Simulated Blood Typing Lab
advertisement

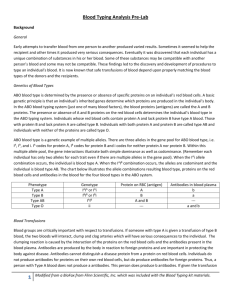
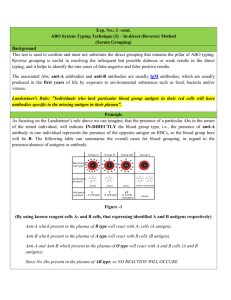
Simulated ABO Blood-Typing Activities Introduction Blood typing involves identifying substances called antigens present on red blood cells (RBC). A person normally produces antibodies against those antigens not present on their RBCs but does not produce antibodies against those that are present. Thus, a person with antigen A has anti-B antibodies, etc. In the United States, 45% of the population is type O, 39% is type A, 12% is type B, and 4% is type AB. Blood type is determined by multiple alleles IA, IB and i. IA and IB are co-dominant and both are dominant over i. Genotypes IA IA and IAi result in blood type A. Genotypes IB IB and IBi result in blood type B. Genotype IAIB results in blood type AB. Genotype ii results in blood type O. Table 1 ABO System Blood Type Antigens present in Blood Antibodies present in Blood Can Receive Blood from: Can Give Blood to Groups: A A B O, A A, AB B B A O, B B, AB AB A and B None O, A, B, AB AB O None A and B O O, A, B, AB Blood typing is performed with a serum that contains specific antibodies. For ABO blood typing, antibodies against A and B antigen (these antibodies are also called anti-A and anti-B antibodies) are used. If clumping or clotting occurs in the test blood upon exposure to the A antibodies (anti-A serum), the blood contains the A antigen. If clumping or clotting occurs in the test blood upon exposure to the B antibodies (anti-B serum), the blood contains the B antigen. If clumping or clotting occurs with both A and B antibodies (anti-A and anti-B sera), the type is AB, and if no clumping occurs with either serum type, the type is O. Table 2 Reactions on ABO blood typing slides Reaction Blood Type Left A antibodies (anti-A serum) Right B antibodies (anti-B serum) clumping no clumping Type A no clumping clumping Type B clumping clumping Type AB no clumping no clumping Type O Objective In this investigation, your group will determine the blood type of four unknown bottles (labeled 1-4) and four individuals (Smith, Jones, Green and Brown). Materials Wax pencil Simulated blood types 1-4 Anti-A serum Glass slide Simulated blood types (people) Anti-B serum CAUTION! These chemicals may stain your clothes and other personal items. Be very careful when using and transporting them. Part 1: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Determine the blood type contained in the unknown vials labeled 1-4. Place 2 drops of blood from the numbered vial on each end of the blood typing slides. Place 2 drops of anti-A serum on top of the blood on the left side of the slide. Place 2 drops of anti-B serum on top of the blood on the right side of the slide. If a color change occurs then that antigen is present. Record your results on your data table and collect results from other members of your lab group. Part 2: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Determine the blood types of Brown, Jones, Green and Smith. Place 2 drops of blood from one person on each end of the blood typing slides. Place 2 drops of anti-A serum on top of the blood on the left side of the slide. Place 2 drops of anti-B serum on top of the blood on the right side of the slide. If a color change occurs then that antigen is present. Record your results on your data table and collect results from other members of your lab group. Simulated ABO Blood Typing Activity Name: ______________________________ Biology 5.0 Date: _________________ Period: ______ Blood Typing Analysis Part 1 Bottle # Reaction in Left Side (anti-A serum) Reaction in Right Side (anti-B serum) Blood Typing Result 1 2 3 4 1. Which blood type(s) showed clumping when anti-A serum was added? 2. Which blood type(s) showed clumping when anti-B serum was added? 3. If clumping occurs when both anti-A and anti-B serum are added, what is the blood type? 4. If clumping does not occur with either anti-A or anti-B serum, what is the blood type? 5. Type AB Blood is sometimes called a “universal recipient”. Explain why. 6. Type O blood is sometimes called a “universal donor”. Explain why. 7. Why is a person with type O blood unable to receive blood from any type other than O? Part 2 Name Reaction in Left Side (anti-A serum) Reaction in Right Side (anti-B serum) Blood Typing Result Mr. Smith Ms. Jones Mr. Green Ms. Brown 1. If Ms. Brown were serving as a donor, what blood type(s) could receive her blood safely? 2. Which person among the 4 represented by the simulated blood samples can receive donated blood from Ms. Jones? 3. What blood type does this person have? Explain your answer: For the following questions, assume individuals are heterozygous for type A (IAi) or B (IBi). 4. If Ms. Jones and Mr. Green married and had children, what blood types would be possible in their children? 5. If Mr. Smith and Ms. Brown had children, what blood types would be possible in their children? 6. If Ms. Jones and Mr. Smith had children, what blood types would be possible in their children? 7. If Ms. Brown and Mr. Green had children, what blood types would be possible in their children? 8. In which case(s) above do the blood types of the children differ entirely from those of the parents?