15.4 Disorders of the Respiratory System
advertisement
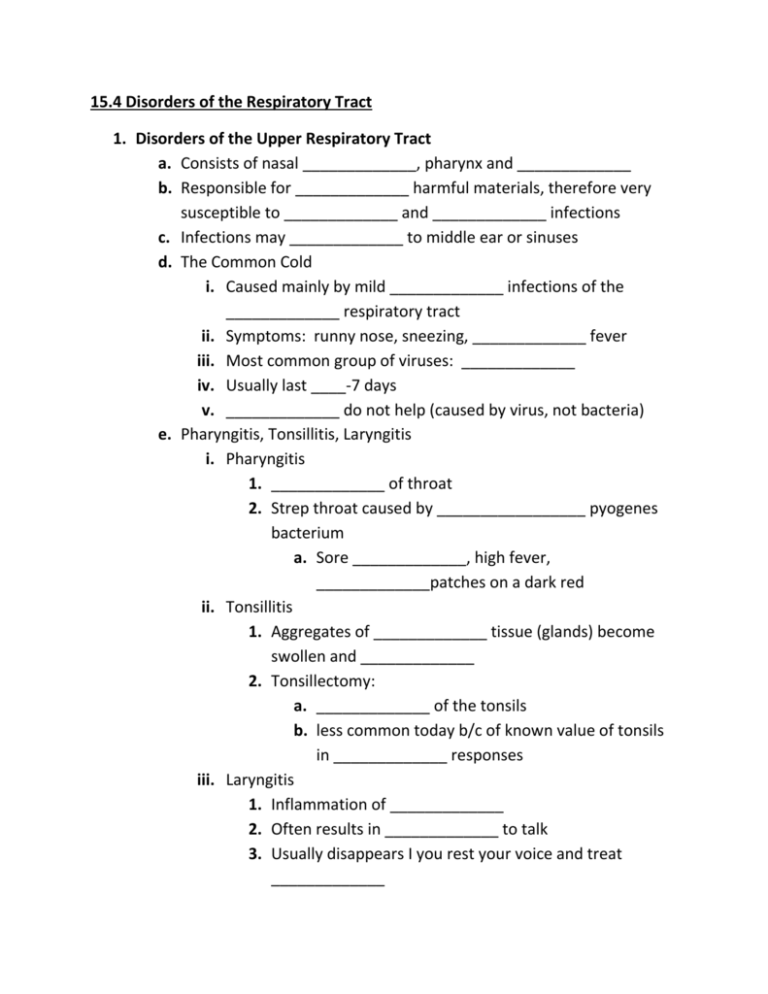
15.4 Disorders of the Respiratory Tract 1. Disorders of the Upper Respiratory Tract a. Consists of nasal _____________, pharynx and _____________ b. Responsible for _____________ harmful materials, therefore very susceptible to _____________ and _____________ infections c. Infections may _____________ to middle ear or sinuses d. The Common Cold i. Caused mainly by mild _____________ infections of the _____________ respiratory tract ii. Symptoms: runny nose, sneezing, _____________ fever iii. Most common group of viruses: _____________ iv. Usually last ____-7 days v. _____________ do not help (caused by virus, not bacteria) e. Pharyngitis, Tonsillitis, Laryngitis i. Pharyngitis 1. _____________ of throat 2. Strep throat caused by _________________ pyogenes bacterium a. Sore _____________, high fever, _____________patches on a dark red ii. Tonsillitis 1. Aggregates of _____________ tissue (glands) become swollen and _____________ 2. Tonsillectomy: a. _____________ of the tonsils b. less common today b/c of known value of tonsils in _____________ responses iii. Laryngitis 1. Inflammation of _____________ 2. Often results in _____________ to talk 3. Usually disappears I you rest your voice and treat _____________ f. Sinusitis i. Inflammation of the _____________ (facial) sinuses ii. Occurs if openings to sinuses are _____________ iii. Symptoms: runny nose, _____________, facial pain iv. Treatment: depends of cause, but rinsing sinuses with warm _____________ solution helps remove irritants and mucus g. Otitis Media i. Inflammation of the _____________ _____________ ii. Nasal infections often spread and become ear infections in children iii. Symptoms: _____________ (dizziness), hearing loss, fever iv. Treatment: tubes may be placed in ears, antibiotics Complete p.292 #1-2 15.4 Disorders of the Respiratory Tract 1. Disorders of the Upper Respiratory Tract a. Consists of nasal cavities, pharynx and larynx b. Responsible for filtering harmful materials, therefore very susceptible to viral and bacterial infections c. Infections may spread to middle ear or sinuses d. The Common Cold i. Caused mainly by mild viral infections of the upper respiratory tract ii. Symptoms: runny nose, sneezing, mild fever iii. Most common group of viruses: rhinoviruses iv. Usually last 3-7 days v. Antibiotics do not help (caused by virus, not bacteria) e. Pharyngitis, Tonsillitis, Laryngitis i. Pharyngitis 1. Inflammation of throat 2. Strep throat caused by streptococcus pyogenes bacterium a. Sore throat, high fever, white patches on a dark red ii. Tonsillitis 1. Aggregates of lymphoid tissue (glands) become swollen and inflamed 2. Tonsillectomy: a. removal of the tonsils b. less common today b/c of known value of tonsils in immune responses iii. Laryngitis 1. Inflammation of larynx 2. Often results in inability to talk 3. Usually disappears I you rest your voice and treat infection f. Sinusitis i. Inflammation of the cranial (facial) sinuses ii. Occurs if openings to sinuses are blocked iii. Symptoms: runny nose, headache, facial pain iv. Treatment: depends of cause, but rinsing sinuses with warm saline helps remove irritants and mucus g. Otitis Media i. Inflammation of the middle ear ii. Nasal infections often spread and become ear infections in children iii. Symptoms: vertigo (dizziness), hearing loss, fever iv. Treatment: tubes may be placed in ears, antibiotics Complete p.292 #1-2 15.4 Disorders of the Respiratory Tract (Continued) 2. Disorders of the Lower Respiratory Tract a. Disorders of the Trachea and Bronchi i. Choking 1. Caused by a blocked trachea 2. Heimlich maneuver may be used to clear blocked air way 3. Tracheostomy: insertion of a breathing tube into an incision mad in the trachea ii. Acute bronchitis 1. Acute = sudden onset 2. Inflammation of the primary and secondary bronch 3. Preceded by a viral infection that leads to a secondary bacterial infection 4. Symptoms: a deep non-productive cough that produces mucus and sometimes pus 5. Treatment: antibiotics iii. Chronic bronchitis 1. Chronic = long-term 2. Airways inflamed and filled with mucus 3. Cough that brings up mucus 4. Bronchi are damaged 5. Often caused by smoking (smoker’s cough) iv. Asthma 1. Disease of bronchi and bronchioles 2. Symptoms: wheezing, breathlessness, cough, expectoration of mucus 3. Airways are extremely sensitive to irritants such as animal dander, dust and cigarettes, and become inflamed 4. Smooth muscle undergoes spasms 5. No cure for asthma, just controlled with drugs b. Diseases of the Lungs i. Pneumonia 1. Infection of the lungs where bronchi or alveoli fill with thick fluid 2. Symptoms: high fever, headache, chest pain 3. Causes: bacteria, viruses, other infectious agents ii. Pulmonary tuberculosis 1. Caused by bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis 2. TB skin test shows if person has been exposed iii. Emphysema 1. Chronic and incurable 2. Alveoli are damaged and lung functioning diminished 3. Usually caused by smoking iv. Cystic Fibrosis 1. Genetic disorder 2. Increases mucus secretions and makes it hard to breathe 3. No cure 4. Most people affected with CF die by age 30 v. Pulmonary fibrosis 1. Build up of connective tissue in lungs, causing loss of elasticity 2. Reduces lung volumes vi. Lung cancer 1. 87% of lung cancers are associated with smoking Complete p.295 #1-2 15.4 Disorders of the Respiratory Tract (Continued) 1. Disorders of the Lower Respiratory Tract a. Disorders of the Trachea and Bronchi i. Choking 1. Caused by a blocked _________________ 2. _________________ maneuver may be used to clear blocked air way 3. Tracheostomy: insertion of a _________________ tube into an incision made in the trachea ii. Acute bronchitis 1. Acute = sudden onset 2. _________________ of the primary and secondary bronchi 3. Preceded by a _________________ infection that leads to a secondary bacterial infection 4. Symptoms: a deep non-productive cough that produces mucus and sometimes _________________ 5. Treatment: antibiotics iii. Chronic bronchitis 1. Chronic = long-term 2. Airways _________________ and filled with mucus 3. Cough that brings up _________________ 4. Bronchi are _________________ 5. Often caused by _________________ (smoker’s cough) iv. Asthma 1. Disease of _________________ and bronchioles 2. Symptoms: wheezing, breathlessness, cough, expectoration of mucus 3. Airways are extremely _________________ to irritants such as animal dander, dust and cigarettes, and become inflamed 4. Smooth _________________ undergoes spasms 5. No cure for asthma, just controlled with drugs b. Diseases of the Lungs i. Pneumonia 1. _________________ of the lungs where bronchi or _________________ fill with thick fluid 2. Symptoms: high fever, headache, chest pain 3. Causes: bacteria, viruses, other infectious agents ii. Pulmonary tuberculosis 1. Caused by bacterium _________________ tuberculosis 2. TB _________________ test shows if person has been exposed iii. Emphysema 1. Chronic and incurable 2. _________________ are damaged and lung functioning diminished 3. Usually caused by _________________ iv. Cystic Fibrosis 1. _________________ disorder 2. Increases mucus secretions and makes it hard to breathe 3. No cure 4. Most people affected with CF die by age ________ v. Pulmonary fibrosis 1. Build-up of _________________ tissue in lungs, causing loss of _________________ 2. Reduces lung _________________ vi. Lung cancer 1. 87% of lung cancers are associated with _________________ Complete p.295 #1-2









