Cell Membrane - Solon City Schools
advertisement

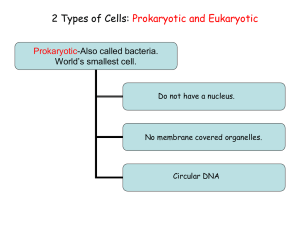
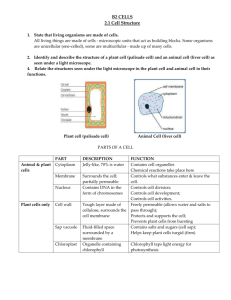
Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Cell’s outer covering Gives the cell shape and holds it together Controls materials that move in and out of the cell such as: oxygen, nutrients, wastes, carbon dioxide Cyto = cell Made mostly of water Translucent, grayish, jellylike Flows Gel-like substance that surrounds the nucleus It is the place most activities take place Contains the many tiny parts of a cell, proteins, sugars, fats, starches, salt, minerals, and vitamins Cell Wall Organelles Chloroplasts Stiff covering outside the cell membrane of a plant cell Protects and supports the plant Thicker and tougher than cell membrane Allows materials pass through Small part of a cell with a special job Means “little organ” Such as; mitochondria, vacuoles, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, lysosomes Green structure in a plant cell where food is produced Contains chlorophyll Chlorophyll Nucleus Green chemical in plant cells that allows plants to use the sun’s energy to make food Largest, most visible part of a cell Has its own membrane Is the control center of the cell’s activities Round or oval-shaped Rod-shaped structure in the cytoplasm that supplies the cell with energy Give off wastes such as water and carbon dioxide Mitochondria Vacuoles Endoplasmic Reticulum Sac-like space in a cell’s cytoplasm for storing materials such as food or waste Plant vacuoles are larger than those in animals Network of tube-like passageways Helps make and transport proteins These proteins are needed for communication, growth, repair, and replacement of cells Ribosome Golgi Bodies Along inner branches of the Endoplasmic Reticulum Makes proteins and drop them into the passageways. Some float around free in the cytoplasm Stack of flat, pancake-shaped discs Modify, sort, package, and store carbohydrates and proteins until they are needed They ship out the materials to other locations, both in and out of cell Make lysosomes Lysosomes Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic Cells Round organelles that digest cell nutrients Garbage collectors Break down products that might harm the cell Contain chemicals that help the white blood cells break down harmful germs Cells containing a nucleus Contained in plants, animals, fungi, and protists Does not have a nucleus Bacteria cells are prokaryotic What are the differences between a plant cell and animal cell? Both have: Cell Membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm with organelles Plant Cell: Has chloroplasts which contain chlorophyll and allows the plant to make its own food. Has a cell wall made of cellulose. This wall is thicker and tougher than the cell membrane. It protects and supports the plant. It allows water, carbon dioxide and oxygen to pass through it. Animal Cell: Does not contain a cell wall or chloroplasts