Chapter 6 Lesson 2 Plates and How they move - Gallion-Wiki
advertisement

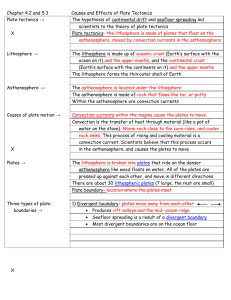
Science Chapter 6 Lesson 2 2-Column Notes What Are Plates and How Do They Move? Pp. 240-244 Name____________________________#_____ Earth’s Plates Fit like jigsaw puzzle Lithosphere Rigid upper mantle, made of plates of rock. Some plates 10,000km +, some smaller. Some mostly oceanic while others are mostly continental Asthenosphere Plates sit on asthenosphere. Flows like taffy, pliable. Plate tectonics Plate boundaries-3 types Theory that lithosphere is divided into plates that are always moving Plate movements build Earth’s largest landforms. Move, break, shrink, grow 2 or more plates move away from each other. Divergent boundaries Mid-ocean ridge Rift Sea-floor spreading Example--Mid Atlantic Ridge Transform fault boundaries Example-- San Andreas Fault Convergent boundaries Continental>Continental ex. Continental>oceanic ex. Oceanic >oceanic ex. Chain of mountains that run through oceans Deep valley where plates move apart-plates separate and hot rock from mantle moves up and forms new crust-new lithosphere This process is sea floor spreading 2 plates move past each other. Crust is NOT formed or destroyed. Plates grind against each other in opposite directions. Causes earthquakes 2 plates push into each other. •Plates bend and fold forming mountain ranges Himalayas- Mt Everest •Oceanic sinks under continental forming mountains a nd volcanoes and trench •One plate sinks under the other causing a deep trench and melting of asthenosphere Plate Movements Change Earth’s Surface Evidence of movement Pangea Shapes of continents Rock types along edges of continents Same kinds of plants and animals fossils Earth’s magnetic field in rocks Matching rock types Atlantic is growing; Pacific Ocean is shrinking; Af rica is shifting north