File
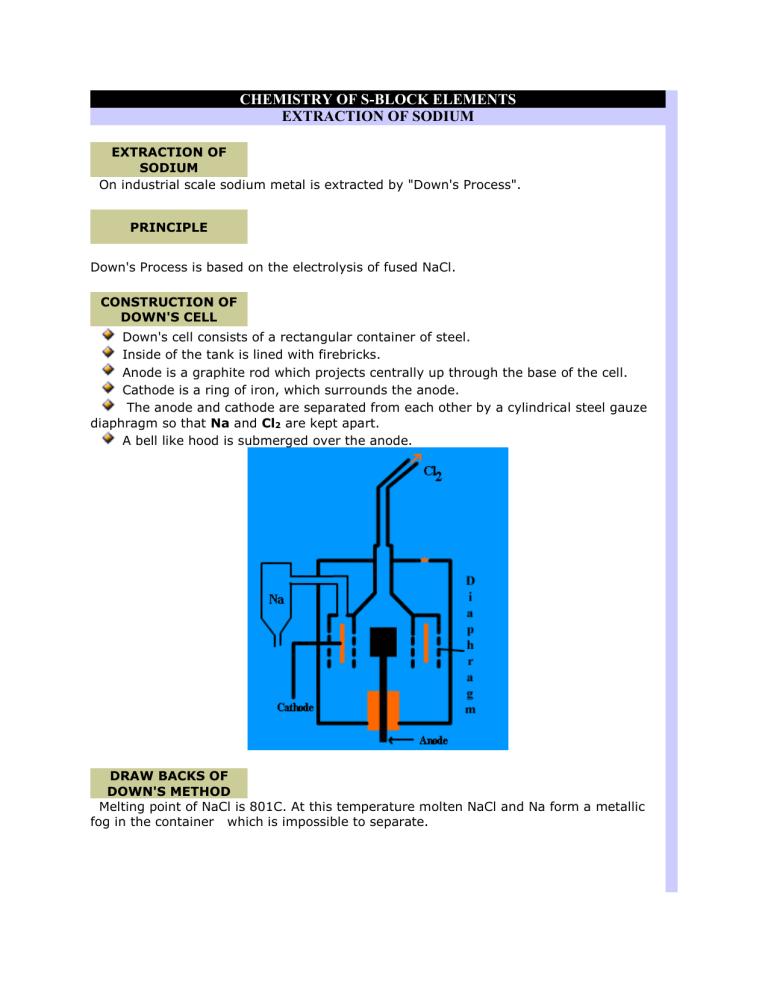
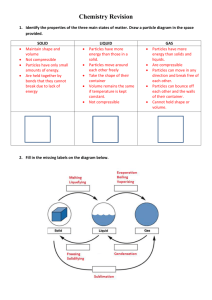
CHEMISTRY OF S-BLOCK ELEMENTS
EXTRACTION OF SODIUM
EXTRACTION OF
SODIUM
On industrial scale sodium metal is extracted by "Down's Process".
PRINCIPLE
Down's Process is based on the electrolysis of fused NaCl.
CONSTRUCTION OF
DOWN'S CELL
Down's cell consists of a rectangular container of steel.
Inside of the tank is lined with firebricks.
Anode is a graphite rod which projects centrally up through the base of the cell.
Cathode is a ring of iron, which surrounds the anode.
The anode and cathode are separated from each other by a cylindrical steel gauze diaphragm so that Na and Cl
2
are kept apart.
A bell like hood is submerged over the anode.
DRAW BACKS OF
DOWN'S METHOD
Melting point of NaCl is 801C. At this temperature molten NaCl and Na form a metallic fog in the container which is impossible to separate.
STEPS TO OVER COME
THIS DIFFICULTY
In order to overcome this difficulty instead of only NaCl, a mixture of NaCl and CaCl electrolyzed in down's cell. The melting point of this mixture is 600C. At 600C no metallic fog is formed.
2
is
COMPOSITION OF CHARGE:
NaCl = 42%
CaCl2 = 58%
THE PROCESS
When an electric current is passed through the molten mixture of NaCl and CaCl
2
, NaCl decomposes in to Na + and Cl ion. Na + ions migrate towards cathode while Cl rises to the top and is tapped off by a pipe. Chlorine is collected at the anode.
ions towards the anode. The molten sodium collects in the cathode compartment where it
THE CHEMISTRY OF
REACTION
Fused NaCl contains sodium and chloride ions.
2NaCl 2Na + + 2Cl -
ELECTROCHEMICAL
CHANGES
At cathode
Na + -ions migrate to cathode where they are reduced to Na.
2Na + + 2e -
2Na (Reduction)
At anode
Cl -ions migrate to anode and oxidised to form chlorine gas.
2Cl -
Cl
2
+ 2e (Oxidation)
Overall Reaction
2Na + + 2e 2Na
2Cl Cl
2
+ 2e -
__________________
2Na + + 2Cl 2Na + Cl
2
CHEMISTRY OF SODIUM CARBONATE ( Na
2
CO
3
)
Soda Ash
INDUSTRIAL PREPARATION OF
SODIUM CARBONATE
On industrial scale sodium carbonate is prepared by Ammonia Solvay Process.
Raw Materials
1. Sodium Chloride
2. Lime Stone (CaCO
3
)
3. Ammonia
Details of the process
At first stage a saturated solution of sodium chloride is prepared which is also known
"BRINE".
Composition of solution of NaCl (brine) is 28% m/m.
Steps of preparation
Ammoniation of Brine
In this stage saturated brine is allowed to flow down an ammoniating tower. This tower is fitted with mushroom shaped baffles. These baffles control the flow of brine and ensure the proper mixing and saturation of ammonia.
Carbonation of ammoniated brine
In the second step, ammoniated brine is allowed to trickle down a carbonating tower known as solvay tower. This tower is also fitted with baffle plates. Here brine is mixed with carbon dioxide gas, produced by heating lime stone in a separate chamber called
"kiln".
CaCO
3
CaO + CO
2 the baffle plates ensure the flow of solution and breaks up carbon dioxide into small bubbles to produce good conditions for reaction.
Flow Chart
Chemistry of Solvay tower
CO
2
reacts with ammonia to form ammonium carbonate.
2NH
3
+ CO
2
+ H
2
O
(NH4)
2
CO
3
Ammonium carbonate further reacts with CO
2
to form ammonium bicarbonate.
(NH4)
2
CO
3
+ CO
2
+ H
2
O
2NH
4
HCO
3
(aq.)
Ammonium bicarbonate then react with NaCl to form sodium bicarbonate.
NH
4
HCO
3
+ NaCl
NaHCO
3
+ NH
4
Cl
Due to exothermic nature of above reactions, solubility of NaHCO this effect , lower part of Solvay tower is cooled , ppt of NaHCO vacuum filtration and washed to remove ammonium salts.
3
increases. To counter
3
are separated by
Conversion of NaHCO
3
to Na
2
CO
3
Dry sodium bicarbonate is heated in rotary furnace called "CALCINER" to give anhydrous sodium carbonate or soda ash. Carbon dioxide is recirculated to carbonation tower.
2NaHCO
3
Na
2
CO
3
+ CO
2
+ H
2
O
Ammonia recovery process
When CaCO
3
is heated, CaO is obtained along with CO
2
. CaO is treated with water to form Ca(OH)
2
.
CaO + H
2
O
Ca(OH)
2
Quick lime is heated with NH
4
Cl to form NH
3
and calcium chloride (by product).
Ammonia is used again in this process.
2NH
4
Cl + Ca(OH)
2
CaCl2 + 2NH
3
+ 2H
2
O
CHEMISTRY OF SODIUM HYDROXIDE
Commercial name : caustic soda
On industrial scale sodium hydroxide can be prepared by the following methods.
1) Castner - Kellner Process.
2) Gibb's Method.
3) Nelson's Method.
Castner - Kellener Process
Principle
In castner-kellner method NaOH is prepared by the electrolysis of aqueous solution of
NaCl(Brine).
Concentration of brine
25 % mass/mass
i.e. 25 gm of NaCl is dissolved in 75 gm of water.
Castner-kellner cell
It is a rectangular tank of steel.
Inside of tank is lined with "ebonite".
Anode is made of titanium.
Flowing layer of mercury (Hg) at the bottom of tank serves as cathode.
Details of process
Ionization of NaCl
2NaCl 2Na + + 2Cl -
When electric current is passed through brine, +ve and -ve ions migrate towards their respective electrodes. Na + ions are discharged at mercury cathode. The sodium deposited at mercury forms SODIUM AMALGAM. Chlorine produced at the anode is removed from the top of the cell.
Reaction at cathode
2Na + +2 e 2Na
Na forms amalgam.
Na + Hg Na/Hg
Na + ions are discharged in preference to H
Na+/Na: E.P. = -2.71 volt
H+/H : E.P. = 0.00 volt
+ ions due to high over voltage.
Reaction at anode
2Cl Cl
2
+ 2e -
Formation of NaOH
Amalgam moves to another chamber called "denuder", where it is treated with water to produce NaOH which is in liquid state. Solid NaOH is obtained by the evaporation of this solution.
2Na/Hg + 2H
2
O 2NaOH + H
2
+ 2Hg
Advantages of castner's process
NaOH obtained is highly pure.
The process is very efficient.
Possible reaction between NaOH and Cl
2
is avoided as NaOH is obtained in a separated chamber.
Disadvantages
High electricity consumption.
Environmental pollution due to escape of Hg vapours.
What is plaster of Paris? How is it prepared?
Calcium Sulphate hemi hydrated is commonly known as "plaster of Paris". Chemical formula: CaSO
4
.1/2H
2
O
Plaster of Paris is prepared by gypsum.
Preparation
When gypsum is heated up to 100 0 C ,it loses some molecules of water of crystallization and forms an amorphous white solid known as plaster of Paris.
CaSO4.2H2O CaSO
4
.1/2H
2
O+ 3/2H
2
O
Properties
Plaster of Paris when mixed with water sets within few minutes. The setting of plaster of
Paris takes place with expansion and its surface becomes very smooth .Due to this property plaster of Paris is used in moulds.
What is Epsom salt? How is it prepared
Magnesium Sulphate hepta hydrated is commonly known as "Epsom salt".
Chemical formula: MgSO
4
.7H
2
O
Properties & uses
It is a semi transparent white crystalline solid.
It is soluble in water.
It is used as purgative in medicines.
It is used in Paper, soap and ceramics industry.
Methods of preparation
Epsom can be prepared by treating suitable substance with Sulphuric acid
From Mg:
:
Mg + H
2
SO
4
MgSO
4
+ H
is obtained.
2
From MgCO
3
MgCO
3
when treated with H
2
SO
4
. MgSO
4
MgCO
3
+ H
2
SO
4
MgSO
4
+ H
2
O + CO
2
From Mg(OH)
2:
Mg(OH)
2
+ H
2
SO
4
MgSO
4
+ 2H
2
O
From MgO :
MgO + H
2
SO
4
MgSO
4
+ H
2
O
Effect of Heat
When Epsom is heated, it loses water of crystallization to form anhydrous magnesium sulphate.
MgSO
4
.7H
2
O MgSO
4
+ 7H
2
O
BLEACHING POWDER
Chemical name : Calcium chloro hypo chloride.
Commercial name : Bleaching powder.
Chemical formula : Ca(OCl)Cl.H
2
O or CaOCl
2
.H
2
O.
It is a dirty white amorphous powder with pungent smell of chlorine gas.
Industrial Preparation of Bleaching Powder
On industrial scale it is prepared by "Hasen-Clever Method".
Raw Material
1. Slaked lime Ca(OH)
2
2. Chlorine gas
Hasen-Clever Plant
The plant consists of four cylinder of cast-iron. Each cylinder is about 2 to 3m long .Each cylinder is provided with a stirrer to ensure the mixing of substances. There is an inlet in the upper most cylinder for Ca(OH)
2
. The bottom cylinder has an inlet for Cl
2
and outlet for bleaching powder. Each cylinder is connected to the other by means of pipes.
Procedure
Slaked lime is introduced in the first cylinder with the help of compressed air .Cl
2
gas is introduced from the lower most cylinder .In this way these two substances meet, when proper saturation is reached, the product is separated from the last cylinder as bleaching powder.
Ca(OH)
2
+ Cl
2
Ca(OCl)Cl.H
2
O
Properties
It is a strong bleaching agent. Due to liberation of chlorine gas in aqueous solution it decolorize different fabrics. It is also an antiseptic.
Reaction with water:
Ca(OC)Cl + H
2
O
Ca(OH)
2
+ Cl
2
With HCl:
Ca(OCl)Cl + 2HCl
CaCl
With CO
2
:
2Ca(OCl)Cl + CO
2
+ H
2
+ Cl
2
+ H
2
O
2
O
CaCO
3
+ CaCl
2
+2HOCl
Uses
As oxidizing and bleaching agent it is used in textile and other industries. It is also used in the purification of drinking water.
How would convert magnesite in to Mg(OH)
2
?
Chemically magnesite is magnesium carbonate (MgCO
3
).
First magnesite is heated, on heating it decomposes to MgO.
MgCO
3
MgO + CO
2
MgO is heated with carbon and chlorine to produce MgCl
2
.
MgO + Cl
2
+ C
MgCl
2
+ CO
Finally MgCl
2
is treated with Ca(OH)
2
to produce Mg(OH)
2
.
MgCl
2
+ Ca(OH)
2
Mg(OH)
2
+ CaCl
2