Acid Base Chem
advertisement

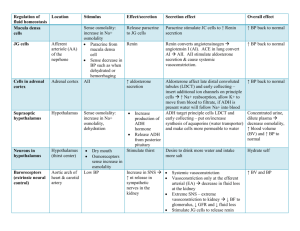
Acid Base Chem Ruth Olson In a person with severe renal artery stenosis, all would be inc. above normal except: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Plasma [rennin] Plasma [antiotensin II] BP in glomerular capillaries R to blood flow in efferent artertiole Systemic arterial BP **When there is autoregulation: when there is a higher pressure, the arterial won’t constrict Autoregulation of an Give an ACE inhibitor to the previous patient might lead to acute renal failure (reduced kidney function) by: 1. 2. 3. These are 3 basic way we manage H+ ions. Lungs is a rapid way to get rid of H+ions. The kidneys is slow and powerful … that’s what she said. H+ ions concentration is measured on a logarithmic scale. This conversion gives you manageable numbers 4. 5. Inhibiting renal tubule K+ reabsorption Inc renal resistance to BF 3. Causing plasma proteins to be excreted in the urine Causing systemic arterial hypertension Reducing glomerular filtration rate Hypertensive patients who receive transplanted kidneys from normotensive patient donors often remain normotensive after surgery. Which of the following is the most likely explanation of the normalization of blood pressure in these transplant paitents 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Hypoaldosteronism due to immunosuppression Loss of sympathetic nerve supply to kidneys Central role of kidney sin long-term BP control Immune reaction to kidney transplant Normal stress response after surgery The power of beet juice. Concerning the measurement o frenal plasma flow and GFR: Think of the buffers of H+ sponges. In general the buffers prevent non-volatile acids (which you can’t breathe off) from increasing the [H+] by 47,500 times! Effectiveness of a buffer system depends on [reactants] and pK of system and pH of body fluids. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Inulin is a good GFR marker bc it is feely filtered in the glomeruli and it is not reabsorbed, or secreted, by the renal tubules Inulin concentration in the proximal tubules lumen inc. progressively as water is reabsorbed in that segment of the nephron PAH is a good marker of renal plasma flo because it is freely filtered and is rapidly secrete by the proximal tubule; as a result very little PAH reaches the renal vein A and C are correct All are correct Acid Base Chem Ruth Olson Bicarb: Is the most important buffer in extracellular fluid even though the concentration of the components are low and pK of the system is 6.1, which is not very close to normal extracellular fluid pH (7.4). Reason: the components of the system (CO2 and HCO3-) are closely regulated by the lungs and kidneys There are bicarb transporters. There is a H+/Na+ antiporter as well. Remember that for one bicarb to be absorbed you have to have one H. No new bicarb. Doesn’t give you the ability to eliminate non-volatile acids kidneys do! Transport of the H in the more distal parts of the nephron uses a primary active transporter. Intercalated cells H+ ion secretion. It’s important to recognize that pH is generally normal in the tubular fluid. Regulation of H+ Bulk of bicarb reasborp is in proximal tubule 85% Inc pCO2 inc. H+ secretion respiratory acidosis (you compensate via renal HCO3reabsorption or formation; can’t fix it via hyperventilating) Acid Base Chem Ruth Olson Inc EC H+ increases H+ secretion metabolic (can compensate by hyperventilation) or respiratory acidosis Inc tubular fluid buffers inc H+ secretion metabolic or respiratory acidosis. Renal Compensations for Acid-Base Disorders Acidosis:Inc. H+ secretion & Inc HCO3reabsorption and production o All HCO3- is titrated and excess H+ in tubule is buffered o Cl- is also secreted o Buffers other than bicarb generate new bicarb Alkadosis: Dec H+ secretion & Dec. HCO3reabsorption and HCO3- loss in urine Importance of Renal Tubular Buffers: without them, to excrete > 60mmol nonvalatile acids each day as free H+, we’d need to excrete 2000 L/ day! One new bicarb and elimination of one H+ Buffers other than bicarb generate a new bicarb! Buffering of secreted H+: filtered PO4and generation of “new” HCO3- Enzymes that break down glutamine are activated by acidosis Acid Base Chem Ruth Olson One new bicarb for each H excreted. Total of three. Every H secreted creates a bicarb.