Circulatory System Outline: Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Flow
advertisement

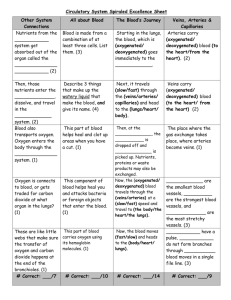
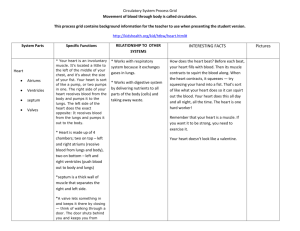
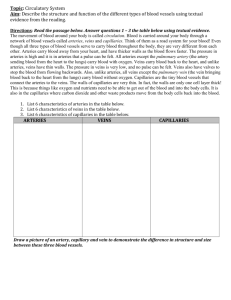
Circulatory System Outline Parts of the System heart, blood, blood vessels Types of blood vessels artery, vein, capillary Function of the heart valve To act like a pump to circulate blood throughout the body Why? o To deliver materials to all the cells of the body and to pick up waste that needs to be removed Function and Structure of Blood Vessels Arteries o Function: To transport blood with oxygen (oxygenated) away from the heart to the body. They usually transport blood with oxygen (oxygenated) away from the heart towards the body. (exception: the artery that takes blood from the heart to the lungs with little/no oxygen) o Structure: large blood vessel; thick, elastic walls, expand and contract to withstand blood pressure from the heart Veins o Function: To transport (return) blood to the heart from the body. They usually transport blood without oxygen (unoxygenated) towards the heart from the body. (exception: the vein that takes blood from the lungs to the heart with oxygen) o Structure: thinner walls than arteries; need body muscles to contract veins and move blood back towards the heart; valves help move the blood in the correct direction Capillaries o Function: To exchange materials with the cells of the body (oxygen, nutrients, water, waste products) o Structure: tinniest of blood vessels; walls are only 1-cell thick; connect arteries to veins o How do materials get exchanged? Animal cells have a semi-permeable cell membrane that contain pores (tiny holes) that act like doors to allow materials to enter and exit. The capillary walls are made of cells. So, the cells of the capillary walls allow materials to pass through them and into the body’s cells and vice versa. Blood Flow in the Human Body & Heart Think of it as two loops! One loop contains O2, and one does not General Blood Flow is: Heart (R) Lungs Heart (L) Body Repeat Blood without oxygen enters the right side of the heart and gets sent to the lungs to pick up O2 and drop off CO2. Blood with oxygen enters the left side of the heart and gets sent out of the heart to the body to drop off oxygen, it also picks up and/or drops off other materials along the way (ex. nutrients/water from the intestines, waste from body cells/organs, etc.) Additional Facts Human body contains ~5.5 liters Aorta is the largest artery Red blood cells carry oxygen White blood cells fight infection Blood is mostly water Materials the blood transports are carried in the liquid part of blood (except for oxygen) Images of the above information: Blood flow through the heart Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide exchange in the lung