Practice Exam 3

PRACTICE EXAM 3
Chapters 8-9
1.
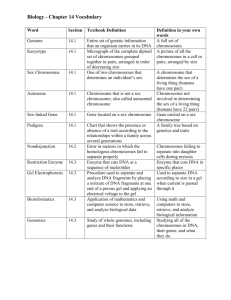
The creation of offspring carrying genetic information from a single parent is called
A) asexual reproduction.
B) sexual reproduction.
C) a life cycle.
D) regeneration.
E) spontaneous generation.
2.
Which of the following statements regarding sexual and asexual reproduction is true?
A) Cell division only occurs after sexual reproduction.
B) Only offspring from asexual reproduction inherit traits from two parents.
C) Sexual reproduction typically includes the development of unfertilized eggs.
D) Sexual reproduction is more likely to increase genetic variation than is asexual reproduction.
E) Only asexual reproduction results from the union of a sperm and an egg.
3.
Sister chromatids are
A) found right after a cell divides.
B) tightly linked together at a centromere.
C) formed when chromatids separate during cell division.
D) made only of DNA.
E) unique to prokaryotes.
4.
Eukaryotic cells spend most of their cell cycle in which phase?
A) interphase
B) prophase
C) metaphase
D) anaphase
E) telophase
5.
The genetic material is duplicated during
A) the mitotic phase.
B) G1.
C) the S phase.
D) G2.
E) mitosis.
6.
The process by which the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell divides to produce two cells is called
A) mitosis.
B) cytokinesis.
C) binary fission.
D) telophase.
E) spindle formation.
7.
Which of the following must occur for a plant or animal to grow and develop normally?
A) The organism must receive a supply of the appropriate hormones from its parents.
B) The organism must be able to control the timing and rate of cell division in different parts of its body.
C) Sufficient light must be available to stimulate cell division.
D) Sufficient oxygen must be available to stimulate cell division.
E) Dividing cells must be freed from attachment sites.
8.
You are asked to culture an unidentified sample of animal tissue. You notice that the cells seem to fail to exhibit density dependent inhibition. The source of this tissue sample is most likely
A) a scar.
B) a cancer.
C) skin.
D) a fetal liver.
E) the sperm producing tissue of the testis.
9.
A benign tumor differs from a malignant tumor in that a benign tumor
A) is cancerous.
B) spreads from the original site.
C) does not metastasize.
D) never causes health problems.
E) can only arise in the brain, whereas a malignant tumor can arise anywhere in the body.
10.
Which of the following statements regarding the function of mitosis is false?
A) Mitosis allows organisms to grow.
B) Mitosis allows organisms to generate genetic diversity.
C) Mitosis allows organisms to reproduce asexually.
D) Mitosis allows organisms to repair tissues.
E) Mitosis allows organisms to regenerate lost parts.
11.
Both mitosis and meiosis are preceded by
A) prometaphase.
B) interphase.
C) prophase.
D) telophase.
E) anaphase.
12.
Independent orientation of chromosomes at metaphase I results in an increase in the number of
A) gametes.
B) homologous chromosomes.
C) possible combinations of characteristics.
D) sex chromosomes.
E) points of crossing over.
13.
Karyotyping
A) shows chromosomes as they appear in metaphase of meiosis II.
B) can reveal alterations in chromosome number.
C) examines points of crossing over.
D) reveals the results of independent orientation of chromosomes during meiosis I.
E) reveals the presence of cancerous genes.
14.
Which of the following statements regarding Down syndrome is false?
A) Trisomy 21 usually leads to Down syndrome.
B) A human embryo with an abnormal number of chromosomes is usually spontaneously aborted.
C) Down syndrome is the most common serious birth defect in the United States.
D) People with Down syndrome usually have a life span much shorter than normal.
E) Women with Down syndrome cannot reproduce.
15.
Nondisjunction occurs when
A) a portion of a chromosome breaks off and is lost.
B) chromosomes replicate too many times.
C) two chromosomes fuse into one.
D) members of a chromosome pair fail to separate.
E) an entire pair of chromosomes is lost during meiosis I.
16.
If a chromosome fragment breaks off and then reattaches to the original chromosome, but in the reverse direction, the resulting chromosomal abnormality is called a(n)
A) deletion.
B) inversion.
C) translocation.
D) nondisjunction.
E) reciprocal translocation.
17.
Cancer is not usually inherited because
A) the chromosomal changes in cancer are usually confined to somatic cells.
B) people with cancer usually die before reproducing.
C) cancer typically causes disruptions of meiosis.
D) the causes of cancer are not usually genetic.
E) the cancerous cells usually interfere with the ability to produce gametes.
18.
Mendel conducted his most memorable experiments on
A) peas.
B) roses.
C) guinea pigs.
D) fruit flies.
E) clones.
19.
Varieties of plants in which self fertilization produces offspring that are identical to the parents are referred to as
A) hybrids.
B) the F2 generation.
C) monohybrid crosses.
D) independent crosses.
E) true breeding.
20.
A monohybrid cross is
A) the second generation of a self fertilized plant.
B) a breeding experiment in which the parental varieties have only one trait in common.
C) a breeding experiment in which the parental varieties differ in only one character.
D) a triploid plant that results from breeding two very different plants.
E) a breeding experiment in which the parental varieties have only one prominent trait.
21.
Which of the following statements regarding genotypes and phenotypes is false?
A) The genetic makeup of an organism constitutes its genotype.
B) An organism with two different alleles for a single trait is said to be heterozygous for that trait.
C) Alleles are alternate forms of a gene.
D) An allele that is fully expressed is referred to as recessive.
E) The expressed physical traits of an organism are called its phenotype.
22.
All the offspring of a cross between a black eyed mendelien and an orange eyed mendelien have black eyes. This means that the allele for black eyes is ________ the allele for orange eyes.
A) codominant to
B) recessive to
C) more aggressive than
D) dominant to
E) better than
23.
All the offspring of a cross between a black eyed mendelien and an orange eyed mendelien have black eyes. What is the expected phenotypic ratio of a cross between two orange eyed mendeliens?
A) 3 black eyed:1 orange eyed
B) 0 black eyed:1 orange eyed
C) 1 black eyed:3 orange eyed
D) 1 black eyed:0 orange eyed
E) 1 black eyed:1 orange eyed
24.
The alleles of a gene are found at ________ chromosomes.
A) the same locus on homologous mitochondrial
B) the same locus on heterologous
C) different loci on homologous
D) different loci on heterologous
E) the same locus on homologous
25.
Mendel's law of independent assortment states that
A) chromosomes sort independently of each other during mitosis and meiosis.
B) genes sort independently of each other in animals but not in plants.
C) independent sorting of genes produces polyploid plants under some circumstances.
D) each pair of alleles segregates independently of the other pairs of alleles during gamete formation.
E) genes are sorted concurrently during gamete formation.
26.
A testcross is
A) a mating between an individual of unknown genotype and an individual homozygous recessive for the trait of
interest.
B) a mating between an individual of unknown genotype and an individual heterozygous for the trait of interest.
C) a mating between an individual of unknown genotype and an individual homozygous dominant for the trait of
interest.
D) a mating between two individuals heterozygous for the trait of interest.
E) a mating between two individuals of unknown genotype.
27.
A carrier of a genetic disorder who does not show symptoms is most likely to be
________ to transmit it to offspring.
A) heterozygous for the trait and able
B) heterozygous for the trait and unable
C) homozygous for the trait and able
D) homozygous for the trait and unable
E) heterozygous for the trait and unlikely
28.
Most genetic disorders of humans are caused by
A) multiple alleles.
B) recessive alleles.
C) drinking during pregnancy.
D) a mutation that occurs in the egg, sperm, or zygote.
E) dominant alleles.
29.
All the offspring of a cross between a red flowered plant and a white flowered plant have pink flowers. This means that the allele for red flowers is ________ to the allele for white flowers.
A) dominant
B) codominant
C) pleiotropic
D) incompletely dominant
E) recessive
30.
A person with AB blood illustrates the principle of
A) incomplete dominance.
B) codominance.
C) pleiotropy.
D) polygenic inheritance.
E) blending inheritance.
31.
Which of the following terms refers to a situation where a single phenotypic character is determined by the additive effects of two or more genes?
A) incomplete dominance
B) codominance
C) pleiotropy
D) polygenic inheritance
E) blending inheritance
32.
The individual features of all organisms are the result of
A) genetics.
B) the environment.
C) genetics and cytoplasmic determinants.
D) the environment and individual needs.
E) genetics and the environment.
33.
What is the normal complement of sex chromosomes in a human male?
A) two X chromosomes
B) two Y chromosomes
C) two X chromosomes and one Y chromosome
D) one X chromosome and one Y chromosome
E) one Y chromosome
34.
A color blind woman marries a man who is not color blind. All of their sons, but none of their daughters, are color blind. Which of the following statements correctly explains these results?
A) The gene for color vision is incompletely dominant to the gene for sex determination.
B) The gene for color vision is completely dominant to the gene for sex determination.
C) The gene for color vision is codominant with the gene for sex determination.
D) The gene for color vision is linked to the X chromosome.
E) The gene for color vision is linked to the Y chromosome.
35.
Female inheritance patterns cannot be analyzed by simply studying the X chromosome because
A) the X chromosome is too fragile for long term analysis.
B) the X chromosome is too susceptible to mutations.
C) the X chromosome is obtained from both father and mother.
D) the X chromosome is too difficult to isolate from the other chromosomes.
E) the X chromosome is physically too large to analyze accurately.
Chapter 10
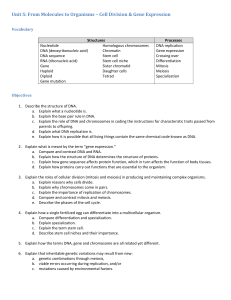
1.
The monomers of DNA and RNA are a.
amino acids. b.
monosaccharides. c.
nucleotides. d.
fatty acids. e.
nucleic acids.
2.
DNA replication a.
occurs through the addition of nucleotides to the end of the DNA molecule. b.
results in the formation of four new DNA strands. c.
uses each strand of a DNA molecule as a template for the creation of a new strand. d.
begins when two DNA molecules join together to exchange segments.
3.
If one strand of DNA is CGGTAC, the corresponding strand would be
A) GCCTAG.
B) CGGTAC.
C) GCCAUC.
D) TAACGT.
E) GCCATG.
4.
Which of the following enzymes catalyzes the elongation of a new DNA strand?
A) helicase
B) primase
C) ligase
D) single stranded binding protein
E) DNA polymerase
5.
Which of the following options best depicts the flow of information when a gene directs the synthesis of a cellular component? a.
RNA → DNA → RNA → protein b.
DNA → RNA → protein c.
protein → RNA → DNA d.
DNA → amino acid → RNA → protein e.
DNA → tRNA → mRNA → protein
6.
Experiments have demonstrated that the "words" of the genetic code (the units that specify amino acids) are a.
single nucleotides. b.
two nucleotide sequences. c.
three nucleotide sequences. d.
nucleotide sequences of various lengths. e.
enzymes.
7.
Which of the following occurs when RNA polymerase attaches to the DNA? a.
elongation of the growing RNA molecule b.
termination of the RNA molecule c.
addition of nucleotides to the DNA template d.
initiation of a new RNA molecule e.
initiation of a new polypeptide chain
8.
Where do transcription and translation occur in prokaryotic cells? a.
on the plasma membrane b.
in the nucleus c.
in the cytoplasm d.
in chromatophores e.
in the cell wall
9.
Which of the following takes place during translation? a.
the conversion of genetic information from the language of nucleic acids to the language of proteins b.
the conversion of genetic information from DNA nucleotides into RNA nucleotides c.
the addition of nucleotides to a DNA template d.
the conversion of genetic information from the language of proteins to the language of enzymes e.
DNA replication
10.
A base substitution mutation in a gene does not always result in a different protein.
Which of the following factors could account for this? a.
the fact that the mutation affects only the sequence of the protein's amino acids, so the protein stays the same b.
the double ring structure of adenine and guanine c.
a correcting mechanism that is part of the mRNA molecule d.
the fact that such mutations are usually accompanied by a complementary deletion e.
the fact that some amino acids are specified from more than one codon
11.
DNA ligase binds
A) exons together.
B) polymerase to the promotor.
C) nucleotides together.
D) introns together.
E) an intron to an exon.
Chapters 8-9 ANSWERS
1.
The creation of offspring carrying genetic information from a single parent is called
A) asexual reproduction.
B) sexual reproduction.
C) a life cycle.
D) regeneration.
E) spontaneous generation.
Answer: A
Topic: Opening Essay
Skill: Factual Recall
2.
Which of the following statements regarding sexual and asexual reproduction is true?
A) Cell division only occurs after sexual reproduction.
B) Only offspring from asexual reproduction inherit traits from two parents.
C) Sexual reproduction typically includes the development of unfertilized eggs.
D) Sexual reproduction is more likely to increase genetic variation than is asexual reproduction.
E) Only asexual reproduction results from the union of a sperm and an egg.
Answer: D
Topic: Opening Essay, 8.1
Skill: Conceptual Understanding
3.
Sister chromatids are
A) found right after a cell divides.
B) tightly linked together at a centromere.
C) formed when chromatids separate during cell division.
D) made only of DNA.
E) unique to prokaryotes.
Answer: B
Topic: 8.4
Skill: Factual Recall
4.
Eukaryotic cells spend most of their cell cycle in which phase?
A) interphase
B) prophase
C) metaphase
D) anaphase
E) telophase
Answer: A
Topic: 8.5
Skill: Factual Recall
5.
The genetic material is duplicated during
A) the mitotic phase.
B) G1.
C) the S phase.
D) G2.
E) mitosis.
Answer: C
Topic: 8.5
Skill: Application
6.
The process by which the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell divides to produce two cells is called
A) mitosis.
B) cytokinesis.
C) binary fission.
D) telophase.
E) spindle formation.
Answer: B
Topic: 8.5
Skill: Factual Recall
7.
The phase of mitosis during which the nuclear envelope fragments and the nucleoli disappear is called
A) interphase.
B) prophase.
C) metaphase.
D) anaphase.
E) telophase.
Answer: B
Topic: 8.6
Skill: Factual Recall
8.
Which of the following must occur for a plant or animal to grow and develop normally?
A) The organism must receive a supply of the appropriate hormones from its parents.
B) The organism must be able to control the timing and rate of cell division in different parts of its body.
C) Sufficient light must be available to stimulate cell division.
D) Sufficient oxygen must be available to stimulate cell division.
E) Dividing cells must be freed from attachment sites.
Answer: B
Topic: 8.8
Skill: Conceptual Understanding
9.
You are asked to culture an unidentified sample of animal tissue. You notice that the cells seem to fail to exhibit density dependent inhibition. The source of this tissue sample is most likely
A) a scar.
B) a cancer.
C) skin.
D) a fetal liver.
E) the sperm producing tissue of the testis.
Answer: B
Topic: 8.10
Skill: Application
10.
A benign tumor differs from a malignant tumor in that a benign tumor
A) is cancerous.
B) spreads from the original site.
C) does not metastasize.
D) never causes health problems.
E) can only arise in the brain, whereas a malignant tumor can arise anywhere in the body.
Answer: C
Topic: 8.10
Skill: Factual Recall
11.
Which of the following statements regarding the function of mitosis is false?
A) Mitosis allows organisms to grow.
B) Mitosis allows organisms to generate genetic diversity.
C) Mitosis allows organisms to reproduce asexually.
D) Mitosis allows organisms to repair tissues.
E) Mitosis allows organisms to regenerate lost parts.
Answer: B
Topic: 8.11
Skill: Factual Recall
12.
Both mitosis and meiosis are preceded by
A) prometaphase.
B) interphase.
C) prophase.
D) telophase.
E) anaphase.
Answer: B
Topic: 8.15
Skill: Factual Recall
13.
Independent orientation of chromosomes at metaphase I results in an increase in the number of
A) gametes.
B) homologous chromosomes.
C) possible combinations of characteristics.
D) sex chromosomes.
E) points of crossing over.
Answer: C
Topic: 8.17
Skill: Conceptual Understanding
14.
Karyotyping
A) shows chromosomes as they appear in metaphase of meiosis II.
B) can reveal alterations in chromosome number.
C) examines points of crossing over.
D) reveals the results of independent orientation of chromosomes during meiosis I.
E) reveals the presence of cancerous genes.
Answer: B
Topic: 8.19
15.
Which of the following statements regarding Down syndrome is false?
A) Trisomy 21 usually leads to Down syndrome.
B) A human embryo with an abnormal number of chromosomes is usually spontaneously aborted.
C) Down syndrome is the most common serious birth defect in the United States.
D) People with Down syndrome usually have a life span much shorter than normal.
E) Women with Down syndrome cannot reproduce.
Answer: E
Topic: 8.20
Skill: Factual Recall
16.
Nondisjunction occurs when
A) a portion of a chromosome breaks off and is lost.
B) chromosomes replicate too many times.
C) two chromosomes fuse into one.
D) members of a chromosome pair fail to separate.
E) an entire pair of chromosomes is lost during meiosis I.
Answer: D
Topic: 8.21
Skill: Factual Recall
17.
If a chromosome fragment breaks off and then reattaches to the original chromosome, but in the reverse direction, the resulting chromosomal abnormality is called a(n)
A) deletion.
B) inversion.
C) translocation.
D) nondisjunction.
E) reciprocal translocation.
Answer: B
Topic: 8.24
Skill: Factual Recall
18.
Cancer is not usually inherited because
A) the chromosomal changes in cancer are usually confined to somatic cells.
B) people with cancer usually die before reproducing.
C) cancer typically causes disruptions of meiosis.
D) the causes of cancer are not usually genetic.
E) the cancerous cells usually interfere with the ability to produce gametes.
Answer: A
Topic: 8.24
Skill: Conceptual Understanding
19.
Mendel conducted his most memorable experiments on
A) peas.
B) roses.
C) guinea pigs.
D) fruit flies.
E) clones.
Answer: A
Topic: 9.2
Skill: Factual Recall
20.
Varieties of plants in which self fertilization produces offspring that are identical to the parents are referred to as
A) hybrids.
B) the F2 generation.
C) monohybrid crosses.
D) independent crosses.
E) true breeding.
Answer: E
Topic: 9.2
Skill: Conceptual Understanding
21.
A monohybrid cross is
A) the second generation of a self fertilized plant.
B) a breeding experiment in which the parental varieties have only one trait in common.
C) a breeding experiment in which the parental varieties differ in only one character.
D) a triploid plant that results from breeding two very different plants.
E) a breeding experiment in which the parental varieties have only one prominent trait.
Answer: C
Topic: 9.3
Skill: Conceptual Understanding
22.
Which of the following statements regarding genotypes and phenotypes is false?
A) The genetic makeup of an organism constitutes its genotype.
B) An organism with two different alleles for a single trait is said to be heterozygous for that trait.
C) Alleles are alternate forms of a gene.
D) An allele that is fully expressed is referred to as recessive.
E) The expressed physical traits of an organism are called its phenotype.
Answer: D
Topic: 9.3
Skill: Factual Recall
23.
All the offspring of a cross between a black eyed mendelien and an orange eyed mendelien have black eyes. This means that the allele for black eyes is ________ the allele for orange eyes.
A) codominant to
B) recessive to
C) more aggressive than
D) dominant to
E) better than
Answer: D
Topic: 9.3
Skill: Conceptual Understanding
24.
All the offspring of a cross between a black eyed mendelien and an orange eyed mendelien have black eyes. What is the expected phenotypic ratio of a cross between two orange eyed mendeliens?
A) 3 black eyed:1 orange eyed
B) 0 black eyed:1 orange eyed
C) 1 black eyed:3 orange eyed
D) 1 black eyed:0 orange eyed
E) 1 black eyed:1 orange eyed
Answer: B
Topic: 9.3
Skill: Application
25.
The alleles of a gene are found at ________ chromosomes.
A) the same locus on homologous mitochondrial
B) the same locus on heterologous
C) different loci on homologous
D) different loci on heterologous
E) the same locus on homologous
Answer: E
Topic: 9.4
Skill: Factual Recall
26.
Mendel's law of independent assortment states that
A) chromosomes sort independently of each other during mitosis and meiosis.
B) genes sort independently of each other in animals but not in plants.
C) independent sorting of genes produces polyploid plants under some circumstances.
D) each pair of alleles segregates independently of the other pairs of alleles during gamete formation.
E) genes are sorted concurrently during gamete formation.
Answer: D
Topic: 9.5
Skill: Conceptual Understanding
27.
A testcross is
A) a mating between an individual of unknown genotype and an individual homozygous recessive for the trait of
interest.
B) a mating between an individual of unknown genotype and an individual heterozygous for the trait of interest.
C) a mating between an individual of unknown genotype and an individual homozygous dominant for the trait of
interest.
D) a mating between two individuals heterozygous for the trait of interest.
E) a mating between two individuals of unknown genotype.
Answer: A
Topic: 9.6
Skill: Conceptual Understanding
28.
A carrier of a genetic disorder who does not show symptoms is most likely to be ________ to transmit it to offspring.
A) heterozygous for the trait and able
B) heterozygous for the trait and unable
C) homozygous for the trait and able
D) homozygous for the trait and unable
E) heterozygous for the trait and unlikely
Answer: A
Topic: 9.8
Skill: Conceptual Understanding
29.
Most genetic disorders of humans are caused by
A) multiple alleles.
B) recessive alleles.
C) drinking during pregnancy.
D) a mutation that occurs in the egg, sperm, or zygote.
E) dominant alleles.
Answer: B
Topic: 9.9
Skill: Factual Recall
30.
All the offspring of a cross between a red flowered plant and a white flowered plant have pink flowers. This means that the allele for red flowers is ________ to the allele for white flowers.
A) dominant
B) codominant
C) pleiotropic
D) incompletely dominant
E) recessive
Answer: D
Topic: 9.11
Skill: Conceptual Understanding
31.
A person with AB blood illustrates the principle of
A) incomplete dominance.
B) codominance.
C) pleiotropy.
D) polygenic inheritance.
E) blending inheritance.
Answer: B
Topic: 9.12
Skill: Factual Recall
32.
Which of the following terms refers to a situation where a single phenotypic character is determined by the additive effects of two or more genes?
A) incomplete dominance
B) codominance
C) pleiotropy
D) polygenic inheritance
E) blending inheritance
Answer: D
Topic: 9.14
Skill: Factual Recall
33.
The individual features of all organisms are the result of
A) genetics.
B) the environment.
C) genetics and cytoplasmic determinants.
D) the environment and individual needs.
E) genetics and the environment.
Answer: E
Topic: 9.15
Skill: Conceptual Understanding
34.
Genes located close together on the same chromosomes are referred to as ________ genes and generally ________.
A) associated . . . sort independently during meiosis
B) linked . . . sort independently during meiosis
C) homologous . . . are inherited together
D) linked . . . do not sort independently during meiosis
E) codependent . . . do not sort independently during meiosis
Answer: D
Topic: 9.17
Skill: Conceptual Understanding
35.
What is the normal complement of sex chromosomes in a human male?
A) two X chromosomes
B) two Y chromosomes
C) two X chromosomes and one Y chromosome
D) one X chromosome and one Y chromosome
E) one Y chromosome
Answer: D
Topic: 9.20
Skill: Factual Recall
36.
A color blind woman marries a man who is not color blind. All of their sons, but none of their daughters, are color blind. Which of the following statements correctly explains these
results?
A) The gene for color vision is incompletely dominant to the gene for sex determination.
B) The gene for color vision is completely dominant to the gene for sex determination.
C) The gene for color vision is codominant with the gene for sex determination.
D) The gene for color vision is linked to the X chromosome.
E) The gene for color vision is linked to the Y chromosome.
Answer: D
Topic: 9.22
Skill: Application
37.
Female inheritance patterns cannot be analyzed by simply studying the X chromosome because
A) the X chromosome is too fragile for long term analysis.
B) the X chromosome is too susceptible to mutations.
C) the X chromosome is obtained from both father and mother.
D) the X chromosome is too difficult to isolate from the other chromosomes.
E) the X chromosome is physically too large to analyze accurately.
Answer: C
Topic: 9.23
Evolution Connection
Skill: Conceptual Understanding
Chapter 10 ANSWERS
1.
The monomers of DNA and RNA are a.
amino acids. b.
monosaccharides. c.
nucleotides. d.
fatty acids. e.
nucleic acids.
Answer: C
Topic: 10.2
Skill: Factual Recall
2.
DNA replication a.
occurs through the addition of nucleotides to the end of the DNA molecule. b.
results in the formation of four new DNA strands. c.
uses each strand of a DNA molecule as a template for the creation of a new strand. d.
begins when two DNA molecules join together to exchange segments.
Answer: D
Topic: 10.4
Skill: Factual Recall
3.
If one strand of DNA is CGGTAC, the corresponding strand would be
A) GCCTAG.
B) CGGTAC.
C) GCCAUC.
D) TAACGT.
E) GCCATG.
Answer: E
Topic: 10.4
Skill: Application
4.
Which of the following enzymes catalyzes the elongation of a new DNA strand?
A) helicase
B) primase
C) ligase
D) single stranded binding protein
E) DNA polymerase
Answer: E
Topic: 10.5
Skill: Factual Recall
5.
Which of the following options best depicts the flow of information when a gene directs the synthesis of a cellular component? a.
RNA → DNA → RNA → protein b.
DNA → RNA → protein c.
protein → RNA → DNA d.
DNA → amino acid → RNA → protein e.
DNA → tRNA → mRNA → protein
Answer: B
Topic: 10.6
Skill: Factual Recall
6.
Experiments have demonstrated that the "words" of the genetic code (the units that specify amino acids) are a.
single nucleotides. b.
two nucleotide sequences. c.
three nucleotide sequences. d.
nucleotide sequences of various lengths. e.
enzymes.
Answer: C
Topic: 10.7
Skill: Factual Recall
7.
Which of the following occurs when RNA polymerase attaches to the DNA? a.
elongation of the growing RNA molecule b.
termination of the RNA molecule c.
addition of nucleotides to the DNA template d.
initiation of a new RNA molecule e.
initiation of a new polypeptide chain
Answer: D
Topic: 10.9
Skill: Conceptual Understanding
8.
Where do transcription and translation occur in prokaryotic cells? a.
on the plasma membrane b.
in the nucleus c.
in the cytoplasm d.
in chromatophores e.
in the cell wall
Answer: C
Topic: 10.10
Skill: Factual Recall
9.
Which of the following takes place during translation? a.
the conversion of genetic information from the language of nucleic acids to the language of proteins b.
the conversion of genetic information from DNA nucleotides into RNA nucleotides c.
the addition of nucleotides to a DNA template d.
the conversion of genetic information from the language of proteins to the language of enzymes e.
DNA replication
Answer: A
Topic: 10.11
Skill: Conceptual Understanding
10.
A base substitution mutation in a gene does not always result in a different protein.
Which of the following factors could account for this? a.
the fact that the mutation affects only the sequence of the protein's amino acids, so the protein stays the same b.
the double ring structure of adenine and guanine
c.
a correcting mechanism that is part of the mRNA molecule d.
the fact that such mutations are usually accompanied by a complementary deletion e.
the fact that some amino acids are specified from more than one codon
Answer: E
Topic: 10.8
Skill: Conceptual Understanding
11.
DNA ligase binds
A) exons together.
B) polymerase to the promotor.
C) nucleotides together.
D) introns together.
E) an intron to an exon.
Answer: C
Topic: 12.1
Skill: Factual Recall