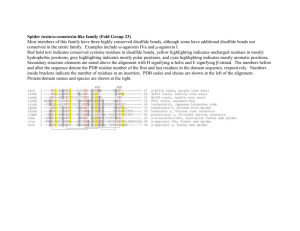
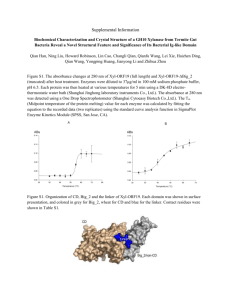
Mutation number
advertisement
Mutation number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Mutation in Nipah G (aa residues) 72-111 112-145 146-182 196-212 213-247 248-277 278-307 337-371 372-393 400-436 437-464 + + + + + + Cell surface binding to 293T cells + + + + - + - Protein Produced (28 NiV-G-Fc) 12 13 14 508-532 533-558 559-587 Supplementary Table I. Deletion analysis of NiV-G. Based on the predicted folding patterns of the extracellular domain of Hendra G protein1, systematic deletions were made to the ectodomain of Nipah G to remove predicted units of secondary structures. The indicated amino acid residues were deleted using the QuickChange™ site-directed mutagenesis kit according to the manufacturer’s directions (Stratagene, San Diego, CA). Protein production was measure by an Fc ELISA (see Supp. Methods 1) and values that were greater than 0.1ug/ml of unconcentrated supernatant were considered positive. Each mutant was also analyzed for its ability to bind 293T in a flow cytometry assay. Deletion number 11 (residues 437-464) produced protein comparable to wild type NiV-G-Fc and did not bind to 293T cells. This construct, named 28 Niv-G-Fc, was chosen to serve as a negative control for immunoprecipation experiments. 1. Yu, M., Hansson, E., Langedijk, J. P., Eaton, B. T. & Wang, L. F. The attachment protein of Hendra virus has high structural similarity but limited primary sequence homology compared with viruses in the genus Paramyxovirus. Virology 251, 227-33 (1998).