Net Ionic Equations Sec. 4.2 Precipitation Reactions
advertisement

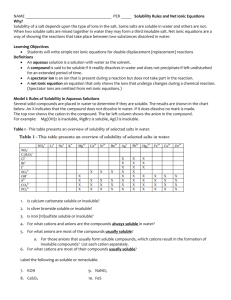
Sec. 4.2 Precipitation Reactions 1 A precipitation reaction occurs when two ionic compounds react together to form a soluble and an insoluble product Precipitation rxns are also called double replacement reactions ◦ AC + BD AD + BC where one product is a ppt. Products can be predicted using Solubility Rules 2 See Table 4.1 Solubility Guidelines For common Ionic Compounds in Water 3 Example: Aqueous solutions of silver nitrate and sodium chloride are mixed together AgNO3 (aq) + NaCl (aq) AgCl (s) + NaNO3 (aq) AgCl (s) is the ppt since “all chlorides are soluble except Ag+, Hg22+, and Pb2+” 4 Example: Aqueous solutions of potassium hydroxide and iron (III) iodide are mixed. 3KOH (aq) + FeI3 (aq) 3KI (aq) + Fe(OH)3 (s) Fe(OH)3 (s) is the ppt since “all hydroxides are insoluble except Ca2+, Sr2+, and Ba2+ 5 Ionic Equations– chemical equations that show the soluble reactants/products as ions ◦ Ex: AgNO3 (aq) + NaCl (aq) AgCl (s) + NaNO3 (aq) Ag+(aq) + NO3-(aq) + Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) AgCl(s) + Na+(aq) + NO3- (aq) Ex: 3KOH (aq) + FeI3 (aq) 3KI (aq) + Fe(OH)3 (s) 3K+(aq) + 3OH-(aq) + Fe3+(aq) + 3I-(aq) 3K+(aq) +3I- (aq) + Fe(OH)3 (s) 6 Net Ionic Equations (NIE’s) – chemical equations that show only the ions responsible for the precipitate The soluble ions are called spectator ions ◦ AgNO3 (aq) + NaCl (aq) AgCl (s) + NaNO3 (aq) ◦ Ag+ (aq) + NO3- (aq) + Na+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) AgCl (s) + Na+ (aq) + NO3- (aq) ◦ NIE: Ag+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) AgCl (s) 7 • • Ex: 3KOH (aq) + FeI3 (aq) 3KI (aq) + Fe(OH)3 (s) 3K+(aq) + 3OH-(aq) + Fe3+(aq) + 3I-(aq) 3K+(aq) + 3I- (aq) + Fe(OH)3 (s) • 3K+(aq) + 3OH-(aq) + Fe3+(aq) + 3I-(aq) 3K+(aq) +3I- (aq) + Fe(OH)3 (s) • NIE: 3OH-(aq) + Fe3+(aq) Fe(OH)3 (s) 8 You try it: ◦ Write the net ionic equation for the following reaction: Aqueous solutions of manganese (IV) acetate and lithium phosphate are reacted together 3Mn(C2H3O2)4 (aq) + 4Li3PO4 (aq) Mn3(PO4)4 (s) + 12LiC2H3O2 (aq) 3Mn4+ (aq) + 4C2H3O2- (aq) + 12Li+ (aq) + 4PO43- (aq) Mn3(PO4)4 (s) + 12Li+ (aq) + C2H3O2- (aq) NIE: 3Mn4+ (aq) + 4PO43- (aq) Mn3(PO4)4 (s) 9 Guidelines to writing net ionic equations (NIE’s) Identify the reaction type based on the given reactants Write the balanced molecular equation for the reaction Rewrite the equation to show the ions that form in solution when each soluble strong electrolyte breaks up into its component ions Soluble strong electrolytes: soluble ionic compounds, strong acids, strong bases Leave elements, molecular compounds, weak and nonelectrolytes, solids, liquids, and gases in their original form (no ions) Soluble weak electrolytes: soluble molecular compounds, weak acids, weak bases Identify and cancel spectator ions that occur on both sides of the equation 10