Linkage Mapping/Recombination
advertisement
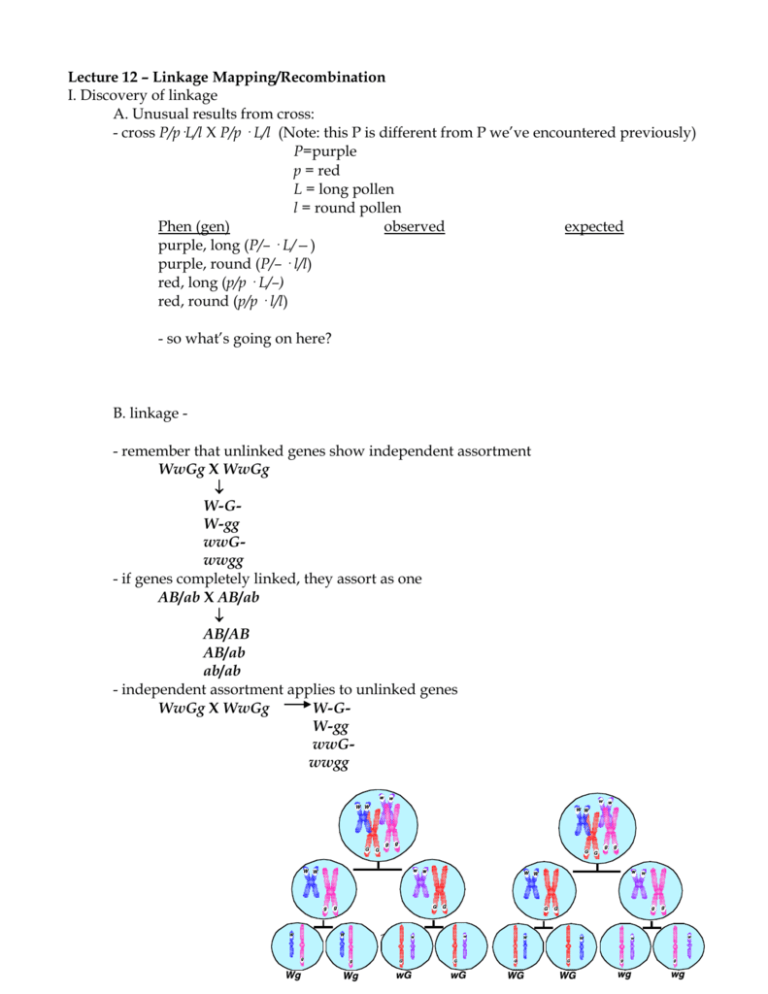
Lecture 12 – Linkage Mapping/Recombination I. Discovery of linkage A. Unusual results from cross: - cross P/p·L/l X P/p · L/l (Note: this P is different from P we’ve encountered previously) P=purple p = red L = long pollen l = round pollen Phen (gen) observed expected purple, long (P/– · L/—) purple, round (P/– · l/l) red, long (p/p · L/–) red, round (p/p · l/l) - so what’s going on here? B. linkage - remember that unlinked genes show independent assortment WwGg X WwGg W-GW-gg wwGwwgg - if genes completely linked, they assort as one AB/ab X AB/ab AB/AB AB/ab ab/ab - independent assortment applies to unlinked genes WwGg X WwGg W-GW-gg wwGwwgg 1 - What about linked genes? AB/ab X AB/ab AB/AB AB/ab ab/ab C. Recombination - if purple, round and red, long P and L are linked, where did come from? Answer: - crossing-over - gene occupies well defined site, or locus - alleles of genes occupy corresponding locations on homologous chromosomes 2 - crossing-over occures in prophase /metaphase I - exchange consists of breaking and rejoining of 2 chromatids with reciprocal exchange of equal, corresponding segments - may be multiple crossovers between homologous chromatids - site of crossing-over is ~random, > length between loci = >probability of crossover D. few more points about recombination: - recombination only results when crossover occurs between markers - double crossover between markers is not detected II. genetic notation/more terms A. cis vs trans may be represented by 1. cis (aka coupling) 2. trans (aka repulsion) B. Parental vs. nonparental 1. parental combination 2. nonparental combination III. Distinguishing linked from unlinked – use test cross 3 A. Consider 2 examples: AaBb X aabb AaBb Aabb aaBb aabb CcDd X ccdd CcDd Ccdd ccDd ccdd B. Often, considering only male progeny is~equivalent to test cross (if x-linked) w+ = red eyes w = white eyes wm+/wm+ female X w+m/Y male m+ = normal wings m = mini wings wm+/w+m & wm+/Y wm+/Y (white eye, normal wing) w+m/Y (red eye, mini wing) wm/Y (white eye, mini wing) w+m+/Y (red eye, normal wing) - what if mutations is in cis? wm/wm female X w+m+/Y male wm/w+m+ & wm/Y + + w m /w m & w +m+/Y wm/w m & wm/Y wm+/wm & wm/Y w+m/wm & w+m/Y C. Recombination is suppressed in Drosophila males cn = cinnabar eyes cn+ = red eyes 4 bw = brown eyes bw+ = red eyes cn bw/+ + female X cn bw/cn bw male + +/cn bw cn bw/cn bw cn +/cn bw + bw/cn bw cn bw/cn bw female X cn bw/ + + male cn bw/+ + cn bw/cn bw IV. Summary A. Two modes of reassortment 1. independent assortment 2. recombination B. Few additional points 1. if perfectly linked 2. maximum recombination is 50% because: 5