Notes For Power Point - Fort Bend Independent School District
advertisement
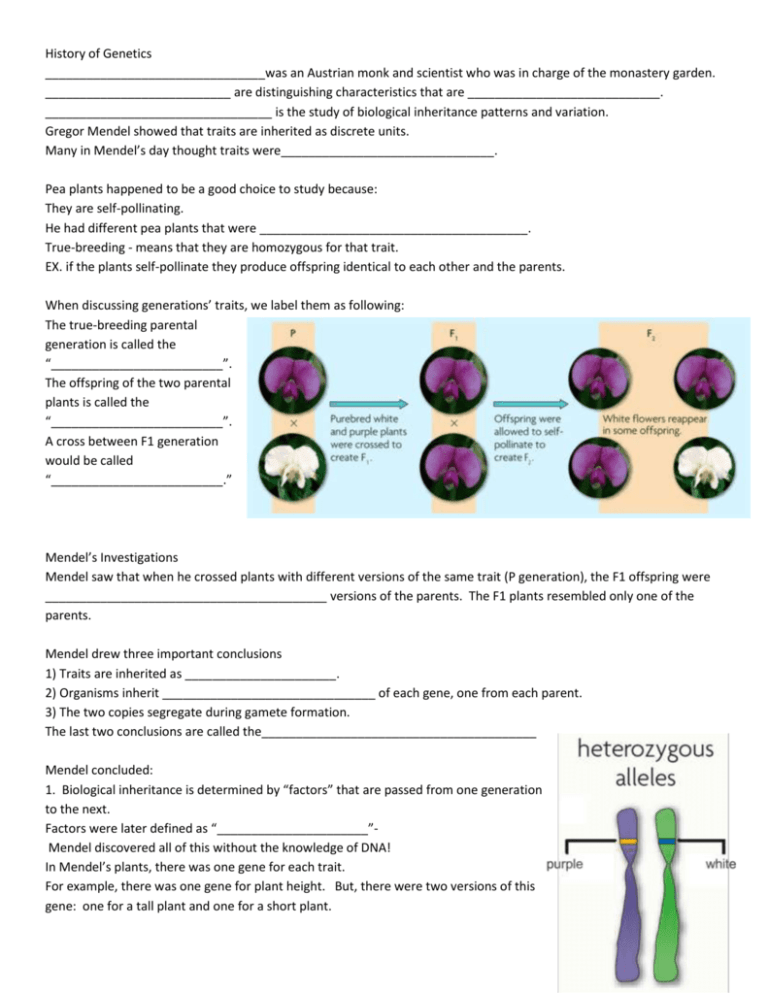
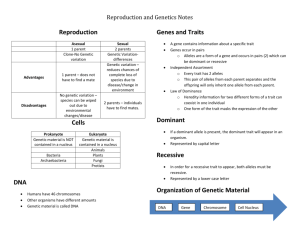
History of Genetics ________________________________was an Austrian monk and scientist who was in charge of the monastery garden. ___________________________ are distinguishing characteristics that are ____________________________. _________________________________ is the study of biological inheritance patterns and variation. Gregor Mendel showed that traits are inherited as discrete units. Many in Mendel’s day thought traits were_______________________________. Pea plants happened to be a good choice to study because: They are self-pollinating. He had different pea plants that were _______________________________________. True-breeding - means that they are homozygous for that trait. EX. if the plants self-pollinate they produce offspring identical to each other and the parents. When discussing generations’ traits, we label them as following: The true-breeding parental generation is called the “_________________________”. The offspring of the two parental plants is called the “_________________________”. A cross between F1 generation would be called “_________________________.” Mendel’s Investigations Mendel saw that when he crossed plants with different versions of the same trait (P generation), the F1 offspring were _________________________________________ versions of the parents. The F1 plants resembled only one of the parents. Mendel drew three important conclusions 1) Traits are inherited as ______________________. 2) Organisms inherit _______________________________ of each gene, one from each parent. 3) The two copies segregate during gamete formation. The last two conclusions are called the________________________________________ Mendel concluded: 1. Biological inheritance is determined by “factors” that are passed from one generation to the next. Factors were later defined as “______________________”Mendel discovered all of this without the knowledge of DNA! In Mendel’s plants, there was one gene for each trait. For example, there was one gene for plant height. But, there were two versions of this gene: one for a tall plant and one for a short plant. ____________________: Different versions of the same gene Remember, genes are used to make ___________________________. Each allele contains the DNA that codes for a slightly different version of the same protein. This gives us the different characteristics for each trait 2. Principal of dominance: Some alleles are _____________________ and some alleles are _________________________________. Recessive alleles are able to be ______________________ ___________________________________ alleles mask recessive alleles The trait that was represented in the F1 generation was the dominant trait. 3. Segregation: Observation: After seeing that his F1 plants looked like only one generation of the P generation plants, Mendel wanted to know what happened to the recessive alleles. Experiment: Mendel self-pollinated the F1 plants, or crossed the F1 plants with each other, to produce the F2 generation. From his F1 crosses, Mendel observed: The versions of the traits coded for by recessive alleles reappeared in the F2 plants. The recessive trait was still there! About ____________________ (or ¼) of the F2 plants exhibited the recessive version of the trait. In this case the recessive phenotype is short. The dominant phenotype, tall, was found in 75% (or ¾) of the F2 plants. Segregation of alleles during meiosis: When the F1 plants produce gametes (sex cells) and self-pollinate, the two alleles for the same gene separate from each other so that each gamete carries only one copy of each gene. Remember, gametes are ______________________________. In the example, we use “T” to represent the dominant, tall allele and “t” to represent the recessive, short allele. _________________ encode proteins that produce a diverse range of ____________________ The same gene can have many versions. A gene is a piece of DNA that directs a cell to make a certain protein. Each gene has a _____________________, a specific position on a pair of __________________________________________. An ____________________________ is any alternative form of a gene occurring at a specific locus on a chromosome. Each parent donates one allele for every gene. _________________________________ describes two alleles that are the ____________________ at a specific locus. ________________________ describes two alleles that are ________________________ at a specific locus. A dominant allele is expressed as a phenotype when at least one allele is dominant. A recessive allele is expressed as a phenotype only when two copies are present. Dominant alleles are represented by _________________ letters; recessive alleles by _____________________ letters. All of an organism’s genetic material is called the _____________________________. A ___________________________ refers to the makeup of a specific set of __________________________. A ___________________________ is the physical expression of a __________________________________. Key Terms in Mendelian Genetics: _________________________- allele that can mask; represented by capital letters (B, D, F, etc.) __________________________- alleles that can be masked; represented by lower case letters (b, d, f, etc.) Phenotype- _____________________________________________ (brown eyes, yellow seed pods) Genotype- _________________________________________; describes the genetic characteristics (BB, dd, Ff) _______________________ (True-Breeding)- having two identical alleles for the same trait (TT, tt); “homo” means same _________________________________- having two different alleles from the same trait (Tt); “hetero” means different Both homozygous dominant and heterozygous genotypes yield a dominant phenotype. __________________________________ illustrate genetic crosses. The Punnett square is a grid system for predicting all possible genotypes resulting from a cross. The axes represent the possible gametes of each parent. The boxes show the possible genotypes of the offspring. The Punnett square yields the ratio of ___________________________ and phenotypes. A _________________________ cross involves ________________________ trait. Monohybrid crosses examine the inheritance of only one specific trait. When you cross a homozygous dominant with a homozygous recessive: all offspring are ___________________________ 100% will show the dominant Phenotype 100% will be heterozygous If you cross two heterozygotes The genotype ratio will be 1:2:1 1 homozygous dominant, 2 heterozygous, 1 homozygous recessive The Phenotype ratio will be 3:1 3 will show the dominant and 1 will show the recessive trait A ______________________________cross involves ____________________ traits. Mendel’s dihybrid crosses with heterozygous plants yielded a 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio. Mendel’s dihybrid crosses led to his second law, the _______________________________________________________. The law of independent assortment states that allele pairs separate __________________________________________ of each other during meiosis. Heredity patterns can be calculated with __________________________. Probability is the likelihood that something will happen. Probability predicts an __________________________________________ of occurrences, not an exact number of occurrences. Sexual reproduction creates _____________________ combination of genes. independent assortment of chromosomes in meiosis random fertilization of gametes Unique phenotypes may give a ________________________________________________________ to some organisms. Crossing over during meiosis increases ___________________________________________. Crossing over is the exchange of chromosome segments between ____________________________________. results in new combinations of genes Chromosomes contain many genes The farther apart two genes are located on a chromosome; the more likely they are to be separated by crossing over. Genes located close together on a chromosome tend to be inherited together, which is called _________________________________. Genetic linkage allows the distance between two genes to be calculated.
![Biology Chapter 3 Study Guide Heredity [12/10/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006638861_1-0d9e410b8030ad1b7ef4ddd4e479e8f1-300x300.png)