WARD_1
advertisement

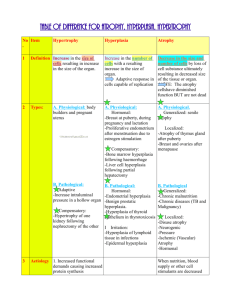
Hypertrophy too big cells Hyperplasia too many cells Some cells are stable/quiescent (liver) some are constantly dividing/labile undergoing mitosis (intestines) Some cells (heart, muscle, neuron) do NOT undergo mitosis often (ever?) Cell division G1 largest, most important gate G2 another important gate The CELLS of each tissue undergo hyperplasia/hypertrophy For example- take out a kidney, cells of the other kidney will get bigger and multiply - Presence of androgens will stimulate hyperplasia in prostate (difficulty peeing - in liver transplant, donor can have a full sized liver in weeks (thanks to hyperplasia) Elaboration of growth factors, hormones & cycle regulators. Stimulation of stem cells. HYPERPLASIA TWO KINDS: FLUIDIC & CELLULAR •Hormonal: -breast at puberty / in pregnancy -pregnant uterus (±); mostly hypertrophy -post-menses (pituitary, ovarian estrogens) re-establish lining •Compensatory: only brings you back to square one (menes has this too) -post-partial hepatectomy -post-unilateral nephrectomy hyperplasia happens in nephrons, NOT glomerulus Pathologic: •Endometrial (chronic estrogen excess) -danger of cancer NORMAL endometrium: undergoing mitosis/ hyperplasia to get back to sq one Hyper estorgenism: more freq/heavier periods… will go beyond sq one Glands are back to back (way too lose to one another) 5% of women will develop endometrial cancer •Prostatic (androgen stimulation) -no danger of cancer (why? No danger of cancer bc there is gene mutation) BPH benign prostatic hyperplasia BIG PROST is difficult to pee with. Indicative of high androgen lvls NOTE: androgens cause hyperplasia in BOTH the gland part of prostate AND the smooth muscle part of prostate •Skin infections due to papilloma virus -warts (stimulation by growth factors) •Pathologic2Partial hepatectomy model -production of GF’s -regeneration from stem (“oval”) cells? (no, stem cells only used when there is an impediment to regeneration/compensatory regeneration) Adrenal hyperplasia in pts with Kushings syndrome (test question?) -moon faced/fat because of hormonal imbalance from adrenal gland - camel hump - high BP HYPERTROPHY •Physiologic: muscles get bigger bc they have higher DNA content (why? Muscles get past G1, nucleus gets bigger and so does cell, but then cell can’t get past G2 so the cell can’t multiply): -skeletal muscle (pumping iron) -uterus in pregnancy (estrogen receptors in the myometrium (not endometrium/lining)) Gravid uterus = pregnant uterus •Pathologic: heart hypertrophy -hypertension makes heart muscle hypertrophy bc it has to pump harder -aortic stenosis a stenotic valve would do more or less the same thing as hypertensin by makin heart pump harder ( Mechanisms: •Increased workload / stretching •Gene induction (transcription, growth factors) •alpha beta myosin heavy chain (fetal) alpha myosin chains in muscle contraction switches to beta myosin chains in an attempt to get to homeopstasis. Beta chains are slower, more powerful and more efficient – also used by fetuses) •Atrial Natriuretic Factor elaboration Atria secretes stuff results in peeing more stuff (incr Na+ lvls hold on to water in body) fetuses make ANF so that their body fluids don’t get to high, this stops in hypertension, but resumes in hypertension/aortic stenosis (why now?) to reduce fluid vol and thus BP •Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum / P-450 story- possible to get hypertrophy in just ONE PART of a cell (like in SER- think about alcoholics barbituates use w/incr SER count would require high dose for same fx) -double-edged sword: P-450 system can create FREE RADICALS -polymorphisms: different ppl have different homeostatic lvls of [SER] (diff sensitivities to Rx) Big left ventricle (right hand side of slide) = aortic stenosis OR hypertension (hyperplasia is not possible in here!) Big right ventricle (left hand side of pic) = pulmonary hypertension or pulmonary stenosis