Chapter 6 Outline
advertisement

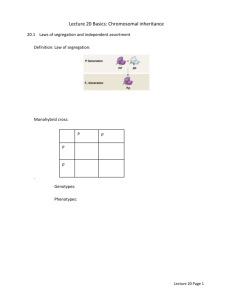
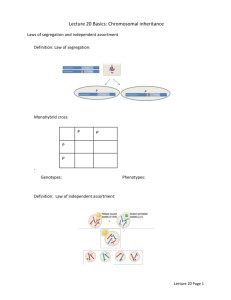
Chapter 6 Outline RECOMBINATION The process by which the haploid products of meiosis differ from the “input” haploid genotypes. This can take place either through independent assortment or crossing-over. Independent Assortment From a series of dihybrid crosses, Mendel was able to identify the Principle of Independent Assortment, which can be stated as: The segregation of different allele pairs occurs independently of each other. The basis for this lies in the fact that the homologous pairs of chromosomes line up on the metaphase independently with respect to each other. Thus, if there are two gene pairs, the di-heterozygote (AaBb) will generate 4 different gametes in equal numbers (AB, ab, Ab, aB). The F2 phenotypic ratio in the di-hybrid cross (AaBb X AaBb) is 9 AB-:3A-bb:3aaB-:1aabb. By performing a tester cross (AaBb X aabb) the phenotypic ratio will reflect the gametic ratio (1:1:1:1). Crossing-over Crossing over between genes on the same chromosome can also result in recombinant products. In this case, a tester cross results in 2 more abundant products (the parentals) and 2 less abundant products (the recombinants). Recombination frequency is a function of the distance between two genes and can be used to generate genetic maps. % recombination = # of recombinants/total # of progeny X 100 1% recombination = 1 map unit (or centimorgan) Map distances are generally additive, although they become less so when distances are greater. Due to multiple cross-overs, the measured recombination frequency between two points on a chromosome can not be greater than 50%. Intermediate points can be used to show the relationship between them. 2 analysis permits determination of goodness of fit 2 =e-o)2/e , where e represents the expected values (based on a hypothesis) and o represents the observed values. This is a measure of deviation to which a certain Probability value (p) may be ascribed. By convention, if p is < 0.05, the hypothesis may be rejected. Degrees of freedom (# of data classes – 1) needs to be known to know which row in the 2 table should be used. Assuming that the hypothesis is correct, p = 0.05 means that if you perform the experiment 100 times, you will get a deviation this large or larger 5 times. Three Point Mapping – mapping three genes at the same time, allows one to take advantage of the rarity of the double cross over class to rapidly determine gene order. When a trihybrid is crossed to a tester strain, 8 classes result: 2 parental, 2 double cross overs, two representing single cross-overs between the mid-point and one outer point and two representing single cross-overs between the mid-point and the other outer point. An effective strategy for three-point mapping is: 1. Regroup data into reciprocal pairs 2. Identify parental (most frequent) 3. Identify double cross-overs (least frequent) and determine gene order, based on which allele pair has to be switched to go from the parental to the double crossover configuration 4. Identify single cross-overs and determine map distances Interference is a measure of the effect of a cross-over in a given region on the likelihood of additional ones in that region. I = 1 – coefficient of coincidence (c.c.) and c.c. = observed double cross-overs/expected double cross-overs. Molecular Model for Recombination Model has to take into account the formation of a heteroduplex region. One viable model involves strand invasion. 1. DNA nicking (endonuclease) followed by chain displacement 2. Strand invasion followed by ligation 3. Resolution by vertical or horizontal cuts (only the vertical cuts give rise to the “standard” cross-over event). SUGGESTED PROBLEMS: 1, 2, 4, 7-10, 12-15, 22-24