Problem set 3
advertisement
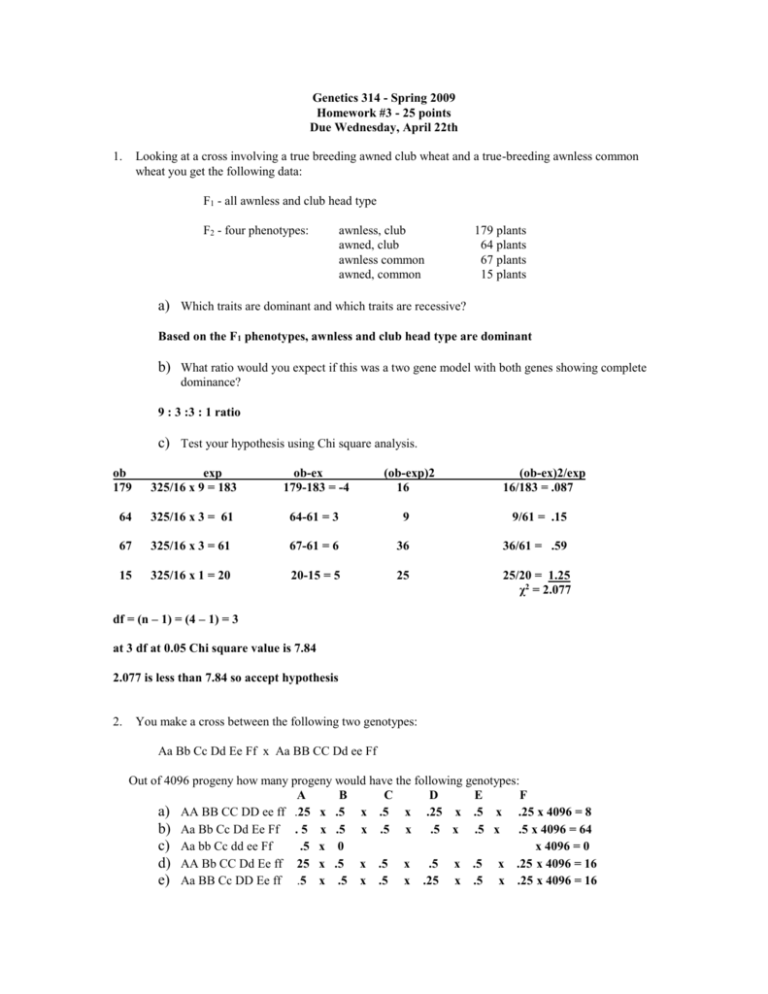
Genetics 314 - Spring 2009 Homework #3 - 25 points Due Wednesday, April 22th 1. Looking at a cross involving a true breeding awned club wheat and a true-breeding awnless common wheat you get the following data: F1 - all awnless and club head type F2 - four phenotypes: awnless, club awned, club awnless common awned, common 179 plants 64 plants 67 plants 15 plants a) Which traits are dominant and which traits are recessive? Based on the F1 phenotypes, awnless and club head type are dominant b) What ratio would you expect if this was a two gene model with both genes showing complete dominance? 9 : 3 :3 : 1 ratio c) Test your hypothesis using Chi square analysis. ob 179 exp 325/16 x 9 = 183 ob-ex 179-183 = -4 (ob-exp)2 16 (ob-ex)2/exp 16/183 = .087 64 325/16 x 3 = 61 64-61 = 3 9 9/61 = .15 67 325/16 x 3 = 61 67-61 = 6 36 36/61 = .59 15 325/16 x 1 = 20 20-15 = 5 25 25/20 = 1.25 χ2 = 2.077 df = (n – 1) = (4 – 1) = 3 at 3 df at 0.05 Chi square value is 7.84 2.077 is less than 7.84 so accept hypothesis 2. You make a cross between the following two genotypes: Aa Bb Cc Dd Ee Ff x Aa BB CC Dd ee Ff Out of 4096 progeny how many progeny would have the following genotypes: A B C D E F a) AA BB CC DD ee ff .25 x .5 x .5 x .25 x .5 x .25 x 4096 = 8 b) Aa Bb Cc Dd Ee Ff . 5 x .5 x .5 x .5 x .5 x .5 x 4096 = 64 c) Aa bb Cc dd ee Ff .5 x 0 x 4096 = 0 d) AA Bb CC Dd Ee ff 25 x .5 x .5 x .5 x .5 x .25 x 4096 = 16 e) Aa BB Cc DD Ee ff .5 x .5 x .5 x .25 x .5 x .25 x 4096 = 16 3. You are asked by a friend to calculate the probabilities of having the following combination of children: a) b) c) d) a) b) c) d) 4. 7 boys - 2 girl 5 boys - 4 girls 3 boys - 6 girls 0 boys - 9 girls 9!/7!2!x.57x.52 = 0.07 9!/5!4!x.55x.54=0.25 9!/3!6!x.53x.56=0.164 9!/0!9!x.50x.59=0.00195 What is the probability of having 5 boys - 4 girls in a specific order (example: boy, girl, girl, boy, girl, girl, boy)? Does it differ from your answer to 3b? Why or why not? The probability of having 5 boys and 4 girls in a specific order is .5 9 = 0.00195. This does differ from your answer in 3b because there you were looking at all the possible combinations of 5 boys and 4 girls whereas here you are only looking at one possibility. 5. You are studying eye color in Fruit flies. You discover flies with slightly different shades of white eyes where the normal (wild type) has red eyes. You wonder if you are observing allelic differences or if the difference is due to different genes. a) What type of cross would you make to determine the genetic control of the eye color b) c) difference? What results would you expect if the difference was due to different alleles? Why? What results would you expect if the difference was due to different genes? Why? a) You would make a complementation cross. b) You would expect the progeny to have white eyes white white a1a1BB X a2a2BB 1 2 a a BB white c) You would expect the progeny to have red eyes white white aaBB X AAbb AaBb red 6. You are studying skin color in snakes. You mate a true breeding brown snake with a yellow snake and all the F1 progeny are black. You mate the F1 snakes and recover the following progeny: phenotype black brown yellow total no. of progeny 41 12 19 72 a) What type of gene action are you observing? b) Test your hypothesis using Chi square analysis. a) you are observing single recessive epistasis (9 : 3 :4) b) ob 41 12 19 exp (72/16)*9=40.5 (72/16)*3=13.5 (72/16)*4=18 (ob-exp)2 (41-40.5)2=0.25 (12-13.5)2=2.25 (18-19)2=1 (ob-exp)2/exp 0.25/40.5=0.006 2.25/13.5=0.167 1/18=0.056 χ2 0.229 df=(n-1)=(3-1)=2 with 2 df at 0.05 level χ2 is 5.99 0.229 is less than 5.99 so accept the hypothesis that this is a 9:3:4 ratio of single recessive epistasis 7. You are studying mouse coat color. You mate a true breeding brown mouse with an albino mouse and all the F1 progeny are black. You mate the F1 mice and recover the following progeny: phenotype no. of progeny black brown albino total 160 60 80 300 a) What type of gene action are you observing? b) Test your hypothesis using Chi square analysis. a) You are observing single recessive epistasis (9 : 3 : 4) b) ob 160 60 80 exp (300/16)*9=169 (300/16)*3=56 (300/16)*4=75 (ob-exp)2 (160-169)2=81 (60-56)2=16 (80-75)2=25 (ob-exp)2/exp 81/169=0.479 16/56=0.286 25/75=0.333 χ2 1.095 df=(n-1)=(3-1)=2 with 2 df at 0.05 level χ2 is 5.99 1.095 is less than 5.99 so accept the hypothesis that this is a 9:3:4 ratio of single recessive epistasis 8. Three traits (colored, full, starchy) have been found to be all on chromosome 9 in corn. A cross was made between two true breeding parents that differed for the three traits and then the F 1 was crossed to a completely homozygous recessive (colorless, shrunken waxy) individual. You get the following results: colored, full, starchy colorless, shrunken, waxy colored, shrunken, waxy colorless, full, starchy colorless, full, waxy colored, shrunken, starchy colored, full, waxy colorless, shrunken, starchy total 17,625 17,375 510 490 3,050 3,250 32 28 42,360 a) What were the phenotypes of the two true breeding parents? What do you base your conclusion on? b) What is the gene order? c) What are the map distances? d) What is the interference value? a) Parents are the same as the phenotypes with the largest numbers: they are colored, full, starchy and colorless, shrunken, waxy. b) Gene order is: colored----starchy----full c) C---2.5 mu---S---------15 mu-----------F C-S S-F (490+510+32+28)/42360=0.025*100=2.50 (3050+3250+32+28)/42360=0.15*100=15 d) 0.025*0.15*42360=159 expected double cross-over events 32+28=60 observed double cross-over events 1-(observed dco/expected dco)= interference value 1-(60/159)=0.623