The structure and function of cells
advertisement

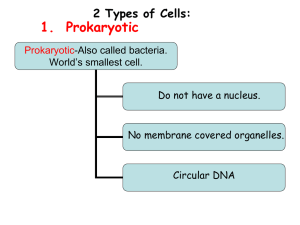
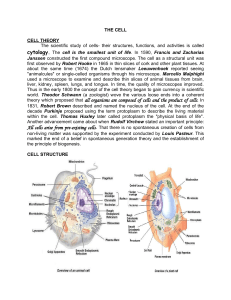
2 Types of Cells: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Prokaryotic-Also called bacteria. World’s smallest cell. Do not have a nucleus. No membrane covered organelles. Circular DNA Eukaryotic Cells: What we have! Complicated internal structure Contain a nucleus Membrane covered organelles Linear DNA Organelles – “Little Organs” Cell structures that carry out specific jobs in cells. Parts of a Cell-Organelles • • • • • • • • • • • • Lysosomes Golgi Apparatus Chloroplasts Chlorophyll Cell Wall Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosomes Mitochondria Vacuoles Cytoskeleton The structure and function of cells • Characteristics of cells: 1. Cell wallSupport and protection, strong and stiff. Made of cellulose. Found only in plant cells. 2. Cell membraneDoorway of cell. In plants, just inside cell wall. In animals, it is the outer covering of the cell. Made of phospholipids. 4 jobs of the cell membrane: Support and protection for the cell Openings called pores in the membrane allow waste material to pass out of the cell. Controls movement of things in and out of cell Forms a barrier between the inside and outside of the cell. Nucleus: Control Center of the Cell • Nucleus: Control center or “brain” of the cell that regulates or controls all activities of the cell. Contains cell’s genetic material. Cytoplasm, Cytoskeleton and the Endoplasmic Reticulum Cytoplasm: Clear, thick, jellylike substance b/tween nucleus and cell membrane. Constantly moves. Cell organelles located here. Cytoskeleton : Web of proteins in cytoplasm. Acts as skeleton. Keeps cell membrane from collapsing. Endoplasmic Reticulum: Clear, tubular passageways in the cell through which substances are transported. Proteins and fats made here and carried around the cell. Ribosomes Attached to the surface of the endoplasmic reticulum. Protein making sites of the cell. The Cell’s Energy Factory-Mitochondria Break down sugar and release energy. This energy powers the cell’s organelles. This process is called cellular respiration. Energy released by the mitochondria is stored in the ATP. (Adenosine Triphosphate) The Cleanup Crew for the Cell Lysosomes • Involved in digestive activities of the cell. • Contain enzymes that break down food. • Digested food then passed on to mitochondria to provide energy to the cell. •When old cell parts outlive their usefulness, lysosomes “eat” them. • This “energy” from an old cell part is recycled back into the cell. • 2 examples of lysosomes being used: Frog’s tail, our fingers The Cell’s Packaging Center Golgi Apparatus or Complex • Packages and transports these materials out of the cell: Proteins The Cell’s Storage Centers- Vacuoles Vacuoles Food, water, and waste are stored in the vacuoles. In plants, when the vacuoles are full of water, they swell and make the plant firm. Plants Only! Chloroplasts • Energy producers for the cell. • Contain chlorophyll, a green substance involved in photosynthesis that captures the sun’s energy. • Captures energy of sunlight to produce food for the plant cell. • Glucose is the simple sugar plants make for food during photosynthesis. A plant’s cell walls are made of a sugar called cellulose. + + + + Classwork! • Complete a DLCD (Draw, Label , Color, and Define) of an animal and plant cell from pages 56-57 in your science book. • First draw or sketch out plant and animal cell with pencil first. • Next, label ALL parts of both cells and give a BRIEF description of each on the back, bottom, or sides of your DLCD. • Last, please color both cells. • Not homework. Put in folders at end of class.