File
advertisement

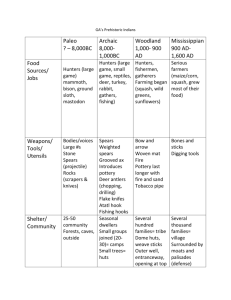
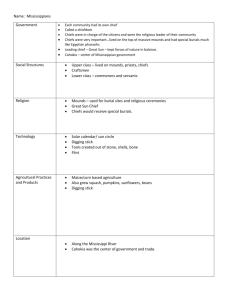
Tradition Weapons Paleo 1. 10,000BC8,000BC 2. Archaic 8,000BC1,000BC Woodland 1,000BC1,000AD Dwellings Large projectile points called Clovis Point 1. Large game such as wooly mammoths bison, sloths, etc. 1. Lived in large groups or bands of about 25-50 Knives and scrappers made from rocks 2. Wild berries 2. Always on the move in search of food— Nomads 3. Spear shafts and axes made from large tree branches 1. Atlatl—throwing device 2. Used fire to burn areas to improve hunting 3. Food 1. Began to hunt smaller game such as deer, rabbit, squirrel, elk, 2. Fish 3. Shellfish (oysters, crab) 3. Dug pits, slept in caves, or just out in the open 1. Seasonal nomads— moved each season 2. Summer months lived in north Georgia 3. Winter months— lived near coast for fish/shell fish 1. Because of agriculture, the Woodlands were able to stay in one place and did not migrate in search of food. 2. First to build permanent housing. 3. First to live in villages—tribes developed 4. Lived in the woods of the southeastern US Used deer antlers to make hooks 1. Developed bow and arrow 2. Arrowheads much smaller 4. Nuts, wild berries 1. Developed agriculture (corn, squash, gourds) 2. Saved nuts and seeds Religionevidence 1. Some evidence of religion. Bodies found buried with red powered. Suggest a belief in the afterlife. Other 1. 2. 3. 4. No pottery Only large spears No homes No religion Only thought was about “Where’s the beef” 1. Some evidence of religion. Bodies found buried with belongings such as pottery, tools, etc. Suggests belief in the after life. 1. First to use pottery. Made out of clay and plants. Not very sturdy. 1. Burial mounds found in various parts of Georgia. Suggests that the Woodland became more religious. Mounds contained bodies, jewelry, figures, tools and other objects 1. Perfected pottery—made of clay and rock. Much more sturdy. 2. Began to add decorations to pottery. Each tribe had own design. 2. Rock Eagle mounds were Woodland mounds. Mississippian 1. 1,000AD1,600 AD Still used the bow and arrow—made it better. 2. Very artistic— decorated bodies with paint, jewelry, feathers, etc. 1. Deer and other wild game still important 2. Crops very important—corn became the most important. Also beans, sunflowers, squash, etc. 1. 2. 3. Smoked tobacco and used it in ceremonies 3. Harvested and stored crops Very elaborate villages—chief lived on top of mound, the plaza of other huts below. Sturdy homes made from clay and wood and thatched roofs. Villages surrounded by river on back side and a moat (wide ditch) and palisades (large fence made from tall posts) on the front to protect from invaders. 1. 2. 3. Large, flattopped mounds with temples and other buildings for ceremonies. Inside mound, burial ground for past chiefs. Excavation of mounds revealed food, tools, ornaments, and objects made from wood, copper (indicates trading among various tribes), seashell, and stone. 1. This is the culture that De Soto discovered. 2. Most elaborate culture (most civilized) 3. Organized into chiefdoms. Each tribe had a chief, with one of these chiefs ruling over many tribes. (Sort of like governors and the president)