Q. 1. How many lone pairs are present in CH 3
advertisement

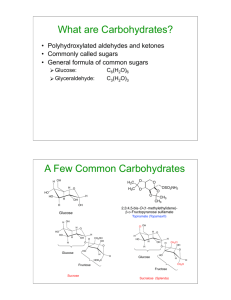
Choose the single correct answer for each of the following questions: (1 Mark each). Q. 1. How many lone pairs are present in CH3-O-CH3 i) 3 ii) 2 iii) 1 iv) 4 Q.2. When any hydrocarbon is added to water, it is: i) Soluble ii) Insoluble iii) Partially soluble iv) None of these Q.3. Which of the following is true for element Carbon: i) Monovalent ii) Divalent iii) Trivalent iv) Tetravalent Q.4. General formula of Alknaes is: i) CnH2n-2 ii) CnH2n+2 iii) CnH2n iv) CnH2n+1 Q.5. General formula of Alkenes is: i) CnH2n-2 ii) CnH2n+2 iii) CnH2n iv) CnH2n+1 Q.6. General formula of Alkynes is: i) CnH2n-2 ii) CnH2n+2 iii) CnH2n iv) CnH2n+1 Q.7. How many constitutional isomers does molecular formula C5H12 have: i) 3 ii) 2 iii) 4 iv) 0 Q.8. Isomers are the compounds that must have same i) Structural formula ii) Molecular formula iii) Physical properties iv) Chemical Properties Q.9. The isomer of butane is i) 1-methyl propane ii) 2-methyl propane iii) 2-methyl butane iv) Cyclobutane Q.10. How many hydrogen atoms are present in a cycloalkane with five carbon atoms i) 6 ii) 8 iii) 10 iv) 12 Chapter 11 Q.1. Which of the following molecule shows cis-trans isomerism: i) 2-butene ii) 1-butene iii) I-pentene iv) 2-methyl butane Q.2. The molecular formula C6H5CH3 belongs to the following group: i) Aliphatic hydrocarbons ii) Saturated hydrocarbons iii) alkyne iv) aromatic hydrocarbons Q.3. Give the correct IUPAC name of CH2=CHCH2CH2CH(CH3)CH2C(CH3)3 i) 5,7,7-trimethyl 1-octene ii) 2,2,4-trimethyl 7-octene iii) 7,7 dimethyl, 1-nonene iv) 5,7,7,7 tetra methyl, 1-heptene Q.4. The product obtained by hydration of ethene is: i) Acetaldehyde ii) Acetic Acid iii) Methanol iv) Ethanol Q.5. The product obtained by hydration of propene is: i) 1-propanol ii) 2-propanol iii) 1-butene iv) 2-butene Q.6. Phenol is: i) An alcohol ii) An aldehyde iii) An aliphatic compound iv) An aromatic compound Q.7. Stereoisomers have: i) Same molecular formula but different structural formula ii) Same molecular and same structural formula iii) Different molecular formula but same structural formula iv) Same molecular formula and same properties Q.8. Chemical name of polymer ‘Teflon’ is: i) Polyethylene ii) Polyvinyl Chloride iii) Polytetrafluoroethylene iv) Polypropylene Q.9. Common name of ‘hydroxybenzene’ is: i) Aniline ii) Phenol iii) Toluene iv) Benzene Q.10. What is i) 1,2-diethylbenzene the IUPAC name of m-diethylbenzene ii) 1,4-diethylbenzene iii) 1,3-diethylbenzene iv) 2,4-diethylbenzene 1. Solubility of ethanol in water is due to: a) Hydrogen bonds b) Covalent bonds c) Ionic bonds d) Van der Waal forces 2. Dehydration of an alcohol leads to the formation of an…………. a) Alkene b) Alkane 3. Aldehydes on oxidation produce: a) Alcohols b) Ketones c) Alkyne d) Aldehyde c) Carboxylic acids d) Alkanes 4. Which of the following compounds has the highest boiling point? a) CH3CH2CH2CH3 c) CH3OCH2CH3 b) CH3CH2CH=CH2 d) CH3CH2CH2OH 5. Which of the following names represents this structure? a) 4-methyl-3-ethyl-1-cyclohexanone b) 3-ethyl-4-methylcyclohexanone c) 3-ethyl-4-methyl-1-cyclohexanone d) 4-methyl-3-ethylcyclohexanone 6. Select the IUPAC name for: (CH3)2CHCH(OH)CH2C(CH3)3. a) 2,5,5-trimethyl-3-hexanol b) 1,1-dimethylisopentanol c) 1,1,4,4-pentamethylbutanol d) 2,5-dimethyl-4-hexanol 7. Which of the following is the correct IUPAC name of the structure shown? a) 4-methylhexanal b) methylhexanal c) 3-proylpropanal d) 3-methylhexanal 8. What is the common name of CH3CH2OCH2CH2CH2CH3? a) Diethylether c) Dibutylether b) Butylethylether d) Ethylbutylether 9. What is the IUPAC name of the compound shown? a) 3-ethyl-2-heptanone b) 3-butyl-2-pentanone c) 5-ethyl-2-heptanone d) 3-ethyl-2-hexanone 10. Which of the following names represents this structure? a) 1-Ethyl-4-methyl-2-pentanone b) 2-Ethyl-4-methyl-cyclopentanone c) 1-Methyl-4-ethyl-3-pentanone d) 1-Methyl-3-thyl-4-pentanone 11. The isomers below are: a) Identical b) Constitutional isomers c) Cis-trans isomers d) Enantiomers 12. Which of the following has lower boiling point? C 13. Oxidation of secondary alcohol gives : a) Aldehyde b) Ketone c) Acid d) No reaction 14. A molecule containing an atom which carries four different atoms or groups attached to it is known as a) Chiral molecule c) Achiral molecue b) Symmetric molecule d) None of these 15. Which class of alcohol is isopropyl alcohol: a) Primary c) Secondary b) Tertiary d) Quaternary 16. Which one of the following is a tertiary alcohol? a) CH3CH2OH c) CH3OH b) CH3CH(OH)CH3 d) (CH3) 3COH 17. The number of chirality centers of the structure given below is: a) 2 b) 3 c) 4 d) 5 18. Which of the following structures is a 3° amide ? a CH3CH2N(CH3)2 a) CH3CH2CONHCH3 CH3CH2CON(CH3)2 b) c) CH3CH2NHCH3 d) 19. Which of the following structures represents triethylammonium iodide? c (CH3CH2)2NH2 I a) CH3CH2NH3 I (CH3CH2)3NH I b) c) (CH3CH2)4N I d) 20. Choose the correct IUPAC name of this compound CH3 CH3 CH3CHCHCHCH2COOH Cl a) 2,4-dimethyl-3-chlorohexanoic acid acid c) 3-chloro-2,4-dimethylhexanoic b) 4-chloro-3,5-dimethylhexanoic acid d) 3,5-dimethyl-4-chlorohexanoic acid 21. What is the common name of the following compound? N CH2CH3 CH3 a) N-ethyl,N-methyl toluene b) N-ethyl,N-methyl aniline c) ethylmethyl aminobenzene d) ethylmethyl aniline 22. Which of the following structures represents N,N-dimethylacetamide? b O CH3 C N(CH3)2 a) O O O H C N(CH3)2 H3C C NHCH3 H C c) b) 23. Which of the following has the higher boiling point? a) CH3CH2COOH b) CH3CH2CH2OCH3 c) CH3COOCH3 d) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH 24. What products are formed when (CH3CH2)2NH is treated with HCl ? a) (CH3CH2)2NH3+ b) (CH3CH2) NH2 c) (CH3CH2)2NH2+Cld) (CH3CH2)3N 25. The reaction of CH3CH2CO2H and C2H5OH / H2SO4 gives a) CH3CH2COOH b) CH3CH2COOCOCH2CH3 c) CH3CH2COOC2H5 d) CH3CH2CONHC2H5 26. Which of the following compounds is more soluble in water? a) CH3(CH2)4COOH b) CH3(CH2)5COOH c) CH3(CH2)6COONa d) CH3(CH2)6COOH 27. What is the classification of the following amine ? N CH3 a) Primary amine b) Tertiary amine c) secondary amine d) quaternary amine NHCH3 d) 28. What are the hydrolysis products of the following ester using H2O/H2SO4? C6H5CH2COOCH2CH3 + a) C6H5CH2COOH + C2H5OH b) C6H5COOH + C2H5OH H2O H2SO4 c) C6H5CH2COOCH2CH3 + H2O d) C6H5CH2COCH3 + CH3OH 29. What products are formed when the following ester is hydrolyzed with water and NaOH? CH3CH2CH2COOC2H5 + H2O NaOH a) CH3 (CH2)2COOC2H5 + H2O C2H5OH b) (CH3)2 CHCOOH + C2H5OH c) CH3CH2CH2COONa + d) CH3CH2COCH3 + C2H5OH 30. Which of the following has the higher boiling point? a) CH3CH2CH2CONH2 b) CH3CH2CONHCH3 c) CH3CON(CH3)2 d) CH3CH2CH2CH3 31. What are the products of the following reaction? c O CH3CNHCH2CH2CH3 + H2O HCl a) CH3COOH + H2NCH2CH2CH3 c) CH3COOH b) CH3CONH2 + CH2CH2CH2OH d) CH3CONHCH3 + CH3CH2CH2NH3Cl + CH3CH2OH 32. What are the products of the hydrolysis of the following amide? O + C H2O NaOH N(CH3)2 a) C6H5COOH + (CH3)2NH b) C6H5COOH + CH3NH2 c) C6H5COONa + (CH3)2NH + H2O d) C6H5CON(CH3)2 + H2O + NaOH 33. Which of the following represents α-isomer of cyclic form of the sugar shown ?c H HOCH2 C CH2OH C C C CHO OH H H OH CH2OH O OH H H H H OH OH CH2OH H OH H O OH OH H OH O CH2OH O OH H OH H OH OH OH H H H OH H H OH OH H H OH H OH H H OH H H a) b) c) d) 34. Which of the following monosaccharides represents L-ketopentose? b CHO HO CH2OH H CH2OH CHO O H O OH H OH HO H HO H H OH H OH HO H HO H H OH CH2OH CH2OH b) a) CH2OH CH2OH c) d) 35. Which of the following cyclic structures represents β-D-fructose? c CH2OH CH2OH O CH2OH CH2OH O CH2OH OH H OH OH OH OH a) CH2OH OH OH H OH O b) H OH CH2OH CH2OH O OH H OH OH c) d) 36. What is the product formed when D-glucose is treated with Cu+2 / OH‾ ? b COOH CHO H H OH HO OH HO H COOH CHO HO H H H HO H H OH OH H OH H OH HO H HO H H OH H OH HO H HO H CH2OH CH2OH a) CH2OH CH2OH d) c) b) 37. What is the product formed when a D-aldopentose is treated with H2 / Pd ? c COOH CHO HO HO H CH3 CH2OH H HO H HO H H OH H OH H OH H OH H OH H OH H OH H OH CH2OH CH2OH a) CH2OH c) b) CH2OH d) 38. Starch consists mainly from? a) Amylose and amylopectine b) Glucose and glycogen c) amylose and glycogen d) glucose and galactose 39. The structure below is corresponding to a disaccharide in the form of : H H O 4 1 H O O 4 1 OH a) α - glycoside b) β - glycoside OH H c) δ- glycoside d) non of the above 40. The hydrolysis of maltose gives two units of : a) α-D-galactose b) β-D-glucose c) α-D-glucose d) β-D-galactose 41. All carbohydrates contain one or more chirality centers except: a) Dihydroxy acetone b) Glucose c) glycerladehyde d) fructose 42. The amino acid given below can be classified as : H H3N C COO CH2CH2CONH2 a) Neutral b) Basic c) Acidic d) Zwitterion 43. The pH at which the amino acid exist primarily in its neutral form is called: a) Hydrogen bond b) Melting point c) isoelectric point d) boiling point 44. The net charge of the zwitterion of an amino acid is : a) -1 b) -2 c) zero d) +1 45. Which of the following structures represents glycine in a solution of pH = 2? b H3 N C COO H3 N C H H a) b) H H H H COOH H2 N C COO H c) 46. The C-terminal of the following peptide chain is ? Arg-His-Ala-Asp a) Arginine c) histidine H2 N C H d) COOH b) Aspartic acid d) alanine 47. Three amino acids joined together by two peptide bond, called……………… a) Tripeptide b) Polypeptide c) dipeptide d) tetrapeptide 48. Which form is predominates at pH (11) for neutral amino acid ? a) Zwitterion c) anionic form (-1) b) Cationic form(+1) d) all of them 49. What is the name of a tripeptide has N-terminal amino acid of tyrosine , leucine and C-terminal amino acid alanine? a) leucyltyrosylalanine b) leucylalanyltyrosine c) alanylleucyltyrosine d) tyrosylalanylleucine 50. All amino acids have a chirality center except: a) Alanine b) Glycine c) histidine d) aspartic acid