The Circulatory System
advertisement
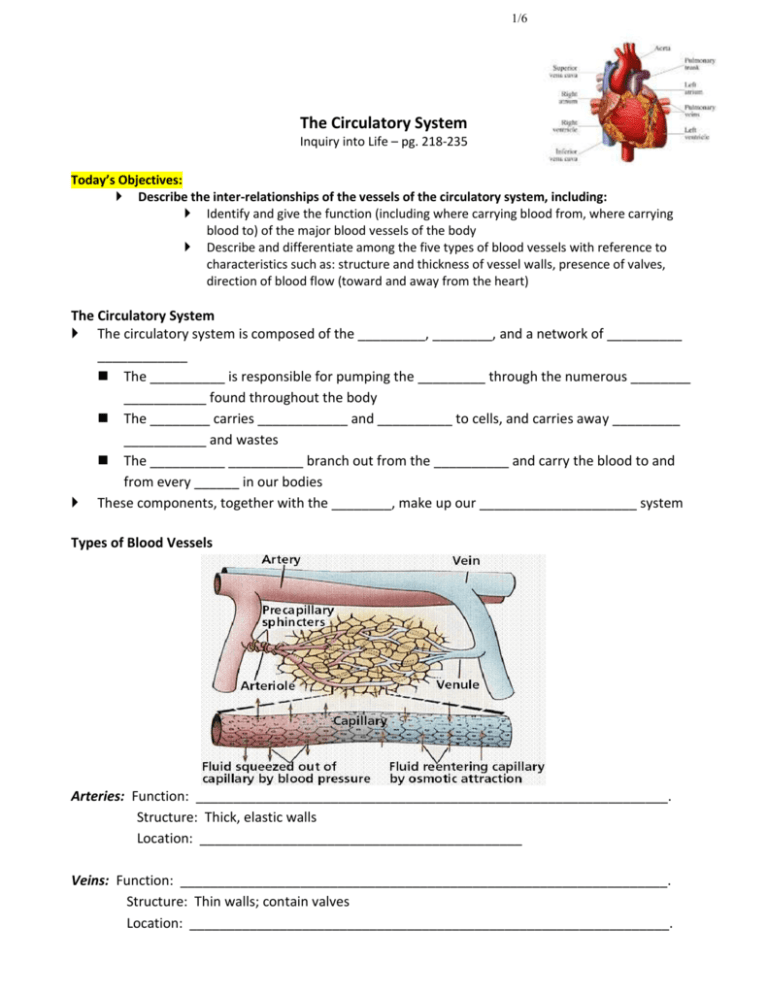
1/6 The Circulatory System Inquiry into Life – pg. 218-235 Today’s Objectives: Describe the inter-relationships of the vessels of the circulatory system, including: Identify and give the function (including where carrying blood from, where carrying blood to) of the major blood vessels of the body Describe and differentiate among the five types of blood vessels with reference to characteristics such as: structure and thickness of vessel walls, presence of valves, direction of blood flow (toward and away from the heart) The Circulatory System The circulatory system is composed of the _________, ________, and a network of __________ ____________ The __________ is responsible for pumping the _________ through the numerous ________ ___________ found throughout the body The ________ carries ____________ and __________ to cells, and carries away _________ ___________ and wastes The __________ __________ branch out from the __________ and carry the blood to and from every ______ in our bodies These components, together with the ________, make up our _____________________ system Types of Blood Vessels Arteries: Function: _______________________________________________________________. Structure: Thick, elastic walls Location: ___________________________________________ Veins: Function: _________________________________________________________________. Structure: Thin walls; contain valves Location: ________________________________________________________________. 2/6 Arterioles and Venules: -All the features of arteries and veins apply to ________________________, but on a ___________________ scale. -Arterioles leading into a particular organ or region, are often equipped with sphincter muscles. When triggered, they can dilate or constrict to regulate _________________, increasing or decreasing blood flow to that particular ______________________________. Capillaries: Function: _____________________________________________________________. Structure: Very thin walls ( 1cell thick) Location: ____________________; within a few cells of each other. Capillaries have __________________________ that can _______________ and ________________ the vessel. If all capillary beds were open at one time, it would ______________________ the blood pressure. If all the capillary beds were _________________, it would increase blood pressure. Major Blood Vessels of the Body The Pulmonary Circuit circulates blood__________________, returning oxygenated blood to the heart. The Systemic Circuit services ________________________________________. 1. Aorta: This is the major blood vessel carrying _________________blood _______of the heart. It leaves the _________________________, loops over top of the heart creating the structure known as the __________________________ and descends along the inside of the backbone. Function: Branches from this blood vessel _________________________________________. 2. Coronary Arteries and Veins: The very first branches off the Aorta are the Coronary arteries. These relatively small blood vessels can be seen on the surface of the heart. Function: Feeds the _______________________. (The heart does not receive its nutrients from the blood that travels through it. The muscle is too dense and thick and the blood is traveling through it to hard and fast.) -Cardiac Vein takes the “_______________________” back to the ____________. 3/6 3. Carotid Arteries: These branches of the aortic arch take the blood to the __________ including the __________. Function: They are highly specialized in that they contain a number of different types of ______________________________: Chemoreceptors that ___________________________, and Pressure Receptors that _________________________________. Maintains homeostasis. 4. Jugular Veins: The match for the Carotid Artery. They do not contain valves. Blood flow is through gravity. Function: They conduct blood out of the __________________________________________ Subclavian Arteries and Veins: Also branch from the _________________. Travels under the _______________________. Function: Branch to feed the ________(brachial artery). Veins collect blood from the arms. 5. 6. Mesenteric Arteries: These arteries branch off from the aorta as it travels _______________________. They go to the intestines where they branch into capillaries that can be identified as villi. Function: Feeding the organs of the ______________________________ and picks up newly digested nutrients in the body. 7. Hepatic Portal Vein: Match to the ______________. Hepatic means liver; portal indicates that there is a capillary bed on both end of it. Function: Brings ___________________________________________________ 8. Hepatic Vein: Once the liver is done with the blood, the blood is returned to the __________________________by the ___________________________. Function: Carries blood from the liver to the _______________________________________. 9. Renal Arteries and Veins: The _______________________________ branch off the dorsal aorta as it passes through the ______________________________________________. Function: The ______________________to the kidneys, while the ________bring blood back to the _____________ Vena Cava. 10. Iliac Arteries and Veins: When the _______________________ gets to the pelvic area. It branches into two Iliac Arteries, one goes down each leg. Off the ____________________ is another branch that feeds the upper leg. This is called the ________________________________. Function: To supply the legs with ________________________ and return ________________ _______________________to the ___________________________________________. 11. Anterior (Superior) and Posterior (Inferior) Vena Cava: Large Vein that collects all the _________________________________ from smaller veins to the heart (right atrium). _____________________________________________. 4/6 Function: The _______________________________ collects blood from the ___________________________________________, while the Posterior Vena Cava collects blood from the lower body. 12. Pulmonary Veins and Arteries: The Pulmonary Circuit is comprised of the ________________________________ and arteries that deal strictly with the ______________________________________. The Systemic Circuit services oxygenated blood to the body tissues. Only Artery in the body that _______________ ________________________. Only Vein in the body that carries __________________ blood. Function: The artery brings _____________________________ to the lungs to get oxygen for the body, while the vein returns _____________________________ to the Left Atrium. Pulmonary and Systemic Circulation Pulmonary Circuit: --Path that goes ________________________________. --From right ventricle through the pulmonary trunk --> pulmonary arteries--> Lung capillaries -->Pulmonary Veins --> Left atrium. --Carries _______________________________ filled blood to lungs for cleaning. --Returns _______________________________________________________. Systemic Circuit: -- Path from ________________________________________________________ of heart. -- Carries ________________________________ blood to body tissues. -- Returns ______________________________________________________________. CAPILLARY FLUID EXCHANGE Gas Exchange in the Lungs ______________ is oxygenated as it passes through ____________________. Oxygen __________ into the blood through the thin walled tissues of the lung capillaries (concentration of oxygen is higher in the air than in the blood) Once in the blood, __________ bonds with __________________(the iron containing protein that is part of the RBC). A single hemoglobin molecule has _________________________ for oxygen and is called ___________________________ when transporting oxygen. 5/6 Gas Exchange in the Body Tissues The blood reaches ____________________________________________. Blood pressure has _____________________. Nutrients (products of digestion) and oxygen _______________________. The larger particles in blood stay where they are because they are too big to get out. These large molecules make the blood _________________________to the tissues. As a result, the water from the tissues is drawn back into the ____________________________ of the capillary bed. When the fluid returns it carries __________________________________ with it. Blood Pressure Blood pressure on arteriole side of capillary is _______________________________________ and will try and push substances out of blood. Osmotic pressure pushes substances into blood Since blood pressure is greater than osmotic pressure, Oxygen, glucose, and water are__________________________ and put in the tissues. Blood pressure on the venule side of capillary is lower than the osmotic pressure and therefore wastes such as _________________________________________________ forced into the blood. FETAL CIRCULATION SYSTEM Fetal systems have FOUR features not present in Adult Systems: 1. OVAL OPENINGS -- An opening between the _______________. -- It is covered by a _____________________________ that acts like a valve. -- Blood flows directly from the right atrium to the _____________________________. -- ______________________________________, which do not work yet. 2. ARTERIAL DUCT -- A ___________________________between the Pulmonary Artery and the Aorta. -- Blood flows from the _____________________________, again bypassing the lungs. 3. UMBILICAL ARTERY AND VEIN -- Umbilical ________________________ (Carbon Dioxide and Urea ) to the Placenta. -- Umbilical Vein takes nutrients (Oxygen and Glucose and Amino Acids) to the _____ from the _______________________. 6/6 4. VENOUS DUCT -- A connection between the Umbilical Vein and the Vena Cava. -- Blood from the __________________________________ through this duct and from there, to the ___________________________ of the heart. PATH OF A BLOOD CELL THROUGH THE BODY Start in the Left Ventricle and go through the Circulation System











