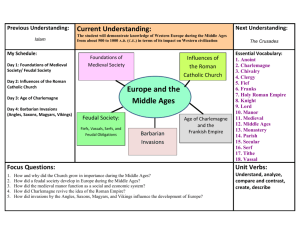
Rise of Feudalism
advertisement

Name _____________________________ WHI – Middle Ages Setting the Stage (page 315) 1. What is the Middle Ages? How long did it last? Invasions Trigger Changes in Western Europe? 2. What were the series of changes that altered government, economy, and culture? a. b. c. 3. Who could read during this time period? 4. Did the Germanic tribes have a written language? 5. What is a dialect? 6. What languages evolved from Latin? 7. Why were new languages forming? Germanic Kingdoms Emerge 1. What did the Germanic kingdoms replace? 2. What institution survived the fall of the Roman Empire? 3. What did the Church provide? 4. What unified Roman society? 5. What unified Germanic society? 6. Who held power in Gaul? Germanic Peoples Adopt Christianity 1. What helped spread Christianity? 2. Define monasteries. 3. Why did monasteries become Europe’s best-educated communities? 1 4. What valuable role did monasteries play during this time of chaos? 5. Define secular. A European Empire Evolves 1. Who controlled the largest and strongest of Europe’s kingdoms? 2. What was the significance of the Battle of Tours? (you already know this!) Charlemagne Takes Center Stage 1. What did Charlemagne spread through his successful conquests? 2. What did he do that had not been accomplished since the Roman Empire? 3. How big was the Carolingian empire? (What countries did it entail?) 4. What historic event occurred in 800 between Charlemagne and the Pope? 5. Why was this coronation so significant?? 6. What were Charlemagne’s most notable achievements? (3 things) Fill in the chart below to summarize how each person listed helped spread Christianity: Method of Spreading Christianity Clovis Benedict Gregory I Charles Martel Charlemagne **Are you working hard or hardly working??? – Ms. Abdalla 2 PROCESSING: 1. After the fall of the Roman Empire, learning declined. How was this trend offset during the early Middle Ages? 2. How does Charlemagne’s empire in medieval Europe compare with the Roman Empire? Setting the Stage (page 322) 1. What is feudalism? New Invasions Trouble Western Europe 1. What completely destroyed the Carolingian Empire? 2. Who invaded from the south? 3. Who struck from the east? 4. Which dreaded invaders came from the north? 5. What is the name of the area where the Vikings lived? 6. Other than being called Vikings, what else were they called? 7. What did they worship? 8. What other occupations were the Vikings? 9. Where did the Vikings reach even before Columbus? 10. Why did the Vikings stop raiding monasteries? 11. What were the Magyars good at? 12. Why did the Magyars raid land? 13. By controlling the Mediterranean Sea what did the Muslims disrupt? 3 14. What was the impact of Viking, Magyar, and Muslim invasions on medieval Europe? Feudalism Structures Society 1. What ancient civilization did we study that also practiced feudalism?? (you should know this…think!!!) 2. Complete the pyramid to illustrate society in feudal Europe 3. What determined someone’s prestige and power? 4. What three groups have medieval writers classified people? a. b. c. 5. Was social status hereditary? 6. Which social class did the majority of people belong to? 7. Define serfs. 8. Why were serfs not considered slaves? 9. How did feudal lords obtain their wealth? Manors: The Economic Side of Feudalism 1. What was a manor? 2. What did lords provide serfs? 4 3. What did serfs provide lords? 4. Typically how many families lived in the village on a manor? 5. How might the decline of trade during the early Middle Ages have contributed to the self-sufficiency of the manor system? 6. Define tithe? 7. How much did a tithe represent? Complete the flow chart below by filling in the causes, which led to the feudalism and the effects of feudalism: Causes Rise of Feudalism Effects PROCESSING: 1. What benefits do you think a medieval manor provided to the serfs who lived there? What were the drawbacks? **Hmm…tired yet? Six more A days til SOL!– Ms. Abdalla Setting the Stage (page 327) 1. Who was constantly fighting during the Middle Ages? Warriors on Horseback 1. Which region invented the leather saddle? 5 2. What became the most important part of an army? 3. Define chivalry. 4. Who are the three masters to whom the knight devoted himself? a. b. c. 5. How do medieval tournaments resemble modern sports competitions? The Literature of Chivalry 1. What is one of the earliest and most famous epic poems? 2. Define troubadours. The Shifting Role of Women 1. What was the church’s view on women? 2. As feudalism spread, did the status of women improve or decline? 3. What privileges did noblewomen have in medieval society? PROCESSING: 1. What positive effects might the code of chivalry have had on feudal society? **Do you miss me yet? Almost done!! - Ms. Abdalla Setting the Stage (page 332) 1. What institution emerged as a very powerful one in feudal Europe? The Scope of Church Authority 1. What did the Church want to influence? 6 2. What was Gelasius’ solution to a conflict between a pope and an emperor? 3. Define clergy. 4. Did the Church have a social hierarchy? What did it consist of? 5. Define sacraments. 6. Why did medieval peasants support the Church? 7. How was the Church’s authority both religious and political? 8. Define excommunication. 9. How is excommunication a powerful tool for the pope? THINK! The Church and the Holy Roman Empire 1. What was the strongest kingdom following the death of Charlemagne? Holy Roman Emperor Clashes with the Pope 1. Define lay investiture. 2. What is the issue between Pope Gregory VII and Emperor Henry IV? 3. Why was Henry’s journey to Canossa a political maneuver? Renewed Church Conflicts Under Frederick I - SKIP! German States Remain Separate 1. What long-lasting political trend kept German states separate during the Middle Ages? **Congratulations! You are done with your Middle Ages packet!!! I will see you all on Tuesday! – Mrs. Moronta 7