International Seminar 2013 Faculty of Agricultural Technology
advertisement
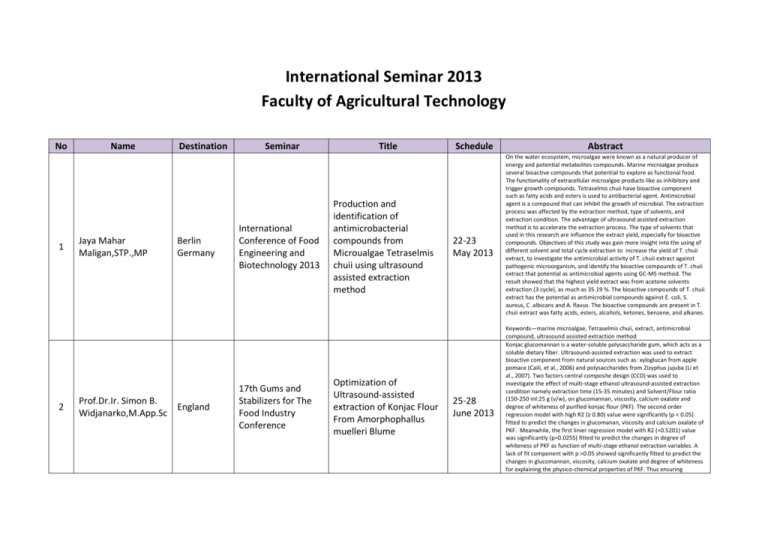
International Seminar 2013 Faculty of Agricultural Technology No 1 2 Name Jaya Mahar Maligan,STP.,MP Destination Berlin Germany Prof.Dr.Ir. Simon B. England Widjanarko,M.App.Sc Seminar International Conference of Food Engineering and Biotechnology 2013 17th Gums and Stabilizers for The Food Industry Conference Title Production and identification of antimicrobacterial compounds from Microualgae Tetraselmis chuii using ultrasound assisted extraction method Optimization of Ultrasound-assisted extraction of Konjac Flour From Amorphophallus muelleri Blume Schedule 22-23 May 2013 25-28 June 2013 Abstract On the water ecosystem, microalgae were known as a natural producer of energy and potential metabolites compounds. Marine microalgae produce several bioactive compounds that potential to explore as functional food. The functionality of extracellular microalgae products like as inhibitory and trigger growth compounds. Tetraselmis chuii have bioactive component such as fatty acids and esters is used to antibacterial agent. Antimicrobial agent is a compound that can inhibit the growth of microbial. The extraction process was affected by the extraction method, type of solvents, and extraction condition. The advantage of ultrasound assisted extraction method is to accelerate the extraction process. The type of solvents that used in this research are influence the extract yield, especially for bioactive compounds. Objectives of this study was gain more insight into the using of different solvent and total cycle extraction to increase the yield of T. chuii extract, to investigate the antimicrobial activity of T. chuii extract against pathogenic microorganism, and identify the bioactive compounds of T. chuii extract that potential as antimicrobial agents using GC-MS method. The result showed that the highest yield extract was from acetone solvents extraction (3 cycle), as much as 35.19 %. The bioactive compounds of T. chuii extract has the potential as antimicrobial compounds against E. coli, S. aureus, C .albicans and A. flavus. The bioactive compounds are present in T. chuii extract was fatty acids, esters, alcohols, ketones, benzene, and alkanes. Keywords—marine microalgae, Tetraselmis chuii, extract, antimicrobial compound, ultrasound assisted extraction method Konjac glucomannan is a water-soluble polysaccharide gum, which acts as a soluble dietary fiber. Ultrasound-assisted extraction was used to extract bioactive component from natural sources such as: xyloglucan from apple pomace (Caili, et al., 2006) and polysaccharides from Zizyphus jujuba (Li et al., 2007). Two factors central composite design (CCD) was used to investigate the effect of multi-stage ethanol ultrasound-assisted extraction condition namely extraction time (15-35 minutes) and Solvent/Flour ratio (150-250 ml:25 g (v/w), on glucomannan, viscosity, calcium oxalate and degree of whiteness of purified konjac flour (PKF). The second order regression model with high R2 (≥ 0.80) value were significantly (p < 0.05) fitted to predict the changes in glucomanan, viscosity and calcium oxalate of PKF. Meanwhile, the first linier regression model with R2 (=0.5201) value was significantly (p=0.0255) fitted to predict the changes in degree of whiteness of PKF as function of multi-stage ethanol extraction variables. A lack of fit component with p >0.05 showed significantly fitted to predict the changes in glucomannan, viscosity, calcium oxalate and degree of whiteness for explaining the physico-chemical properties of PKF. Thus ensuring satisfactory fitness of the response surface model to the significant (p< 0.05) independent variables. Predicted ultrasonically-assisted extraction process for crude konjac flour (CKF) with multi-stage ethanol was extraction time 25.6 minutes and Solvent/Flour ratio was for 8.65:1 (ml/g). The response surface methodology was succesfully employed to optimize purification process conditions of PKF. Rechecking experiment conducted in two duplicates, confirm the optimal conditions. The differences responses between the predicted results and the real experiment were less than 5%. Glucomannan, viscosity, and calcium oxalate were affected by combination treatements of extraction time and S/F ratio, but the degree of whiteness were predominantly influenced by extraction time (p < 0.05). This study can be usefull to the development of industrial purification processes of CKF to enhance the efficacy of a large scale purification processes. Keywords: Konjac flour, Glucomannan, Ca-oxalate, Multi-stage Ethanol extraction, ultrasonic. 3 4 Agustin Krisna Wardani,Ph.D Evi Kurniati,STP.,MT Bangkok Thailand The 25th Annual Meeting of The Thai Society for Biotechnology and International Conference Exploration of newly isolated bacteriophage from beef tripe and chicken intestine as biosanotizing agent for controlling biofilm formation 16-19 Oktober 2013 Kyoto Jepang The 4th International Conference on Sustainable Future for Human Security Potential use os Aspergillus flavus strain KRP1 in biodegradation of mercury contaminant 19-21 Oktober 2013 5 6 Dr.Ir. Joni Kusnadi,Msi Wahyunanto Agung Nugroho,STP.,M.Eng Osaka Jepang The 2nd International Conference on Life Science and Biological Engineering Antibacterial activity againts Escheria Coli and Staphylococcus Aerus of teak (Tectona Grandis) leaves crude extract using ,icrowave assisted extraction 7-9 November 2013 Bali The International Conference and Workshop on Chemical Engineering UNPAR 2013 Effectiveness of the addition of plant growth promoting bacteria (Azospirillum sp) in increasing Chlorella sp growth cultivated in tofu processing wastewater 4-5 Desember 2013









