Chapter 4 Study Guide
advertisement

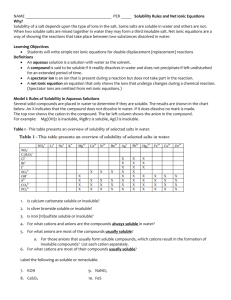
Honors Chemistry Study Guide – Chapter 4 (Sections 4.1-4.4): Aqueous Reactions Test Date: Friday, January 8th On test day you will receive: Chapter Four: - solubility rules activity series of metals & halogens periodic table Solubility o Define aqueous, soluble, and insoluble o Be able to determine if an ionic compound is soluble or insoluble using the solubility rules Electrolytes o Define electrolyte (what is required for a compound to be electrolytic?) o Be able to determine if a compound is ionic, covalent, an acid or base o Identify compounds as either strong, weak, or nonelectrolytes If ionic compound: Soluble = Strong electrolyte Insoluble = Nonelectrolyte (cannot form ions b/c they cannot dissolve, so they cannot be electrolytes) If covalent compound: All Nonelectrolytes (they have no ions, so they cannot be electrolytes) If acid/base: If strong acid/base = Strong electrolyte If base is insoluble = nonelectrolyte Any acid not listed as one of the 7 strong = Weak electrolyte Must know the strong acids and strong bases o Strong Acids = HCl, HI, HBr, HNO3, H2SO4, HClO3, HClO4 o Strong Bases = any SOLUBLE metal hydroxides (ex: NaOH) Double Replacement Precipitation Rxns o Define (and identify in rxns) precipitate o Define (and identify in rxns) spectator ion(s) o Predict the products formed in a double replacement rxn (cations switch partners) and determine the states of matter. Use solubility rules: insoluble = (s) = precipitate formed soluble = (aq) o A precipitation rxn ONLY occurs if a solid is formed [if all products are (aq) = No rxn] Ex: Na3PO4 (aq) + AgNO3 (aq) Products: NaNO3 (aq) + Ag3PO4 (s) Precipitate = silver phosphate o Write complete ionic equations (CIE) and net ionic equations (NIE) IMPORTANT: only (aq) compounds are broken up into ions, every other state of matter remains unchanged in CIE and NIE NIE = no spectators allowed!!! Single Replacement Redox Rxns o Define oxidation (OIL/LEO = oxidation is loss of electrions/lose electrons oxidation) o Define reduction (RIG/GER = reduction is gain of electrons/gain electrons reduction) o When using the activity series, be able to tell which metals are the most reactive (at the top) The more reactive the metal, the easier it is to oxidize and the more metals it can replace below it Also know what it means to be a noble metal and where they are on the activity series o Determine if a single replacement rxn will occur and predict the products if it does Metal that is by itself must be ABOVE the cation in the 2nd reactant in order for these rxns to occur Ex: Na (s) + Cu(NO3)2 (aq) o Na is above Cu this rxn does occur o Products: NaNO3 (aq) + Cu (s) If metal + acid and the rxn occurs, one product is always H2 (g) When the element alone is a HALOGEN gas (F2, Br2, Cl2, I2) Must use the halogen activity series halogen that is alone must be more reactive (listed above) the halogen in the 2nd reactant in order to replace it Ex: F2 (g) + KCl (aq) o Fluorine above iodine this rxn does occur o Products: KF (aq) + I2 (g) o Write complete ionic equations (CIE) and net ionic equations (NIE) IMPORTANT: only (aq) compounds are broken up into ions, every other state of matter remains unchanged in CIE and NIE NIE = no spectators allowed!!!