supplementary material 2015-6-1
advertisement
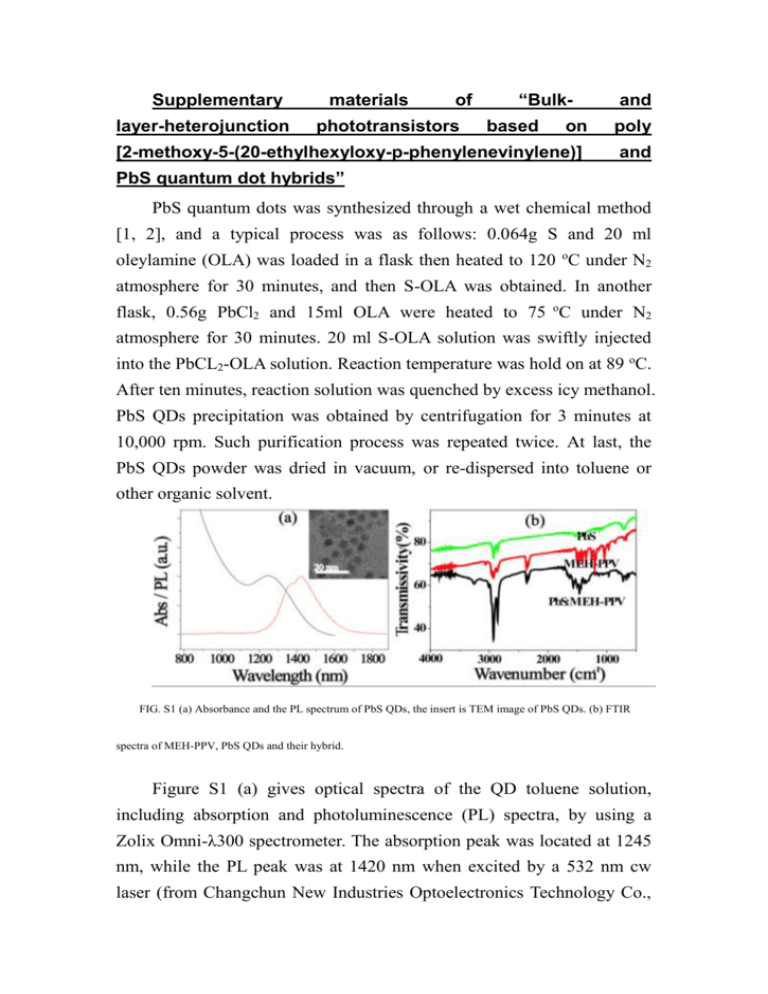
Supplementary layer-heterojunction materials of phototransistors “Bulkbased and on poly [2-methoxy-5-(20-ethylhexyloxy-p-phenylenevinylene)] and PbS quantum dot hybrids” PbS quantum dots was synthesized through a wet chemical method [1, 2], and a typical process was as follows: 0.064g S and 20 ml oleylamine (OLA) was loaded in a flask then heated to 120 oC under N2 atmosphere for 30 minutes, and then S-OLA was obtained. In another flask, 0.56g PbCl2 and 15ml OLA were heated to 75 oC under N2 atmosphere for 30 minutes. 20 ml S-OLA solution was swiftly injected into the PbCL2-OLA solution. Reaction temperature was hold on at 89 oC. After ten minutes, reaction solution was quenched by excess icy methanol. PbS QDs precipitation was obtained by centrifugation for 3 minutes at 10,000 rpm. Such purification process was repeated twice. At last, the PbS QDs powder was dried in vacuum, or re-dispersed into toluene or other organic solvent. FIG. S1 (a) Absorbance and the PL spectrum of PbS QDs, the insert is TEM image of PbS QDs. (b) FTIR spectra of MEH-PPV, PbS QDs and their hybrid. Figure S1 (a) gives optical spectra of the QD toluene solution, including absorption and photoluminescence (PL) spectra, by using a Zolix Omni-λ300 spectrometer. The absorption peak was located at 1245 nm, while the PL peak was at 1420 nm when excited by a 532 nm cw laser (from Changchun New Industries Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd.). According to a four-band-envelope-function formulism, the average diameter of PbS QDs was calculated as 4.8 nm [3]. The TEM image of the QDs was created using a transmission electron microscope (TEM) from FEI Co., Tecnai G2 F20, with 200 kV. Based on the TEM image, the average size of the PbS QDs was 4.8 nm, exhibiting good consistency with the diameter deduced from the absorption spectrum shown in Figure S1 (a) in supplementary materials. The hybrid solution was prepared by combining one volume of MEH-PPV (5 mg/ml) and three volumes of PbS QDs (10 mg/ml) toluene solution. The transmission peaks of PbS QDs, MEH-PPV, and their hybrid were determined using Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra (FTIR-650-spectrometer from Tianjin Gangdong sci.&tech. development Co., Ltd.), as shown in Figure S1 (b). For both PbS QDs and MEH-PPV, FTIR spectra represent the properties of ligand (-OLA) and MEH-PPV, respectively. For the hybrid, the characteristic peaks are viewed as superpositions of the peaks from the PbS QDs and MEH-PPV individuals. Please note that there is no exchange between the ligand of PbS QDs and MEH-PPV, which ensures the consistent heterojunction of the two types. References 1. Yang, Y. and T. Lian, Multiple exciton dissociation and hot electron extraction by ultrafast interfacial electron transfer from PbS QDs. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 2014. 263: p. 229-238. 2. Kim, J.Y., et al., 25th Anniversary Article: Colloidal Quantum Dot Materials and Devices: A Quarter-Century of Advances. Advanced Materials, 2013. 25(36): p. 4986-5010. 3. Kang, I. and F.W. Wise, Electronic structure and optical properties of PbS and PbSe quantum dots. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B., 1997. 14(7): p. 1632-1646.