Cell Growth & Division Worksheet: Mitosis, Chromosomes
advertisement

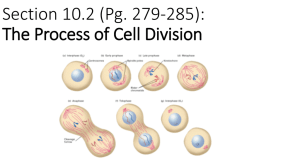
Name __________________________________________ Period __________ Date _______________ Chapter 10 -- Cell Growth & Division Cell Growth • A cell is limited by its cell ____________________ • The ____________________the cell the ____________________it is to move through tissue and get nutrients • In order to stay alive and not grow continuously, the cell will ___________________ Reasons why to divide • DNA • Genetic information ____________________ • Found in the ____________________of the cell • DNA would not be able to keep up with ____________________of the cell • Transport • Rate ____________________ as the cell size increases • Takes too long for ____________________ and ____________________ to move in and out of cell Surface Area to Volume • Surface Area • Area on ____________________ of cell where ____________________ can occur • As a cell ____________________, the surface area ____________________ 1 Cell Division and Reproduction • Asexual Reproduction • Produces ____________________ offspring from a ____________________ parent • Used by many single-celled organisms Ex: ____________________ • Occurs very ____________________ • Sexual Reproduction • Produces genetically ____________________ offspring from two parents • Fusion of _____________ parent cells Chromosomes • Made up of our _______________ • Holds genetic ____________________ • Tight coils or rod like structures • Organisms have a ____________________ amount of chromosomes • Humans have ___________ chromosomes of DNA in every somatic cell Chromosome Structure • Histones are ____________________ that DNA wraps around to make the chromosome shape • Chromosomes are made of two sister ____________________ • ____________________ to each other • ____________________ are in the center of a chromosome • Chromosomes are tightly coiled strings of DNA called ____________________ • Chromatin is the ___________________________ form of DNA 2 Chromosome Numbers • There is a specific ____________________ of chromosomes in each organism • Humans have ____________________ and sex chromosomes • We have ______ sex chromosomes • Either X or Y • We also have _______ autosomes • Which do not code for gender Karyotype • A karyotype is a ____________________ of one set of chromosomes • Shows you sex of organism • Shows your any chromosomal disorders 3 Chromosome Numbers • A ____________________ cell contains 2 sets of each chromosome • Prefix di = 2 • A ____________________ cell contains only 1 set of each chromosome • Half of the total number • Usually sex cells Cell Division in Prokaryotes • Prokaryotes • ________ nucleus • ________ organelles • Ex: Bacteria • Reproduction is ________________ fast • ______________ DNA • Split into _____________ cells • Cell division is called ____________________ ____________________ Eukaryotic Cell Reproduction • Eukaryotes • Have a ____________________ • Have ____________________ • Ex: Humans, plants • Complex reproduction • Everything needs to be ____________________! • Much ____________________ process – about 18 hours! 4 Cell Reproduction • A cell splits to make 2 ____________________ copies • If asexual reproduction • Only 1 cell involved • This occurs in 3 main stages • Interphase – ____________________ • Mitosis – ____________________ of the nucleus • Cytokinesis – Splitting of the ____________________ Interphase • Cell ____________________ • _____________ of cell’s life is spent in interphase • 3 Part of Interphase: • ____________, ______________, and ____________ • Draw a stage of interphase and label the nucleus, centrioles, and cell membrane 5 G1 Phase • The cell is ____________________ • The organelles are ____________________ S Phase • Takes place when cells are too big • S = ____________________ of DNA • DNA is ____________________ so there is a set for each new cell G2 Phase • Cell ____________________ again • Replication of ____________________ • Last stage of interphase • Cell prepares for cell division How is DNA copied? • Each cell has an protein called ____________________ • Enzyme the ____________________ the DNA making 2 identical strands Mitosis • The part of a cell’s life cycle when the cell’s ____________________ divides into 2 ____________________ ____________________ • 4 steps: • ____________________ • ____________________ • ____________________ • ____________________ 6 Prophase • All organelles ____________________ • ____________________ separate and move to opposite pole • ____________________ becomes chromosomes • Centrioles shoot off ____________________ ____________________ • Draw a cell in prophase and label appropriate parts. Metaphase • Chromosomes line up at the ____________________ • Draw a cell in metaphase and label appropriate parts. 7 Anaphase • Centromere ________________________________________ • Sister ____________________ attach to the short spindle fibers • Spindle fibers shorten and bring the sister chromatids to opposite poles • Draw a cell in anaphase and label appropriate parts. Telophase • Chromatids become ____________________ (one at each pole) • Spindle ____________________ • Organelles ____________________ • Draw a cell in telophase and label appropriate parts. 8 Cytokinesis • Once mitosis has ____________________! • Last stage of ____________________ ____________________ • Process is when the ____________________ splits apart • There are now 2 identical cells Cytokinesis in Plant Cells • A cell ____________________ forms between the two nuclei • The cytoplasm divides • A cell ____________________ forms two daughter cells • Draw a plant cell in cytokinesis and label appropriate parts. Cytokinesis in Animal Cells • Cell membrane ____________________ in at equator • Cleavage ____________________ • Draw an animal cell in cytokinesis and label appropriate parts. 9 Mitosis: Division of the Nucleus 4 Phases Cells in Various Stages of the Cell Cycle Label a cell in each stage of the cell cycle. 10 Control of Cell Division • Checkpoints (Regulatory Proteins) • DNA repair enzymes will fix any ____________________, if checkpoint is passed ____________________ will occur • Mitosis checkpoint – if all is correct, the 2 daughter cells will enter G1 phase and ____________________ ____________________ again • If a cell does not meet requirements for checkpoints, the cell will be programmed to ____________________ • ____________________ is controlled cell death When Control is Lost • Enzyme proteins are not functioning ____________________ causing cell to reproduce out of control • Could cause ____________________ • Cancer cells do not ____________________ to body’s ____________________ that control mechanisms Compare/Contrast Draw the difference between normal and cancer cells and label the cells. Normal Cells Cancer Cells 11