Genetics Unit Study Guide
advertisement

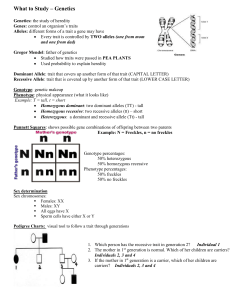
Genetics Unit Study Guide 1. Write the vocabulary word for each definition. a. A “hidden” trait. You need two to experience this inherited trait. ___________________ b. A condition in which the alleles of a gene pair are fully expressed thereby resulting in offspring that is neither dominant nor recessive. ________________________________ c. A form of intermediate inheritance in which one allele for a specific trait is not completely dominant over the other allele. ____________________________________ d. A form of reproduction that does not involve fertilization, and the offspring is a clone of the parent organism._____________________________________________________ e. A form of reproduction that involves fertilization. The offspring is a mix of the parent organisms because of shared DNA. __________________________________________ f. One member of a pair of genes which control the same trait.______________________ g. Organisms which are genetically identical. ____________________________________ h. These may arise from faulty deletions, insertions, or exchanges in the genetic material, as caused by exposure to radiation, chemicals, viruses, etc. Such a change may result in the creation of a new character or trait._______________________________________ i. Two different alleles for the same characteristic.________________________________ j. Two of the same allele for a characteristic._____________________________________ k. You only need one allele of this trait to have the inherited trait.____________________ Allele Asexual Reproduction Carrier Cell Division Characteristic Chromosome Clone Co-Dominance DNA Dominant Gene Heterozygous Word Bank Homozygous Incomplete Dominance Inherited Mutation Pedigree Probability Punnett Square Random Recessive Sexual Reproduction Trait 2. Using the Pedigree above, answer the following questions: a. Is the condition (represented with the darker symbols) most likely a dominant or a recessive trait? Explain. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ b. Is Marcus most likely to be homozygous dominant, homozygous recessive, or heterozygous? Explain. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3. The Moore police are looking at some suspects for various robberies in town. Each crime had blood left at the scene. They have collected the blood of each suspects’ parents to compare against the crime scene blood. Which suspect could have committed which crime? (SHOW YOUR WORK!!!) Crime Scene Scene 1 Scene 2 Scene 3 Scene 4 Suspect A’s Parents Jean Frank Suspect B’s Parents Lucy Bob Blood Found A AB A O Rh Factor + + - Blood Type O A Blood Type B A Rh Factor + Rh Factor + - Create Punnett squares based on the scenario given and state the results. 4. R= normal retina r= abnormal retina A male Rr and a female RR want to know what allelic combinations their child could have. 5. M= normal joint gene m= Marfan syndrome gene A male MM and a female mm want to know what allelic combinations their child could have. 6. H: Tall gene (dominant) h: short gene (recessive) A male Hh and a female Hh want to know what allelic combinations their child have. 7. P= purple flower p= white flower A male PP and a female pp are combined. What allelic combinations could their offspring have? 8. P= purple flower p= white flower A male Pp and a female pp are combined. What allelic combinations could their offspring have? 9. P= purple flower p= white flower A male Pp and a female Pp are combined. What allelic combinations could their offspring have? 10. P= purple flower p= white flower A male PP and a female pp are combined. What allelic combinations could their offspring have? 11. A male with AO blood alleles and a female with AB blood alleles are combined. What allelic combinations could their offspring have? 12. A male with AA blood alleles and a female with BO blood alleles are combined. What allelic combinations could their offspring have? 13. A male with AB blood alleles and a female with OO blood alleles are combined. What allelic combinations could their offspring have? 14. A male with AA blood and a female with AB blood are combined. What allelic combinations could their offspring have? 15. Name three things about meiosis that are different from mitosis. 16. Each of these is an onion cell going through mitosis. Label which phase each cell is in. (PMAT and don’t forget interphase) 1 10 2 11 3 12 4 13 5 14 6 15 7 16 8 17 9 18