14.5 m.u.; e) none of the above. 9. The c gene and the d gene: a) are on the same side of the centromere, with c closest; b) are on the same side of the centromere, with d closest; c) are on opposite sides of the centromere, with d closest; d) are on opposite sides of the centromere, with c closest; e) are on different chromosome homologs- they are not linked. 10. Mutations in the fibrillin-1 gene: a) are dominant; b) are pleiotropic; c) can show variable expressivity; d) are located on chromosome 15; e) all of the above. 7 c+ c+ +d +d 1