bit24982-sm-0001-SuppData
advertisement
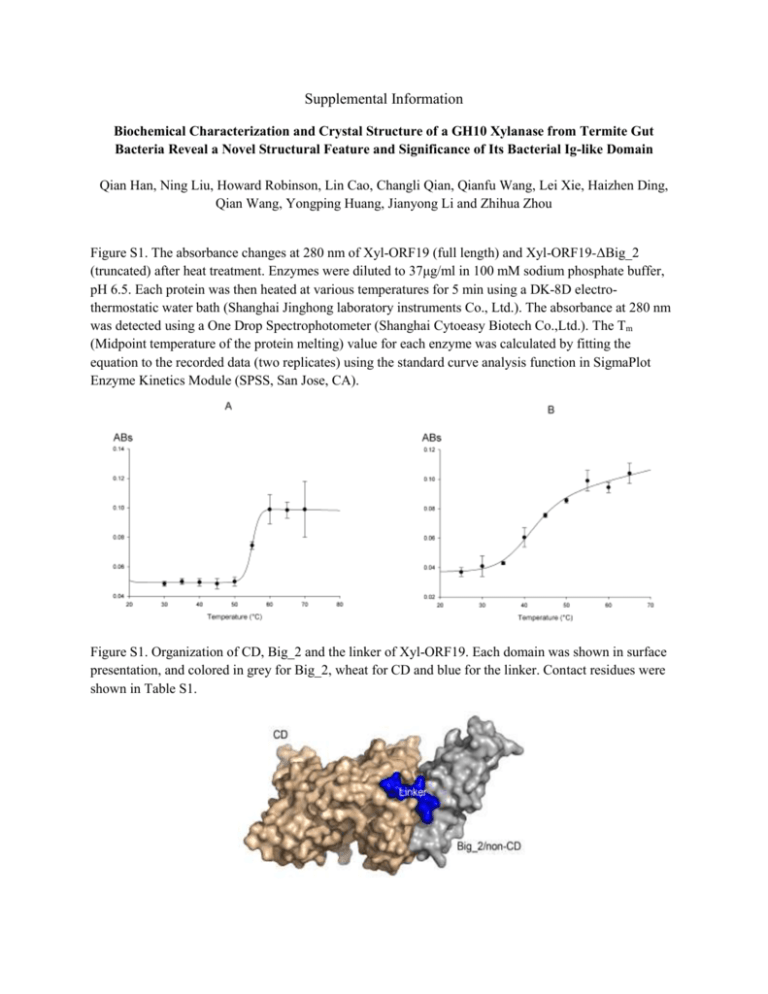
Supplemental Information Biochemical Characterization and Crystal Structure of a GH10 Xylanase from Termite Gut Bacteria Reveal a Novel Structural Feature and Significance of Its Bacterial Ig-like Domain Qian Han, Ning Liu, Howard Robinson, Lin Cao, Changli Qian, Qianfu Wang, Lei Xie, Haizhen Ding, Qian Wang, Yongping Huang, Jianyong Li and Zhihua Zhou Figure S1. The absorbance changes at 280 nm of Xyl-ORF19 (full length) and Xyl-ORF19-ΔBig_2 (truncated) after heat treatment. Enzymes were diluted to 37μg/ml in 100 mM sodium phosphate buffer, pH 6.5. Each protein was then heated at various temperatures for 5 min using a DK-8D electrothermostatic water bath (Shanghai Jinghong laboratory instruments Co., Ltd.). The absorbance at 280 nm was detected using a One Drop Spectrophotometer (Shanghai Cytoeasy Biotech Co.,Ltd.). The Tm (Midpoint temperature of the protein melting) value for each enzyme was calculated by fitting the equation to the recorded data (two replicates) using the standard curve analysis function in SigmaPlot Enzyme Kinetics Module (SPSS, San Jose, CA). Figure S1. Organization of CD, Big_2 and the linker of Xyl-ORF19. Each domain was shown in surface presentation, and colored in grey for Big_2, wheat for CD and blue for the linker. Contact residues were shown in Table S1. Table S1. Interfacing residues between the Big_2 domain (Big_2) and the Catalytic Domain (CD) of Xyl-ORF19 Big_2 Residues TIGQQ LKF GANLFL A A Sequence No. 28-32 69-71 75-80 82 84 DDMTIATNR IL L D AKP TS 393-401 403-404 443 448 453-455 458-459 CD Table S2. Hydrogen bonds formed between the Big_2 domain (Big_2) and the Catalytic Domain (CD) of Xyl-ORF19 Bond No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Big_2 PHE79[N] ALA84[N] GLY75[O] ASN77[O] ASN77[O] ALA82[O] GLY75[O] Bond Length 3.1 2.7 3.6 3.1 3.1 3.1 3.1 CD ALA398[O] ASN400[OD1] ASN400[N] ASN400[N] ASN400[ND2] ASN400[ND2] ARG401[N]