ABO-Rh Blood Typing Lab: Transfusion Compatibility
advertisement

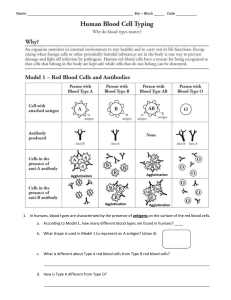
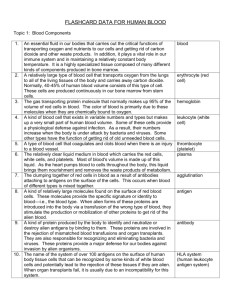
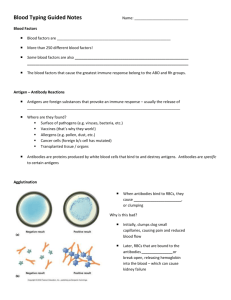
Name:__________________ ABO-Rh Blood Typing/Transfusion Lab Introduction: Patient X was just in a serious car accident that resulted in significant blood loss. They are in need of an urgent blood transfusion. From a blood donor card found in their wallet, it has been determined that they have A+ blood. The only problem is, the blood transfusion bags are not labeled correctly. It is up to you to test the blood types received from 4 different patients and determine which blood can be used in a transfusion. Background: Blood types are classified using the ABO +/- system. Surface proteins on red blood cells (antigens type A, B, and Rh) determine an individual’s blood type. The blood also has proteins called antibodies which attack foreign antigens. The antibodies in blood are antibodies A, B, and Rh. When foreign blood antigens enter the blood, antibodies attack which causes blood clumping or agglutination. To test for blood type, antibodies A, B, and Rh are added to blood samples to observe for agglutination. From this observation you can determine what antigens are located on the blood cell. If you are given a transfusion that does not match your blood type, antibodies in your blood will react with the foreign antigens from the transfusion, causing agglutination. Agglutination of blood can be fatal. It is this reason that it is important to test for blood compatibility before performing a transfusion. Procedure: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Place 5 drops of patient 1 simulated blood in each well on your blood typing tray. Place 3 drops of anti-A serum in well A. Place 3 drops of anti-B serum in well B. Place 3 drops of anti-Rh serum in well Rh. Use SEPARATE stirring sticks to mix the simulated blood and serum in each well for about 10 seconds. Examine each well to determine if the blood has agglutinated. Record your results in data table 1. Answer all questions related to that patient’s blood type. Repeat steps 1-7 for each blood sample. Fill out the last table and answer the related questions. Data Table 1 Simulated Blood Sample Agglutination Agglutination Agglutination in well A in well B in well Rh (+/-) (+/-) (+/-) Blood Type Observations Patient 1 Patient 2 Patient 3 Patient 4 Questions: Patient 1: Which antigens are present in patient 1? What is the blood type? Draw and label a picture of patient 1’s red blood cell with the appropriate antigens on the surface. Also draw and label the antibodies located in the blood. Can patient 1 donate blood to patient X? Why or why not? Patient 2: Which antigens are present in patient 2? What is the blood type? Draw and label a picture of patient 2’s red blood cell with the appropriate antigens on the surface. Also draw and label the antibodies located in the blood. Can patient 2 donate blood to patient X? Why or why not? Patient 3: Which antigens are present in patient 3? What is the blood type? Draw and label a picture of patient 3’s red blood cell with the appropriate antigens on the surface. Also draw and label the antibodies located in the blood. Can patient 3 donate blood to patient X? Why or why not? Patient 4: Which antigens are present in patient 4? What is the blood type? Draw and label a picture of patient 4’s red blood cell with the appropriate antigens on the surface. Also draw and label the antibodies located in the blood. Can patient 4 donate blood to patient X? Why or why not? Fill in the following table with the correct answers ABO +/- Blood Types Summary Table Blood Type Antigen on Red Blood Cells Antibodies in Blood Can Receive Blood From… A+ A- B+ B- AB+ AB- O+ O- Which blood type would be considered the universal recipient? Why? Which blood type would be considered the universal donor? Why? Can Donate Blood To…