Supplemental Material Quantum Confinement
advertisement
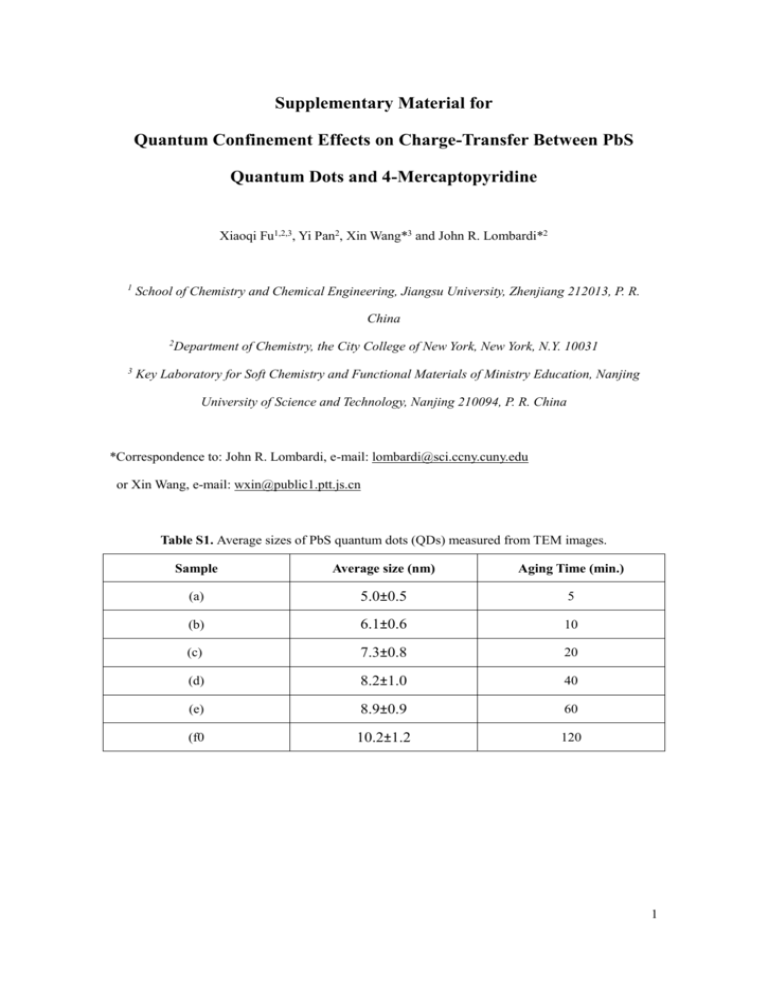
Supplementary Material for Quantum Confinement Effects on Charge-Transfer Between PbS Quantum Dots and 4-Mercaptopyridine Xiaoqi Fu1,2,3, Yi Pan2, Xin Wang*3 and John R. Lombardi*2 1 School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, P. R. China 2 Department of Chemistry, the City College of New York, New York, N.Y. 10031 3 Key Laboratory for Soft Chemistry and Functional Materials of Ministry Education, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210094, P. R. China *Correspondence to: John R. Lombardi, e-mail: lombardi@sci.ccny.cuny.edu or Xin Wang, e-mail: wxin@public1.ptt.js.cn Table S1. Average sizes of PbS quantum dots (QDs) measured from TEM images. Sample Average size (nm) Aging Time (min.) (a) 5.0±0.5 5 (b) 6.1±0.6 10 (c) 7.3±0.8 20 (d) 8.2±1.0 40 (e) 8.9±0.9 60 (f0 10.2±1.2 120 1 Figure S1. TEM images and sizes of PbS QDs: (a) 5.0 ± 0.5 nm, (b) 6.1 ± 0.6 nm, (c) 7.3 ± 0.8 nm (d) 8.2 ± 1.0 nm (e) 8.9 ± 0.9 nm (f) 10.2 ± 1.2 nm. 2