Medieval Period: Historical Background In 1066, the Normans
advertisement

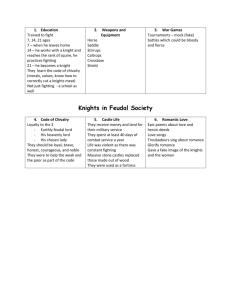
Medieval Period: Historical Background In 1066, the Normans conquered England by defeating the Anglo-Saxons in the Battle of Hastings. Although many Anglo-Saxon traditions and attitudes survived the invasion, the Normans dramatically changed English life by introducing the social, economic and political system called Feudalism. The era is defined by the following characteristics: -Lands were divided among noble overlords. -The lords were served by knights for military protection. -Serfs farmed the land and herded animals. -The knights lived by the code of chivalry which required them to be honorable, courteous, brave and skillful. Literature: Contributions of the knights The concept of chivalry played an important role in shaping the literature of the Medieval period. When chivalry is blended with the elements such as giants, wizards, sorcerers and dragonsROMANCE is created. Filled with fantasy, adventure, and courtly love, romance was one of the most popular literary forms of the period. Romance: a story that presents remote or imaginative incident rather than ordinary realistic experience. The term “Romance” was originally used to refer to medieval tales of the deeds of noble knights and ladies. Characteristics of Medieval Romances: -Embody the ideals of chivalry -Are set in a remote time and place -Emphasize the rank and social distinction -Convey a sense of supernatural -Presents a hero engaged in pure adventure -Include love as a major plot element -Feature spontaneous unmotivated fighting Arthurian Romances and the Knights of Early English Literature The knights were objects of great respect and veneration. They were accorded the highest rank of society and were always a member of the court. They were noted not only as warriors but also as lovers. Knighthood elevated the position of women into one of great importance. It also marked the revival of Middle Ages and devotion to Virgin Mary. Arthurian romances led to the perfection of knighthood as the mystic element presented in the story of King Arthur and the Knights of the Round Table. Knight’s Oath of Homage to Womanhood -Must be faithful -Must act according to the Code of Chivalry -Must win lady love by faithfulness, patience, manliness, and warlike skills. Contributions of Priests: Most of the literature of the period reflected the influence of religion. Mystery Play: A name given to any of the Biblical plays performed (usually in groups or cycles). The name is derived from the Latin Ministerium (mystery). These plays were performed on “pageants” (stages built on large wagons). Unlike the Miraculum or miracle plays which are based on saint’s life or apocryphal miracles of the virgin, mystery plays are based on Bible stories. The Morality Play: Is a type of medieval drama in which the characters are personified abstractions; Everyman, Good Deeds, Faith, Mercy, Anger etc. The two main themes of the religious morality plays are: A. The struggles between good and evil for man’s soul B. The journey on the pilgrimage of life. Morality plays were used to inculcate ethical or educational ideals and to provide thinly disguised political commentary or satire. The Debate: A wordy dispute in which the participants defended two opposite subjects The Drama: This started as a pantomime inside the church, was transferred to the churchyard, thence to market place no longer as pantomime but acted with words. In the transfer to the market place and later to street corners, it was divided or diversified into miracle plays and mystery plays. The Bestiaries: - Collections of pseudo-classical lore in which ‘unnatural natural history’. Examples: Imagined or invented animals or beasts, were held up for reprobation, ridicule or scorn. The Exemplum: -A story for the purpose of teaching a moral lesson taken from incidents in the life of the Virgin or of a saint. The Miraculum: A story based on the life a saint. Contributions of the Common People: Popular Ballad refers to body of poetry which originated among the common people rather than among the courts of kings or the castles of the aristocratic and the educated. The ballads are a part of the spontaneous oral tradition of the English people. The authors are unknown, but certain characteristics are common to all ballads; a. Simplicity of language and situation b. Predominance of dialogue, c. Refrains or repetition of words, phrases or stanzas, d. Supernatural touches. Literature: According to Henry Van Dyke: -Consists of those writings which interpret the meanings of nature and life, in words of charm and power, touched with the personality of the author, in artistic forms of permanent interest. According to Webster: Is the total of preserved writings belonging to a given language or people. Literature Is the class or the total of writings, of a given country or period, which is notable for literary form or expression, as distinguished, on the one hand, from works merely technical or erudite and on the other, from journalistic or other ephemeral writings. According to Henry Van Dyke: Literature -Consists of those writings Definitions. Aims of Literature: Literature: -Entertains and gives pleasure. -It fires the imagination and arouses noble emotions. - It enriches man by enabling him to reflect on life and by filling him with new ideas. Why do people write? - Self-expression. -To preserve truth, ideas and values to form attitudes. -To spread knowledge and information. -To react to the works of other people. -To evaluate, analyze, form valid judgments and make wise decisions. Genres of Literature: Prose – is generally concerned with the presentation of an idea, concept or point of view in a more ordinary and leisurely manner. The appeal of prose is primarily to the intellect and it does not make use of rhyme however, it does possess rhythm but it is not marked and regular as in poetry. Purpose: -To furnish information, instruction or enlightenment Divisions of Prose: Fiction: -Series of imagined facts which illustrates truths about human life. Fiction extends our view and awareness of the different phases of life, of the various types and manifestations of human character and personality, of the complex motives and impulses behind human behavior. Types of Fiction: 1. Short story 2. Novel The Short Story A short story is a brief, artistic form of prose fiction which is centered on a single main incident and is intended to produce a single dominant impression such as sadness, surprise, sympathy, terror etc. -It is characterized with economy, compression and emphasis. -It has a definite time and place. The development of the story happens within a day or even hours usually in one place. -It emphasizes the plot, character, action, setting and theme. The Novel Extensive Form of prose. The novel has expanded scope – the past, present and future. -The novel permits a greater number and variety of characters, a more complicated plot, a more elaborate use of setting, a greater complexity of theme. -It offers an opportunity for character development. Non-fiction 1. The essay 2. Oration 3. Biography 4. Autobiography 5. Memoirs 6. Letters 7. Diaries 8. Journals Poetry: -A rhythmic imaginative language expressing the invention, thought, imagination, taste, passion, and insight of the human soul. Its purpose is to enthrall. KINDS OF POETRY 1. Lyric poetry a. Simple lyric b. Song c. Sonnet d. Elegy e. Ode 2. Narrative poetry a. Ballad b. Metrical tale c. Metrical romance d. Epic 3. Dramatic Poetry a. Dramatic monologue b. Soliloquy c. Character sketch